What is BYOD?
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) is a workplace trend where employees use their personal devices, laptops, phones, and tablets, for both work and personal activities. This flexibility has gained popularity for its cost-effectiveness, productivity gains, and the comfort employees feel with their own devices. However, with the rise of remote work, managing network access and device security has become crucial for maintaining office and overall security.
BYOD policies offer employees greater flexibility, enhancing their work-life balance, which in turn benefits both employees and organizations. Despite these advantages, BYOD introduces significant security risks, causing some organizations to hesitate in adopting such policies. These risks often include the challenges of securing personal devices and protecting against cyber threats, such as ransomware and data breaches.
What Are the Main Benefits of BYOD?
Implementing a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy can substantially reduce business expenses by eliminating the need for company-issued hardware. Employees using their personal devices are already familiar with the interface and functionality, resulting in less time spent on training and more time focused on productive work. According to research by Samsung and Frost & Sullivan, employees who use their own smartphones gain nearly an extra hour of work each day, contributing to a 34% increase in productivity.

BYOD also promotes greater flexibility for employees, helping them manage both personal and professional responsibilities on a single device. This convenience contributes to improved work-life balance and overall job satisfaction, benefits that positively reflect on the organization as well.
What Security Risks Are Associated with BYOD?
Despite its cost-saving and productivity benefits, Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies introduce serious security challenges. Personal devices often lack the robust security controls found in corporate-owned systems, making them more susceptible to malware, data breaches, and unauthorized access. In fact, 50% of companies that allow BYOD have reported security incidents linked to employee devices.
Why Are Personal Devices Harder to Secure?
Employee-owned hardware is frequently underprotected, lacking proper encryption, endpoint security, and centralized management. These weaknesses create openings for cyber attackers, especially when devices connect to unsecured networks or bypass corporate security protocols. Even well-meaning employees can unintentionally expose sensitive data through careless behavior, such as downloading unverified apps or accessing company resources via public Wi-Fi.
In this context, understanding BYOD also means recognizing the broader implications of using personal, often unsecured, devices within professional environments. Without strict enforcement of security policies and comprehensive user education, the risks of BYOD can easily outweigh its rewards.
BYOD in Workplaces
One of the most significant challenges with BYOD is the difficulty of managing and securing multiple network devices within an organization. Many organizations have IT departments that implement security policies, but BYOD devices often lie beyond their direct control. Without proper oversight, ensuring that every network device is secure becomes a daunting task. The IT department needs to deploy comprehensive BYOD network security policies that balance employee privacy with necessary security measures to protect the organization’s data and network.
For instance, device management systems need to be in place to monitor all devices, ensure they are updated with the latest security patches, and maintain encrypted communication channels. Additionally, implementing strict access controls for network access is essential to prevent unauthorized devices from accessing sensitive data.
Peripherals Devices
Peripheral devices, such as phone chargers and USB drives, can introduce significant risks into the workplace. These rogue devices are often engineered for hardware attacks and can cause severe damage once they connect to a network. Even a simple, faulty USB device from an untrustworthy source can pave the way for malware and data theft.
Social engineering tactics, like offering free USB drives or chargers, are common methods used to trick employees into using compromised BYODs. These devices often bypass traditional cybersecurity defenses, making it crucial to have a comprehensive device management system in place.
Spoofed Devices
Spoofed devices are another major threat in a Bring Your Own Device environment. These spoofed peripherals are crafted to mimic everyday technology, such as laptops, enabling them to infiltrate networks unnoticed. By exploiting Layer 1 visibility gaps, spoofed devices can evade detection by conventional security tools like network access control (NAC) and intrusion detection system (IDS). This allows them to carry out malicious activities without triggering alerts.
Lost/Stolen Devices
Lost or stolen devices are a constant risk in Bring Your Own Device environments, where employees use personal devices for work. Without effective device management, organizations become vulnerable to significant security threats. Attackers can quickly gain access to sensitive data if a device is not properly secured. With over 70 million devices lost or stolen each year, and only 7% of those recovered, the importance of robust device management is undeniable.
How to Strengthen BYOD Network Security?
One of the most effective strategies for mitigating BYOD network security risks is implementing cybersecurity education, training, and awareness (SETA) programs. These programs help employees recognize and counter psychological exploitation tactics, such as social engineering. They also promote secure practices for using personal devices. Additionally, enforcing robust BYOD policies is crucial. This ensures the separation of personal and business data on employee devices, helping safeguard sensitive information.
While SETA significantly reduces mistakes caused by human factors, it is not a fail-safe solution. Rogue devices can still evade traditional network security measures, underscoring the importance of Layer 1 visibility to detect and manage every device connected to the network effectively.
A comprehensive device management system is a critical component of BYOD network security, allowing organizations to remotely wipe lost or stolen devices and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. To address these threats effectively, organizations must prioritize visibility at the physical layer. By detecting and accounting for all devices, they can establish a solid foundation for Bring Your Own Device network security. This approach safeguards digital ecosystems, mitigates risks, and ensures better control over the network.
