What is BYOD Security?
BYOD security (Bring Your Own Device) involves measures to mitigate cybersecurity risks associated with using personal devices for work tasks. While BYOD fosters a flexible work environment, it can also introduce significant cybersecurity risks when connected to corporate networks.
Before diving into the risks, it’s important to acknowledge the many benefits of adopting a BYOD security policy.
What Are the Benefits of BYOD?
BYOD reduces enterprise costs by shifting device expenses to employees, who are more productive using familiar personal devices. A study by Samsung and Frost & Sullivan shows a 34% productivity boost, with employees gaining nearly an extra hour of work per day. Additionally, 80% of employees report improved work/life balance when managing a single device. However, security risks remain the main concern deterring organizations from fully embracing BYOD policies (Mobile Device Security).

What Are the Main BYOD Security Risks?
Data breaches pose a major security risk with BYOD. When employees use personal devices to access corporate resources, sensitive data such as customer information, financial records, and trade secrets can be stolen or leaked.
Many organizations still lack a comprehensive strategy to address BYOD security risks. Since personal devices often act as entry points for malicious actors, this oversight increases the overall attack surface. Furthermore, these devices typically have lower security standards than corporate-managed endpoints, making it easier for attackers to exploit them.
The concern grows when organizational data is stored on BYOD devices, making it even more challenging to secure them. As even when not used for work purposes, BYOD still pose a security threat to the organization.
Why Do BYOD Devices Pose a Higher Security Threat?
Lax Security Measures on Personal Devices
Typically, BYOD will have fewer security features than company-owned devices. As BYOD’s are also used for personal purposes, they are frequently neglected. In doing so, however, the BOYD device is more vulnerable to attack. In some cases, lacks the necessary security software or features to notify the user when an attack is taking place.
Furthermore, employees’ role are one of the greatest BYOD security risks to organizations. Carelessness and negligence when using BYODs can have extremely harmful consequences for the enterprise. The lack of BYOD security measures on such devices, and the other concerns listed below, mean that employee awareness can sometimes be the only barrier between a malicious actor and a successful hardware based attack.
Vulnerable Peripherals Devices: A Major BYOD Security Concern
As employees own the BYOD, they have complete discretion in choosing which peripherals assets to use. This of course depends on the BYOD security policy. Whether it be for financial or aesthetic reasons, an employee might be inclined to purchase devices and/or peripherals from site such as Amazon or AliExpress. And, although such websites offer a variety of options, they also offer manipulated and compromised devices. That glow in the dark keyboard selling for $10 is likely not the most secure.
Unsecure Access Locations: The BYOD Risk of Remote Work
With workers working from home, many organizations are adopting work from home cyber security policies on a more permanent basis. In fact, according to Gartner, 47% of organizations will give employees the choice to work from home on a full-time basis. Furthermore, over 80% will allow employees to work from home at least one day a week.
Depending on the organization’s Work From Home (WFH) policy, remote work can essentially mean access from anywhere with a good internet connection. This, however, means employees are working in unsecure environments such as coffee shops, public libraries, and group workspaces. In fact, as BYODs enable the ability work anytime anywhere, almost everywhere becomes an unsecure location. Think about how many times you have access to work emails while waiting for a flight or at a restaurant. When data is stored on the device, the organization is at risk whenever the device is used. Yes, watching Netflix at the airport on a device with company data puts the enterprise at risk.
Lost/Stolen Devices: A Common BYOD Security Risk
Speaking of unsecured locations, pick-pocketers thrive in busy places like airports. And pickpocketing might not only be the criminal activity the perpetrator engages in. Stealing devices might be just the first step in their attack. Accessing the device could be the actual goal. Even a lost device can find its way into a cybercriminal’s hand. If someone steals or loses a BYOD containing company data, the company faces a significant BYOD security threat.
But why do these factors trigger security concerns? The answer lies in the realm of BYOD security risks, specifically rogue devices and hardware based attacks.
Rogue Devices and Hardware Attacks
Rogue devices are malicious hardware components that evade traditional software-based security tools. In BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) environments, these threats are especially serious. Personal devices often lack enterprise-grade protection, making them prime targets for hardware-based attacks requiring physical access.
Spoofed peripherals, compromised chargers, and network implants are common rogue devices. They exploit the physical layer to bypass detection.
A spoofed peripheral mimics a legitimate keyboard or mouse. These appear harmless but slip past endpoint defenses. Similarly, a compromised USB charger, like those in cafés or airports, can deliver malware or steal data while charging your phone. This type of attack, called juice jacking, highlights the everyday BYOD security risks users face.
Even affordable accessories from online stores can hide malicious functions. That low-cost USB stick or mouse could trigger an attack once connected.
Network implants pose another risk. These hidden devices evade solutions like Network Access Control (NAC) and act as man-in-the-middle attackers, intercepting data, injecting malware, and stealing sensitive information silently.
Whether it’s a charger, USB, or network connection, BYOD security solutions must address these often-overlooked threats.
Sepio’s Asset Risk Management platform strengthens BYOD security by detecting rogue devices, spoofed peripherals, and network implants in real time, offering visibility and protection at the physical layer.
