What is Remote Work Security?
Remote work security refers to the strategies, tools, and policies used to protect company data and systems when employees work outside traditional office environments. As remote and hybrid work models become the norm, businesses must ensure that their security infrastructure can handle distributed teams, personal devices, and external networks.
What Are the Top Remote Working Security Risks?
Remote working security risks are the potential threats that arise when employees operate outside the traditional office environment, often relying on personal devices and unsecured networks. These risks can compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data, making organizations vulnerable to cyber threats.
While remote working offers benefits like flexibility and productivity, it also brings challenges. Remote work security concerns, including phishing, malware, and unauthorized access, are more common when employees work from home or other non-secure locations. Organizations must proactively educate employees, implement security measures, and enforce strong policies to mitigate these risks.
How Do Rogue Devices Threaten Remote Work Security?
The past few decades have seen significant advances in technology, communication, and transportation, revolutionizing the way we work and interact. These advancements have brought numerous benefits, particularly in terms of efficiency, productivity, and connectivity. However, they have also introduced new challenges, particularly with remote working security risks. With employees frequently working from various locations worldwide, whether traveling or working remotely, these remote access security risks are more prevalent than ever.
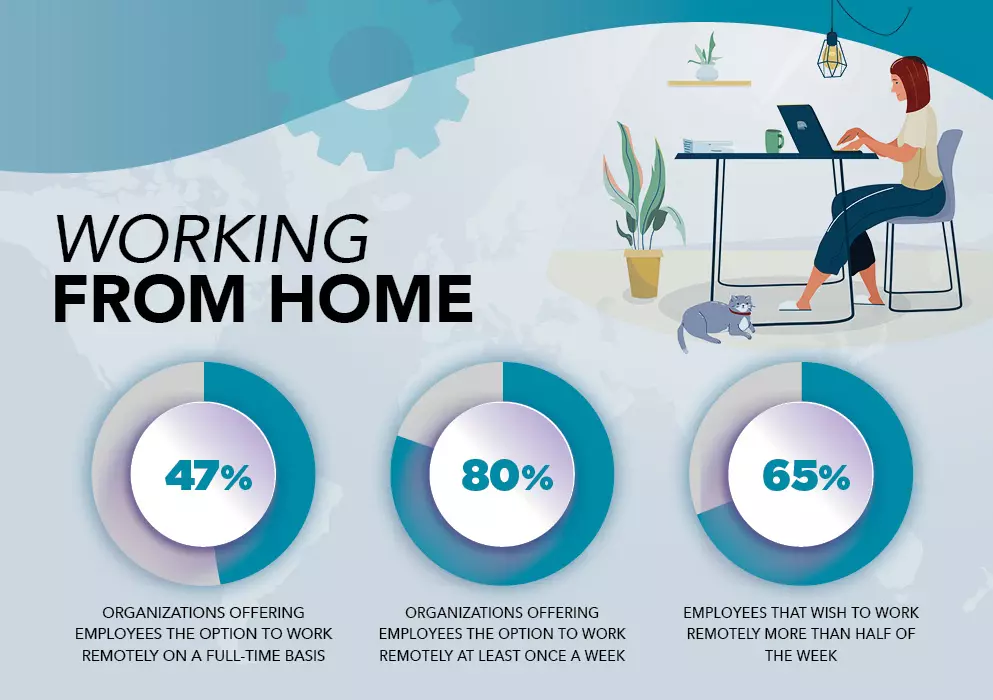
Currently, 70% of people work remotely at least once a week, and 53% work remotely for at least half of the week. While remote work brings convenience and flexibility, it also creates multiple security vulnerabilities. Remote working security risks are amplified when employees use personal devices (BYOD) or connect non-company peripherals to the network, increasing the chances of data breaches and cyberattacks.
Rogue Devices, often associated with remote working cyber security risks, such as spoofed peripherals and network implants, have become the weapon of choice for malicious actors looking to exploit vulnerabilities. These devices can disseminate malware, perform attacks, and lead to data breaches, with long-lasting consequences for organizations.
Key Findings on Remote Working Security
- 70% of people work remotely at least once a week.
- 53% of people work remotely for at least half of the week.
- Careless/uninformed staff cause 25% of all cyberattacks.
- Rogue Devices are becoming an increasingly popular attack tool.