Endpoint and Network Security
Sepio’s platform addresses critical gaps in network device visibility. Sepio’s ARM integrates with existing solutions, such as NAC, EPS, SIEM and SOAR, to enhance the enterprise’s cybersecurity posture. The solution deep network visibility capabilities mean no device goes unmanaged. All IT, OT, IoT, and BYOD connected devices are detected and identified. Moreover, Sepio’s policy enforcement mechanism and Rogue Device Mitigation capabilities instantly block any unapproved or rogue hardware. This enables a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) approach, stopping attackers at the first line of defense.
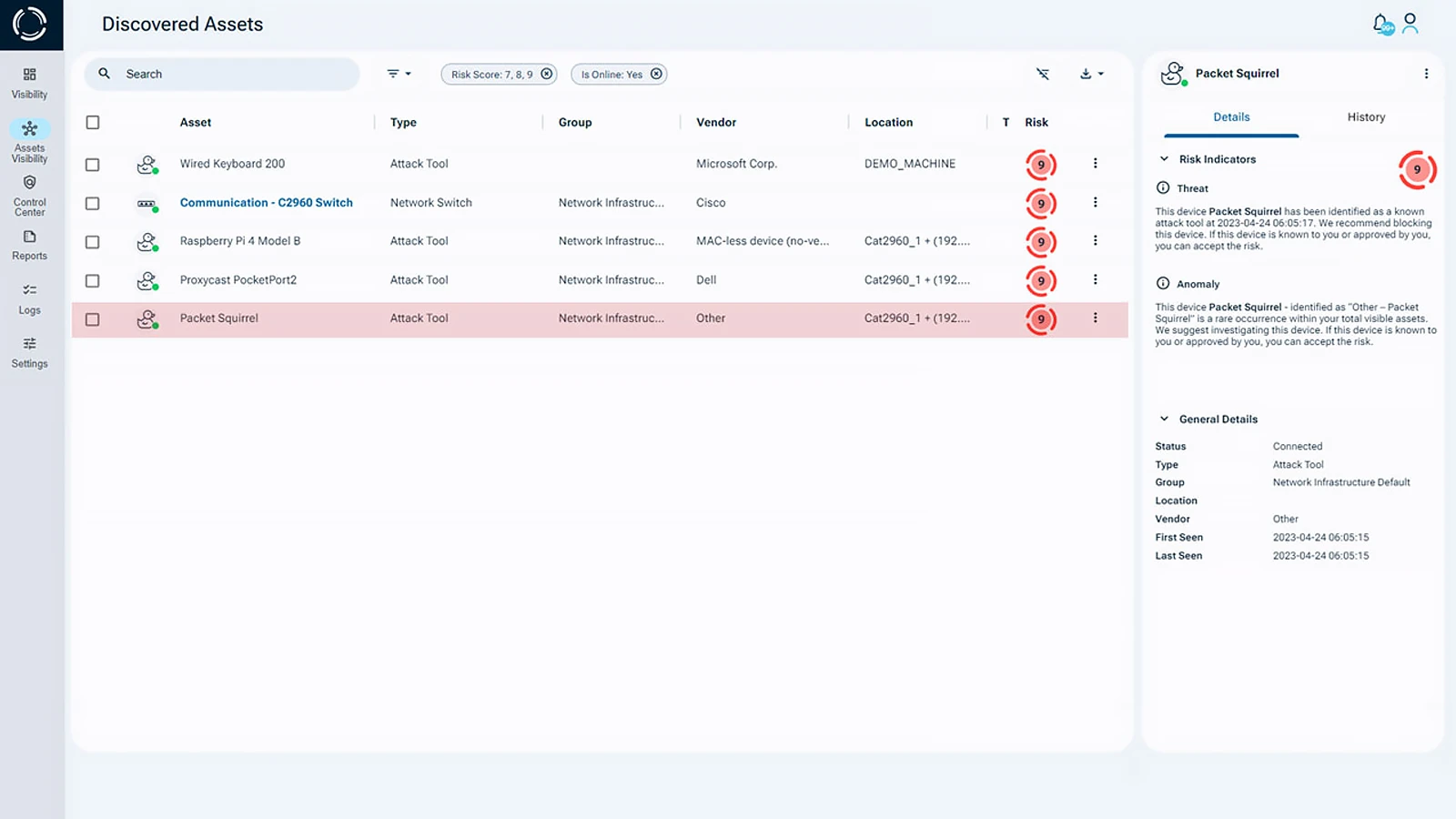
Securing all connected assets within your organization’s network, whether BYOD or corporate, requires more than traditional endpoint security. It demands a comprehensive approach. This includes device management, encrypted connections, and continuous monitoring. Such measures ensure that every Bring Your Own Device used for work is properly protected.
Securing Your BYOD Environment
BYOD allows employees to use personal devices for work. While this offers many benefits, it also introduces security risks that need to be managed. With Sepio’s platform, you can ensure robust endpoint security. This safeguards all devices, whether remote or in-office, as soon as they connect to your network.
See every known and shadow assets on your network. Talk to an expert to understand how to utilize Sepio’s patented technology to secure your devices and gain full control over your asset management.






