What is a Man in the Middle Attack?
A MiTM attack (Man-in-the-Middle attack) is a serious cybersecurity threat in which attackers intercept and manipulate communication between two parties, often without detection. These attacks allow cybercriminals to eavesdrop on or alter messages, putting sensitive data at risk.
The objective of a MiTM attack is to illegally acquire personal data, including login credentials and credit card information. Typically, the targets of such attacks are users of financial applications, e-commerce platforms, and other services that require user authentication.
In this article, we shed light on the nature of MiTM attacks in cybersecurity and how attackers exploit vulnerabilities in communication channels.
How Does a MiTM Attack Work?
A Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attack unfolds through several malicious actions that compromise communication between two parties. First, the attacker intercepts the exchange, deceiving both sides into believing they are communicating directly with each other. Once the connection is established, the attacker begins eavesdropping on the data being transmitted, silently collecting sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or confidential communications. Beyond passive listening, the attacker may modify the data in real time, altering legitimate messages, redirecting users to malicious websites, or injecting harmful content such as malware. In some cases, the attacker impersonates one or both parties, gaining unauthorized access to systems and manipulating the conversation or transactions for malicious gain.
MiTM Attack Techniques
A MiTM attack can occur through various channels, including Wi-Fi, email, web browsers, or any method of data transmission between parties. Common techniques used in MiTM attacks include:
- Eavesdropping: The attacker intercepts data packets as they travel between the two legitimate parties, allowing them to monitor the communication.
- Data Manipulation: The attacker can modify the data being exchanged between the two parties. For example, they can alter the content of emails, change URLs in web requests, or manipulate financial transactions.
- Session Hijacking: Attackers may attempt to take control of an existing session between a user and a website. Potentially impersonating the user.
- SSL Stripping: Attackers may try to downgrade secure HTTPS connections to unencrypted HTTP. Making it easier to intercept and manipulate data.
- Rogue Access Points: Attackers set up rogue Wi-Fi access points with names similar to legitimate networks. Tricking users into connecting to the malicious network.
- ARP Spoofing: Attackers manipulate Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to associate their MAC address with the IP address of the target device. Diverting traffic through their system.