- A Remote Work Policy is essential.
- Company-issued devices will be more beneficial for organizations.
- Rogue Device Mitigation is imperative.
Common Cybersecurity Threats for Remote Workers
Working remotely means employees have remote access to company data on their devices, making them potential cyberattack targets. Around 50% of businesses worldwide are concerned about employees inappropriately sharing company data via personal devices. Additionally, 54% of businesses have experienced data exposure due to lost devices containing sensitive information. Lost devices pose a significant security risk, as hackers can easily bypass passwords and exploit Rogue Devices to access the stolen or lost device’s data. Furthermore, working on public WiFi hotspots can expose information to unsecured networks, magnifying the scope of Remote Working Security Risks.
Using personal devices for remote work poses security challenges, as they often lack the necessary security measures to protect against corporate data breaches and network intrusions. Personal devices are appealing targets for attackers, with 50% of companies that allow bring your own device (BYOD), experiencing breaches through employee-owned devices. Personal devices may have poor authentication measures, relying on single-factor passwords that are easily cracked. Rogue Devices can exploit these weaknesses, including keylogging and bypassing biometric authentication.
Employees Role in CyberSecurity
Careless and uninformed staff contribute to a quarter of all cybersecurity attacks. Remote work increases the chances of such cyber incidents. Employees may unknowingly connect rogue devices, such as manipulated USB devices, to their devices without realizing the risks.
Connecting to public WiFi hotspots or using public charging kiosks can expose employees to compromised routers or manipulated chargers. Social engineering attacks can also target remote employees, with bad actors providing malicious peripherals or exploiting their trust.
Best Practices for Securing Remote Work
Secure Network
- Implement Sepio Asset Risk Management: Sepio protect both endpoints and networks by identifying and handling all connected peripherals.
- Zero Trust Network Access: Embrace the principle of “never trust, always verify” by implementing. Grant access based on a “need-to-know” basis and define granular policies.
- Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): Encrypts your internet connection, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept data.
- Secure Wi-Fi: Use a strong, unique password for your home Wi-Fi network. Avoid public Wi-Fi for work-related tasks.
Secure Devices
- Update Software Regularly: Ensure your operating system, antivirus, and applications are up to date to patch vulnerabilities.
- Enhance Authentication Measures: Promote the use of strong authentication methods such as biometric authentication (fingerprint or facial recognition).
- Strong Passwords: Use complex, unique passwords for all accounts, and consider a password manager to keep track of them.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification, like a code sent to your phone.
- Secure Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP): If using RDP, use Network Level Authentication (NLA) and a VPN for added security.
Data Protection
- Encrypt Data: Use encryption tools for sensitive data, both at rest (on your device) and in transit (while being sent or received).
- Backup Regularly: Keep backups of important files in case of ransomware attacks or data loss. Store backups offline or in the cloud.
- Secure File Sharing: Use secure platforms for file sharing, like encrypted email or enterprise-level solutions.
Awareness and Training
- Security Awareness: Educate yourself on common threats like phishing emails, scams, and social engineering attacks.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Know how to report security incidents to your IT department or manager.
- Remote Work Policies: Understand and follow your company’s remote work cybersecurity policies and guidelines.
Physical Security
- Secure Workspace: Keep work devices physically secure. Lock them when not in use, especially in shared living spaces.
- Avoid Public Screens: Be cautious of people or cameras seeing your work screen, especially when handling sensitive information.
Addressing Remote Working Security Risks
Enterprises often face challenges in providing complete visibility into their hardware assets. Leading to weakened policy enforcement and potential security incidents. To tackle these issues, it’s crucial to have comprehensive visibility into hardware assets, regardless of their characteristics and connectivity interfaces. By embracing practical approaches and adapting to dynamic cybersecurity defenses, organizations can address remote working security risks effectively.
