What is Bring Your Own Device?
Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) is a trend in which employees use their personal devices for both personal and professional purposes within the workplace. This approach offers significant flexibility and convenience, benefiting both employees and employers, especially as reliance on mobile technology grows.
However, the rise of Bring Your Own Device also introduces new cybersecurity risks, making it essential for businesses to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data. In a world dominated by remote and hybrid work models, understanding the implications of Bring Your Own Device is vital for organizations striving to maintain strong cybersecurity protocols.
What Are the Benefits of Bring Your Own Device?
The adoption of Bring Your Own Device policies in enterprises offers several key advantages, but it is essential to balance these benefits with the associated risks. Here are some of the most important benefits:
- Cost Savings: Implementing Bring Your Own Device policies can substantially reduce costs for companies. When employees use their own devices, businesses save on the expense of purchasing and maintaining equipment. This financial benefit allows companies to allocate resources to other critical areas. Additionally, the reduction in IT infrastructure costs can enhance the bottom line, enabling organizations to invest in new technologies or training initiatives.
- Increased Productivity: Employees are often more comfortable and efficient when using their own devices in a Bring Your Own Device environment. Familiarity with personal devices reduces the time spent learning how to use new equipment and software, allowing more time for actual work. Studies show that 50% of employees feel more productive when using their own devices for work purposes.
- Extended Work Time: Research conducted by Samsung and Frost & Sullivan has shown that personal smartphones, in a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) environment, enable employees to gain almost an additional hour of work time each day. This contributes to a 34% boost in overall productivity, demonstrating that employees can perform more tasks and work more efficiently with their own devices. The ability to seamlessly switch between personal and professional tasks also helps employees feel more in control of their work-life balance.
Bring Your Own Device Security Risks
Personal devices often lack the robust security controls found on company-managed hardware, making them more vulnerable to cyber threats such as malware, phishing, and unauthorized access. Additionally, the wide variety of devices and operating systems complicates the enforcement of consistent security policies across the organization.
Many organizations with Bring Your Own Device policies have experienced data breaches stemming from insecure personal devices. Weak or outdated security software, lack of device encryption, and poor password practices further increase the risk. Without strict oversight, employee-owned devices can become an easy entry point for attackers, potentially compromising sensitive corporate data.
Employee Devices as Attack Targets
Employees are a critical line of defense in Bring Your Own Device environments. Without built-in security on personal devices, user awareness often becomes the last barrier against hardware-based attacks.
Ongoing training is essential to help employees recognize threats like phishing and malware. Promoting a culture of cybersecurity awareness encourages responsibility and vigilance, strengthening overall organizational security.
Employee-owned devices often hold sensitive company data, making them attractive targets, especially in unsecured environments. Key risks include:
- Unsecured Access Locations: Public WiFi can expose devices to data interception and remote compromise.
- Public Charging Risks: “Juice jacking” through tampered charging kiosks can install malware or steal data.
Spoofed Peripheral and Malware Risks
Spoofed peripherals, rogue devices that impersonate legitimate Human Interface Devices (HIDs), like “bad USBs”, pose serious security threats. These devices operate at the physical layer, bypassing traditional security software and appearing harmless to users, yet they can install malware and steal data.
Device Theft and Insider Threats
Acquiring lost devices provides malicious actors with an alternative way to access an organization’s network and valuable information. If this happens, even the best security systems and antivirus software may prove ineffective. Password-protected devices are not fully secure, as malicious actors can often bypass a password on a lost or stolen device. Employees should use strong access codes and enable multi-factor authentication to secure their Bring Your Own Device setups.
Insider threats also pose a significant risk to organizations, and Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies can inadvertently facilitate their actions. Mobile device security guidance from NIST highlights how personal devices can introduce risks. Personal mobile devices provide malicious insiders with easier access to corporate networks and systems, making it simpler to exfiltrate sensitive data without raising immediate suspicion.
Bring Your Own Device Security
Various technological solutions can help reduce cybersecurity risks, especially in environments with Bring Your Own Device policies. Here are some key solutions:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data that goes beyond the control of the organization is necessary and it should be performed throughout the data’s life cycle. 76% of companies do not encrypt mobile devices, which makes them extremely vulnerable. Furthermore, the IT department should take control of encryption keys to prevent unauthorized access and to maintain the encryption, should a breach transpire.
- Containerization: This method segregates a portion of the device into its own protected bubble, separate from the other applications and content on the device, and it requires password access.
- Whitelisting: The opposite of blacklisting, whitelisting gives employees access only to a list of approved applications. This can be a more appealing solution to employees as there is a more extensive range of applications and websites that exist.
- Blacklisting: An organization can use this feature to block apps and websites considered security threats or those that could hinder productivity, like games and social networking apps.