- DNS Spoofing: Attackers can compromise the Domain Name System (DNS) to redirect users to malicious websites.
A MiTM attack is particularly dangerous because they exploit trust in communication protocols, often making the breach invisible to users. To prevent such threats, organizations must implement robust security measures, including encryption, secure authentication, and continuous network monitoring.
MiTM Attack and Rogue Devices
One particularly concerning variant of a MiTM attack is the hardware-based approach, in which rogue devices infiltrate communication channels. These attacks require physical access to critical assets, such as Wi-Fi routers, network servers, or ATMs. This enables cyber attackers to attach rogue devices and initiate their malicious activities. By doing so, they compromise the integrity of communication and can cause significant damage.
For example, rogue USB devices, disguised as legitimate hardware, can be used to inject malicious code into systems, effectively bypassing traditional cybersecurity defenses. Similarly, attackers may exploit compromised network cables or switches to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or disrupt the functioning of critical systems.
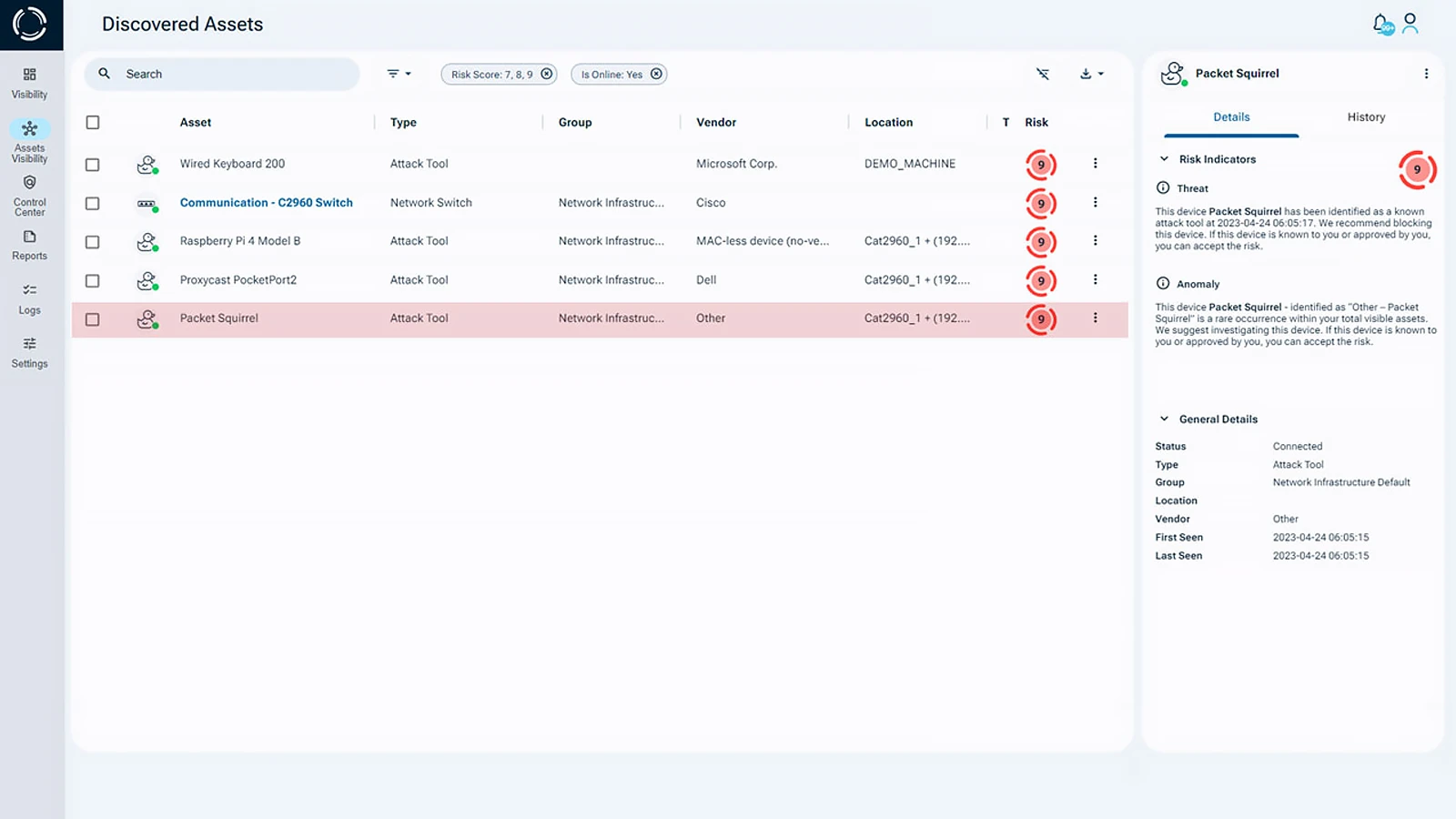
A notable example of a MiTM attack involving hardware is the Black Box attack, which gained attention in 2017 and continues to pose a threat. In this attack, a rogue device is plugged into an ATM’s USB port, intercepting and altering communication between the ATM and cash dispenser. The consequences can be devastating, as the attacker can command the machine to dispense cash, causing substantial financial losses.
Physical Layer Visibility and Endpoint Security
Traditional security solutions often overlook physical layer visibility within the OSI model, creating a critical gap in visibility for network assets. As a result, organizations are left vulnerable to hardware-based threats. Conventional solutions such as Network Access Control (NAC), Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), and Endpoint Protection Systems (EPS) fail to cover the physical layer, allowing rogue devices to go undetected.
For example, a 2023 report revealed that nearly all logical attacks on ATMs in the first half of the year were Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attacks, resulting in losses exceeding $500,000.
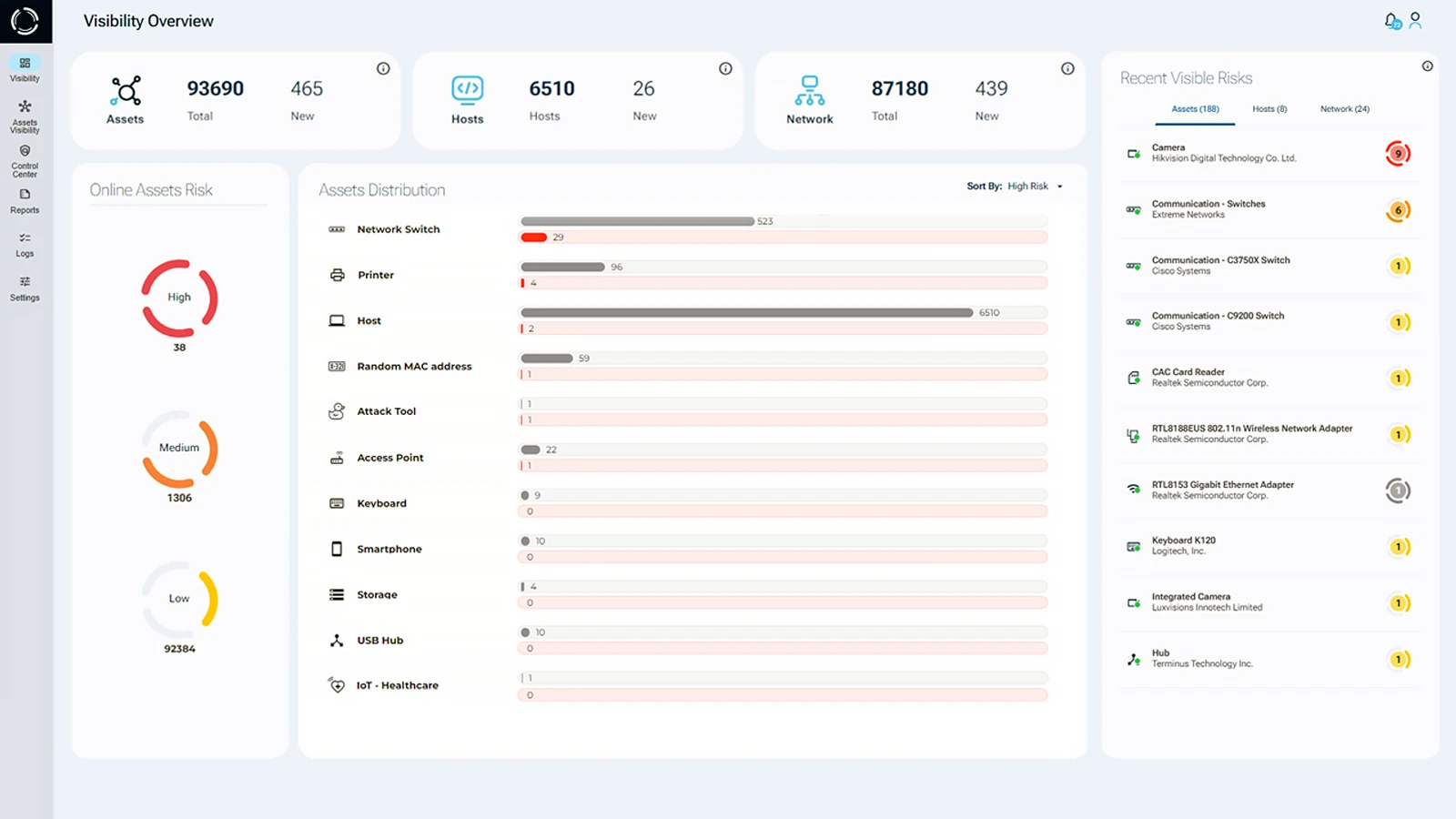