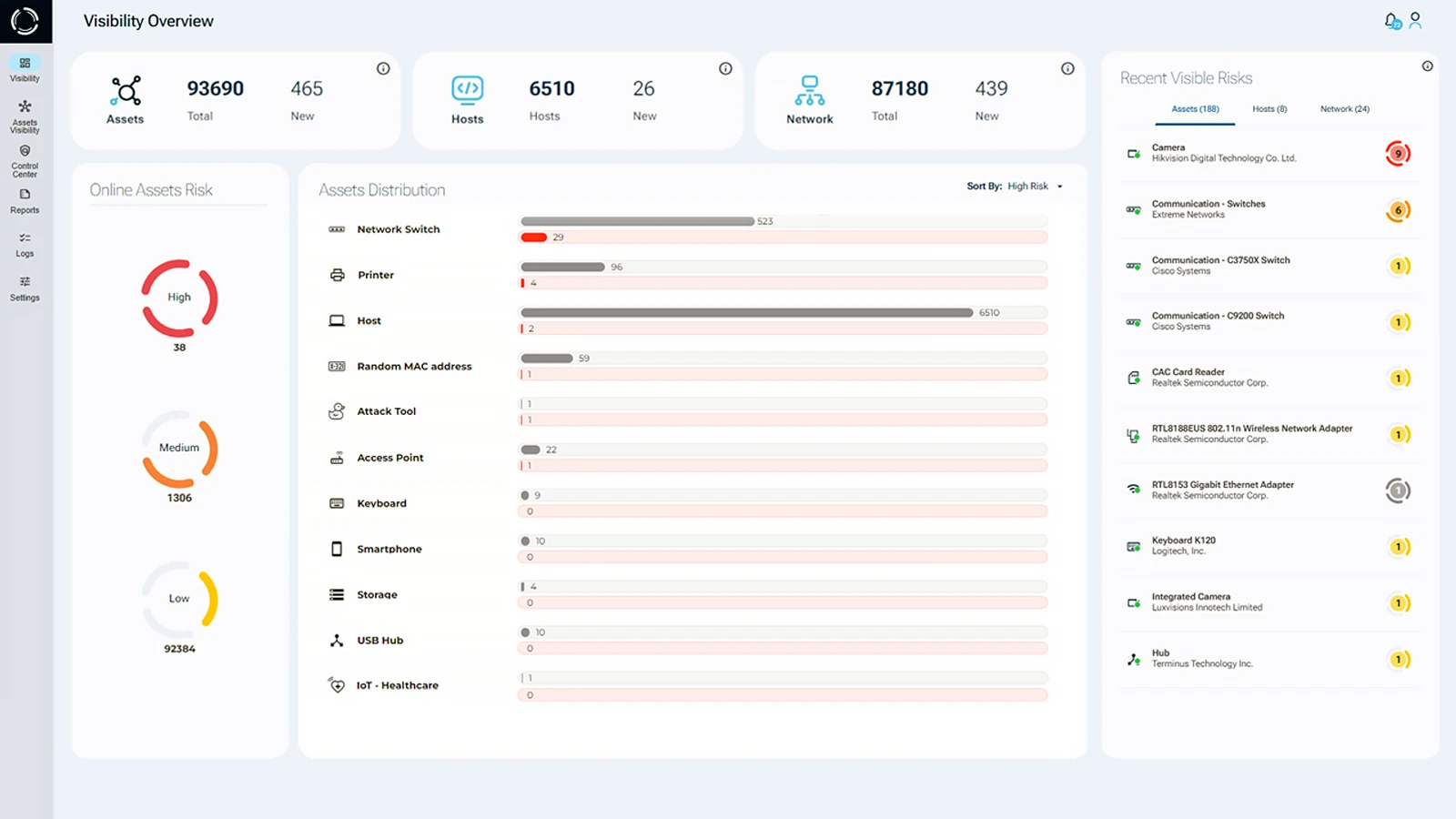
By adopting proactive cybersecurity strategies and leveraging dynamic defenses, organizations can significantly reduce the impact of remote work security. With a robust approach to asset management, monitoring, and security policies, businesses can better protect their remote workforce from potential breaches and mitigate risks associated with unauthorized devices and network access.
Endpoint and Network Cybersecurity
Sepio’s platform play a crucial role in uncovering hidden hardware attacks. Especially those operating over network and USB interfaces. As the leader in rogue device mitigation, offers disruptive solutions that identify, detect, and manage all peripherals, leaving no device unmanaged.