- Antivirus Software: Installing antivirus software on individual devices will enhance security by protecting devices from malware attacks.
Overcoming BYOD Security Risks
IT and security teams often lack full visibility into hardware assets, especially in complex IT, OT, and IoT environments, making BYOD policy enforcement difficult. These visibility gaps can lead to malware attacks and data leaks.
To mitigate these risks, organizations must ensure complete hardware asset visibility across all device types and interfaces. Adopting security measures that detect USB HID emulators and physical layer implants is critical for blocking these threats.
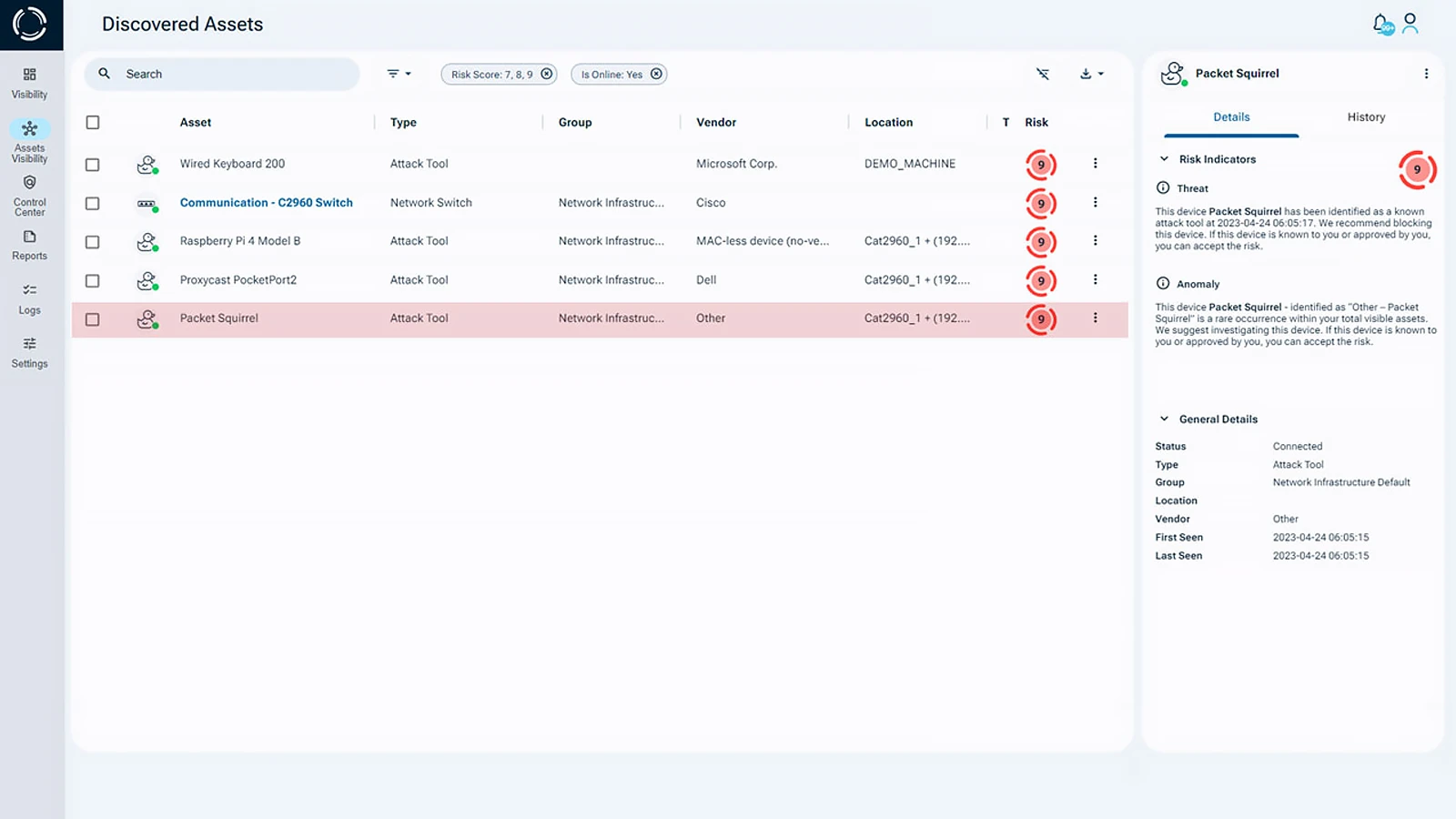
Bring Your Own Device Security Solution
Sepio is the leader in the Rogue Device Mitigation (RDM) market. It is disrupting the cybersecurity industry by uncovering hidden hardware attacks operating over network and USB interfaces.