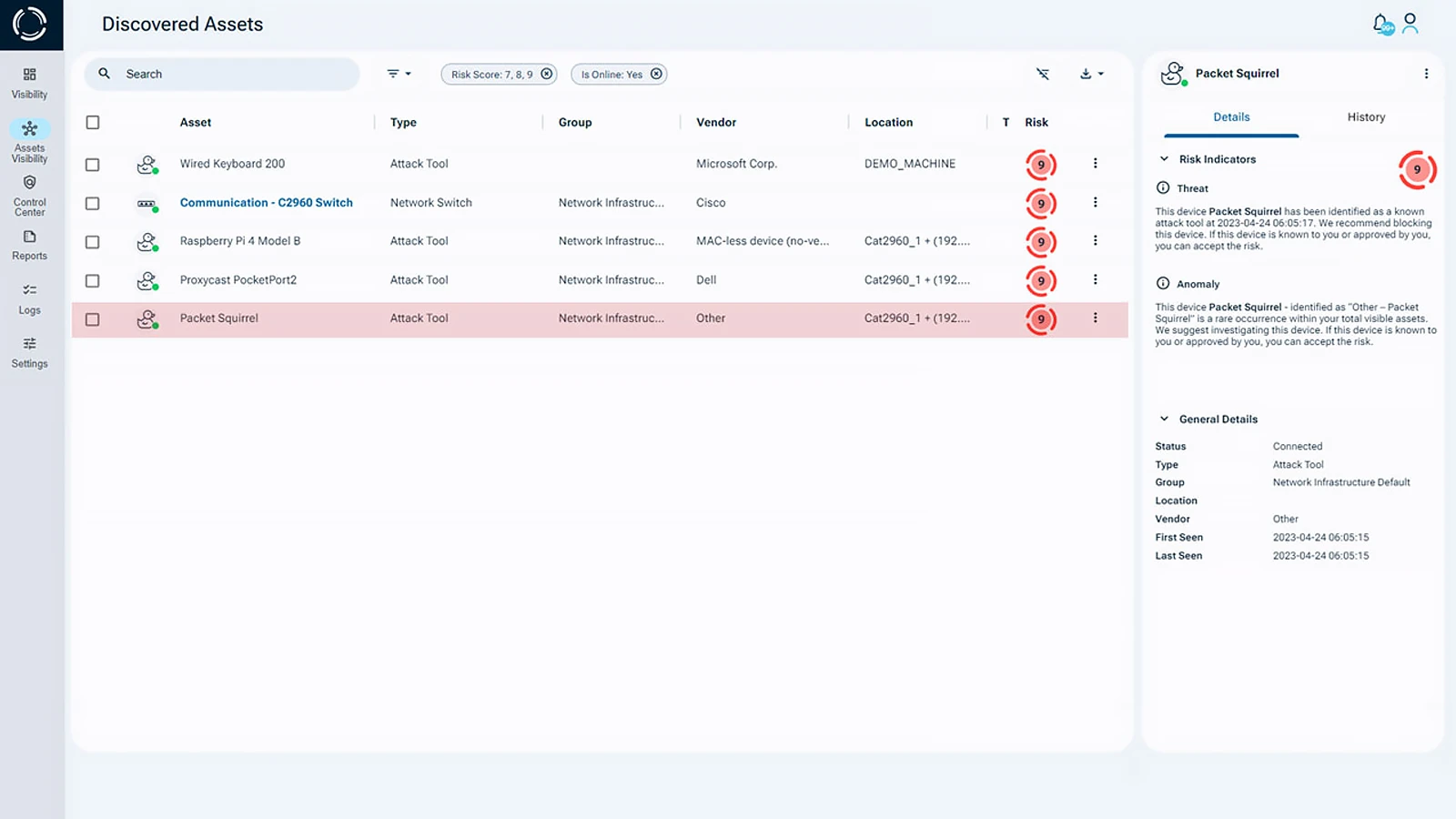
How Can Organizations Mitigate BYOD Security Risks?
To mitigate these risks, strong BYOD security measures are crucial. Consider the following BYOD security best practices:
- Network Segmentation: Separate BYOD devices from critical company resources to contain potential compromises.
- Access Control: Employ robust authentication methods to restrict access to corporate data on BYOD devices.
- Encryption: Safeguard sensitive data by encrypting it both at rest and in transit.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Utilize antivirus, firewalls, and intrusion detection/prevention systems to defend against threats from BYOD devices.
- Monitoring and Incident Response: Continuously monitor network activity and BYOD device behavior to detect and respond to security incidents effectively.
Securing BYOD devices includes protecting them from malware, phishing attacks, and various other BYOD security threats to ensure they don’t become vulnerabilities within your network.
BYOD Security Policy Implementation
A strict BYOD security policy can regulate device use by restricting which devices can be used, as well as where and how. It can also address BYOD security issues by requiring specific security measures on BYODs. While these measures may not detect rogue devices, they can reduce the damage from hardware-based attacks.