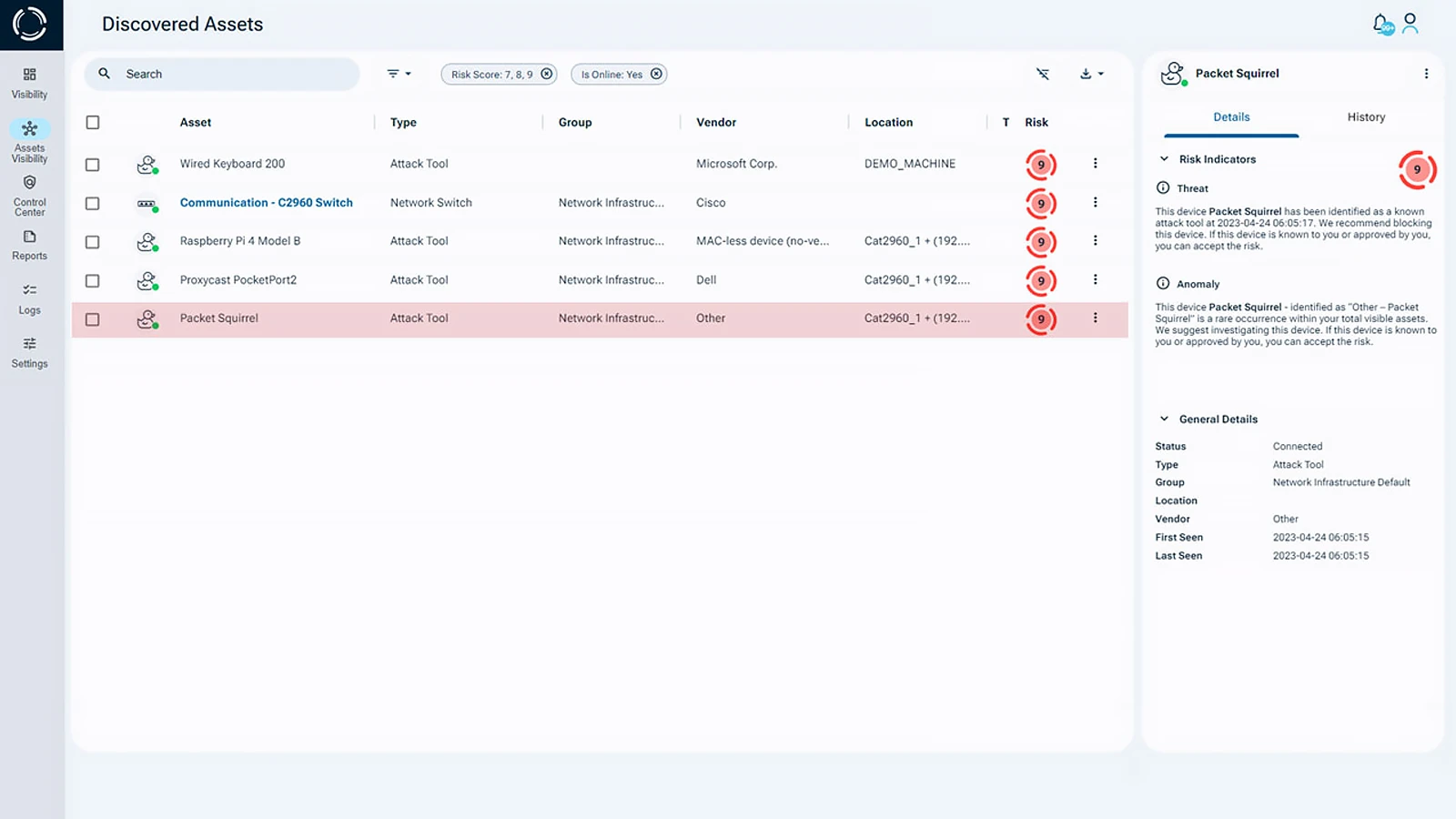
With Sepio Zero Trust Hardware Access (ZTHA), organizations can effectively mitigate the risks of remote working associated with unsecured devices and unauthorized network access. This innovative solution ensures that every known and shadow asset is visible and secure, protecting your organization’s data and devices from potential cyber threats in the remote work environment.
See every known and shadow asset. Prioritize and mitigate risks effectively. Talk to an expert to learn how Sepio’s patented technology can help you gain control over your asset risks and improve cybersecurity posture.
Read the Remote Working Security Risks (pdf)