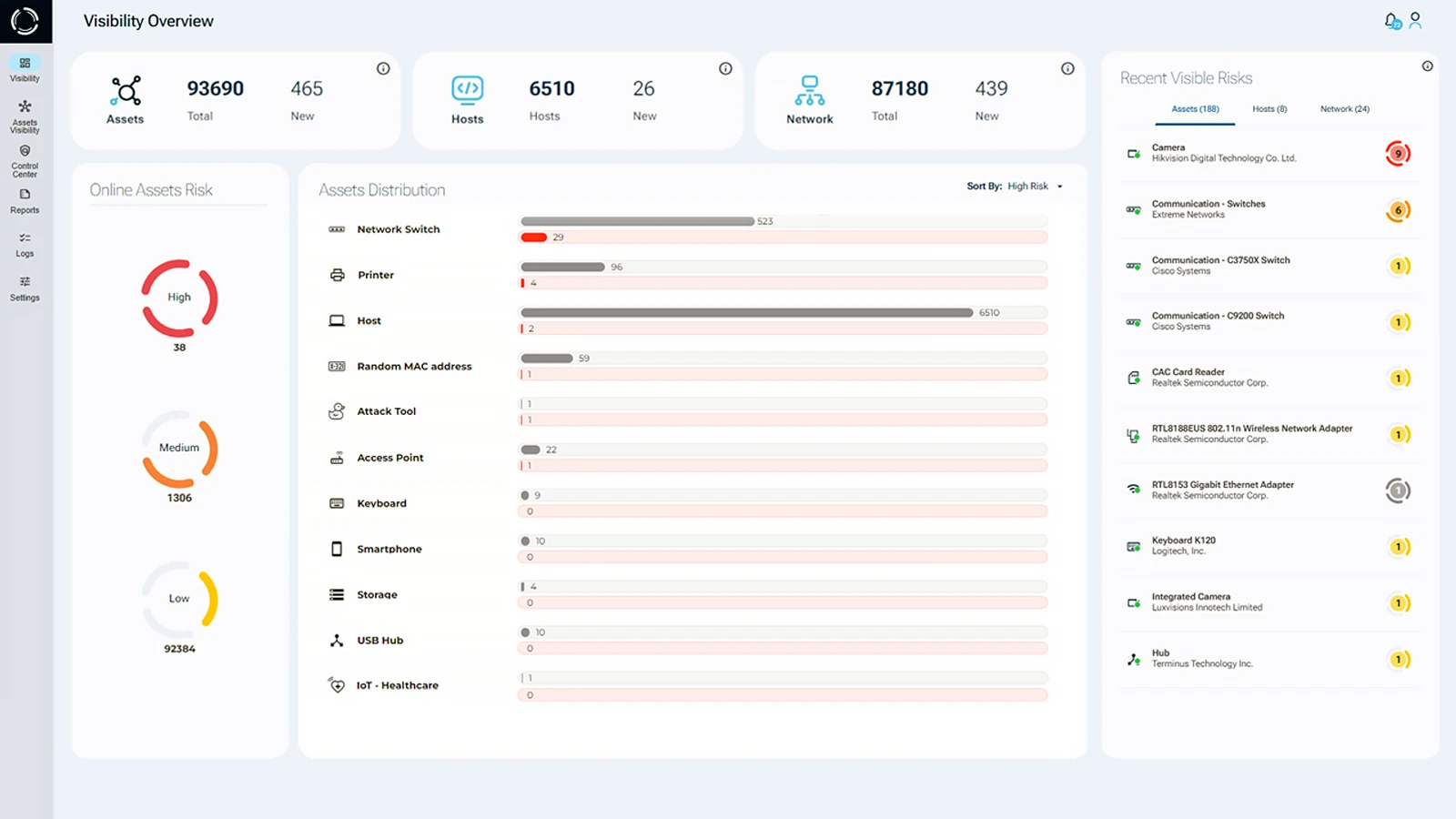
Sepio’s platform, identifies all peripherals. No device goes unmanaged. The only company in the world to undertake physical layer visibility fingerprinting. It generates a digital fingerprint using the device descriptors of all connected peripherals. It then compares these descriptors against a well-established database of malicious devices, effectively initiating automatic attack prevention. With Machine Learning, the software analyses device behavior to identify abnormalities, such as a mouse acting as a keyboard.
See every known and shadow asset. Talk to an expert to understand how to use Sepio’s patented technology to gain control of your asset risks and implement effective Bring Your Own Device security solutions.
For further guidance on secure implementation of BYOD policies, consult the NCSC’s Bring Your Own Device guidance.
Read the Bring Your Own Device - E-Book (pdf)