One of the vulnerabilities that hardware attack exploits is the carelessness of employees when connecting. This applies whether they are attaching a peripheral to their endpoint or linking their endpoint to a network. Enhancing employee awareness of such attacks will, hopefully, make them more cautious when connecting. This, however, is not a full proof solution. As attackers use extremely deceitful social engineering techniques that even some of the most highly trained professionals fail to recognize.
How Does Sepio Enhance BYOD Security?
In the context of BYOD security, Sepio’s (Asset Risk Management) provides a powerful BYOD security solution. Using its unique in-depth probing capabilities, Sepio’s provides detailed hardware level visibility and verification for IoT/OT/IT devices across the network and peripheral infrastructure, whether the device is managed, unmanaged or hidden. By covering unmanaged devices, Sepio enables the enforcement of Zero Trust on BYODs when applicable.
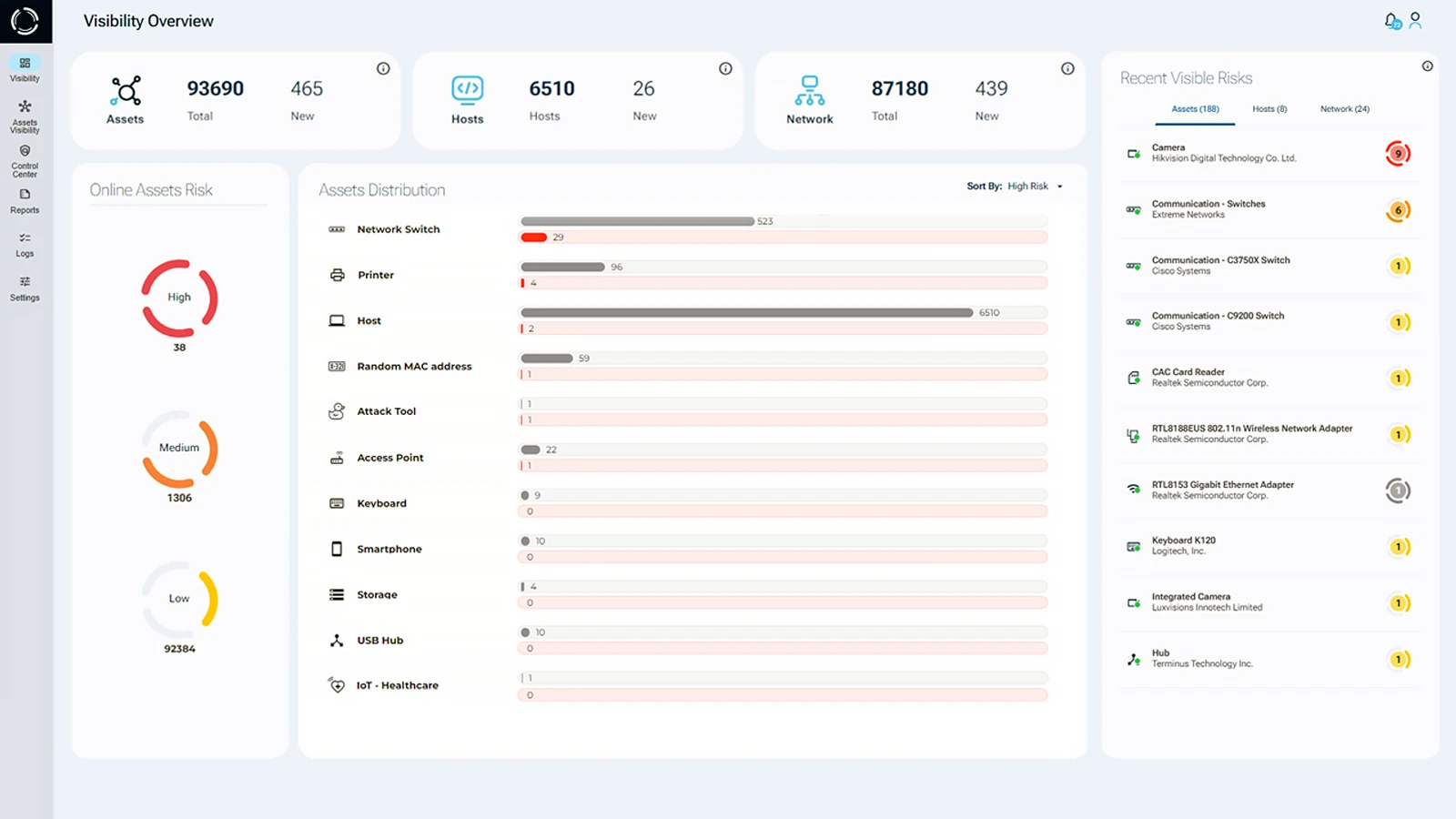
Furthermore, Sepio’s policy enforcement mechanism controls hardware access by applying strict or granular policy controls. Sepio instantly detects policy breaches and automatically blocks offending devices, preventing attacks. With BYODs offering numerous entry points for attackers, a robust BYOD security solution is crucial to mitigate threats effectively.
See every known and shadow asset. Prioritize and mitigate risks.
Talk to an expert. It will help you understand how to use Sepio’s patented technology to gain control of your asset risks.