Sepio’s physical layer analysis addresses this issue by generating Hardware DNA profiles for all known and shadow assets. This significantly enhances visibility, closing security gaps and enabling enterprises to accurately detect and identify assets, no matter their function or location. By evaluating the electrical, mechanical, and functional characteristics of devices, Sepio’s approach ensures impartial, objective assessments, eliminating misleading perceptions or behavioral assumptions. This platform empowers organizations to eliminate network blind spots and bolster overall cybersecurity.
How Can I Prevent a MiTM Attack?
A MiTM attack is a severe security threat, capable of stealing sensitive information such as login credentials, personal data, and financial details. To prevent these types of attacks, Sepio offers an unparalleled solution that provides comprehensive asset visibility. By detecting all hardware devices, whether IT, OT, or IoT, Sepio ensures no assets are left undetected, securing networks against potential threats.
Sepio’s Asset Risk Management (ARM) platform further enhances security by implementing robust policy enforcement. Through its rogue device mitigation feature, ARM instantly identifies and blocks unauthorized or malicious hardware, neutralizing potential MiTM attacks. Additionally, adopting a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) allows organizations to effectively thwart Black Box attacks, ensuring the integrity of their communication channels.
By understanding the nature of Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attacks and leveraging Sepio’s advanced security solutions, organizations can significantly strengthen their defenses against hardware-based threats. By harnessing the power of Layer 1 visibility and implementing comprehensive hardware access control, businesses can protect their communication channels from MiTM attacks. Stay proactive in the face of evolving cyber threats and ensure the security and confidentiality of your digital communications.
Protect Against a MiTM Attack
Talk to an expert and discover how Sepio’s patented technology can protect your organization from MiTM attacks. Gain full control of your hardware, secure your communication channels, and stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
Why Choose Sepio?
- Comprehensive Asset Visibility: Detect IT, OT, and IoT devices in real-time.
- Rogue Device Mitigation: Instantly block malicious hardware to neutralize potential threats like MiTM attacks.
- Enhanced Security: Protect communication channels with Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA).
Safeguard your organization with Sepio’s advanced security solutions. Contact us today to learn how we can eliminate MiTM attack vulnerabilities and secure your network from unauthorized access. Sepio’s Asset Risk Management (ARM) platform offers proactive defense against sophisticated threats like MiTM attacks. Act now to strengthen cybersecurity and protect your network.






