What are Rogue Devices?
Rogue devices are unauthorized hardware that operate on networks without the consent or control of IT administrators. Rogue device detection is crucial, as these devices can compromise the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of networks. Often undetected by IT security teams, rogue devices are typically tampered with by hackers to target and exploit network assets. They can manipulate Ethernet or USB Human Interface Device (HID) interfaces to execute cyberattacks.
Sepio’s platform provides a comprehensive solution for rogue device detection and hardware security. By leveraging advanced machine learning, enhanced device visibility, risk prioritization, and granular access controls, Sepio effectively identifies and neutralizes the threats posed by rogue devices on the network, ensuring robust protection against unauthorized and potentially harmful hardware.
Rogue Device Research
Recent research by TAG and Sepio, makes the case that Rogue implants represent a particularly intense threat to financial institutions. This indicates an increasing need for proficient cyber security in financial institutions. Several example threats, such as ATM Jackpotting, illustrate how rogue devices can generate negative consequences for the financial services sector and other critical infrastructure sectors. Our research report includes detailed case studies showcasing the practical use of this hardware attack tools.
Security Challenges in Financial Institutions
Financial services are crucial to economic growth, driving business operations and providing essential services to individuals and organizations. As a result, financial institutions store vast amounts of sensitive data, including personally identifiable information (PII), making them prime targets for cybercriminals. In fact, financial firms are targeted 300% more often than businesses in other sectors. Consequently, it’s reasonable to assert that financial services organizations face billions of attempted cyberattacks annually.
Rogue Devices Operating at the Physical Layer
Rogue devices are tampered hardware components that evade traditional IT security tools, posing a significant threat to network security. Hackers manipulate these devices, often peripherals like cameras, chargers, mouses, and keyboards, to exploit interfaces such as Ethernet or USB Human Interface Device (HID) for malicious purposes.
Operating at the physical layer, rogue devices can bypass conventional detection methods. For example, a USB HID attack may involve spoofed peripherals that appear legitimate to the system, enabling undetected data breaches or system manipulation. Similarly, spoofed man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks leveraging network devices often bypass existing security measures.
The covert operation of rogue implants significantly increases their threat level. By utilizing hardware-based attack techniques, these devices not only avoid detection but can also execute damaging exploits that compromise critical assets, highlighting the urgent need for advanced security measures to counter this growing risk.
Rogue Devices Cybersecurity Threats
The range of cybersecurity threats posed by rogue devices is surprisingly vast. This stems from the flexible nature of these implants, which can be engineered to carry out a variety of attacks. Hackers, often leveraging techniques inspired by nation-state actors, embed malicious exploits into manipulated hardware. These rogue devices communicate with external environments through interfaces such as USB HID or Ethernet, effectively bypassing conventional security defenses. Below is a summary of key threats associated with rogue network implants:
- Advanced Persistent Threat (APT): APTs, often linked to nation-state actors, are prolonged attacks designed to infiltrate and remain hidden in systems. Rogue devices offer a stealthy entry point, bypassing traditional defenses.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS): Rogue IoT devices can launch internal DDoS attacks, overwhelming critical systems within a network. Vulnerabilities like those in Bluetooth protocols (e.g., BlueBorne, Bleedingbit) further increase the threat.
- Ransomware: Insecure IoT devices serve as entry points for ransomware campaigns. Limited patching and update capabilities make it difficult to mitigate these risks effectively.
Consequences of Rogue Device Threats
Rogue devices can pose considerable threat implications for financial services firms. Particularly when capable adversaries like nation-state actors carry out the attacks. While one must always expect soft consequences like reputational damage after an attack of this type, the more tangible implications of rogue device security attacks on the financial services industry include the following:
Direct Financial Loss
Rogue devices can directly target systems like ATMs, enabling attacks such as ATM Jackpotting. When used in ATMs cyber attacks and other systems that can dispense cash immediately, the financial losses are direct and immediate. It is not difficult to imagine this being done at scale and in a manner that creates a large aggregate loss.
Indirect Financial Loss
Even when rogue devices are discovered and reported before causing damage, the reputational fallout can impact consumer trust and commercial relationships. A minor drop in customer retention or new business acquisition can translate into significant financial losses over time.
Response Costs
Responding to rogue device attacks involves high operational costs. Incident management—including detection, investigation, reporting, and remediation, requires significant time and resources. As with many threats, prevention is far more cost-effective than reaction.
Compliance Costs
Financial institutions face substantial regulatory and compliance burdens after a rogue device incident. These include mandatory reporting, system audits, and providing evidence to external regulators. Proactively detecting rogue devices reduces long-term compliance costs compared to reacting after an incident occurs.
How Are Rogue Devices Detected?
Detecting rogue devices is essential to uncovering hardware-based attacks that bypass traditional security solutions by exploiting the physical layer. Unlike software-based threats, which often rely on vulnerabilities and can be mitigated with patches or updates, rogue devices operate stealthily and evade conventional detection tools. So, how can organizations effectively identify these hidden implants within their networks?
Rogue Devices at the Physical Layer
Sepio’s Asset DNA technology, which operates at the physical layer, focuses on device existence rather than behavior. This approach enables the detection and identification of all devices, managed, unmanaged, and hidden. Powered by complex machine learning algorithms, Sepio’s rogue device detection software accurately identifies the true source of asset risk, eliminating the confusion caused by misleading profiles and behavioral assumptions.
By identifying hardware anomalies and unauthorized devices at the physical level, Sepio empowers organizations to secure their networks against threats that traditional software-centric tools cannot see.
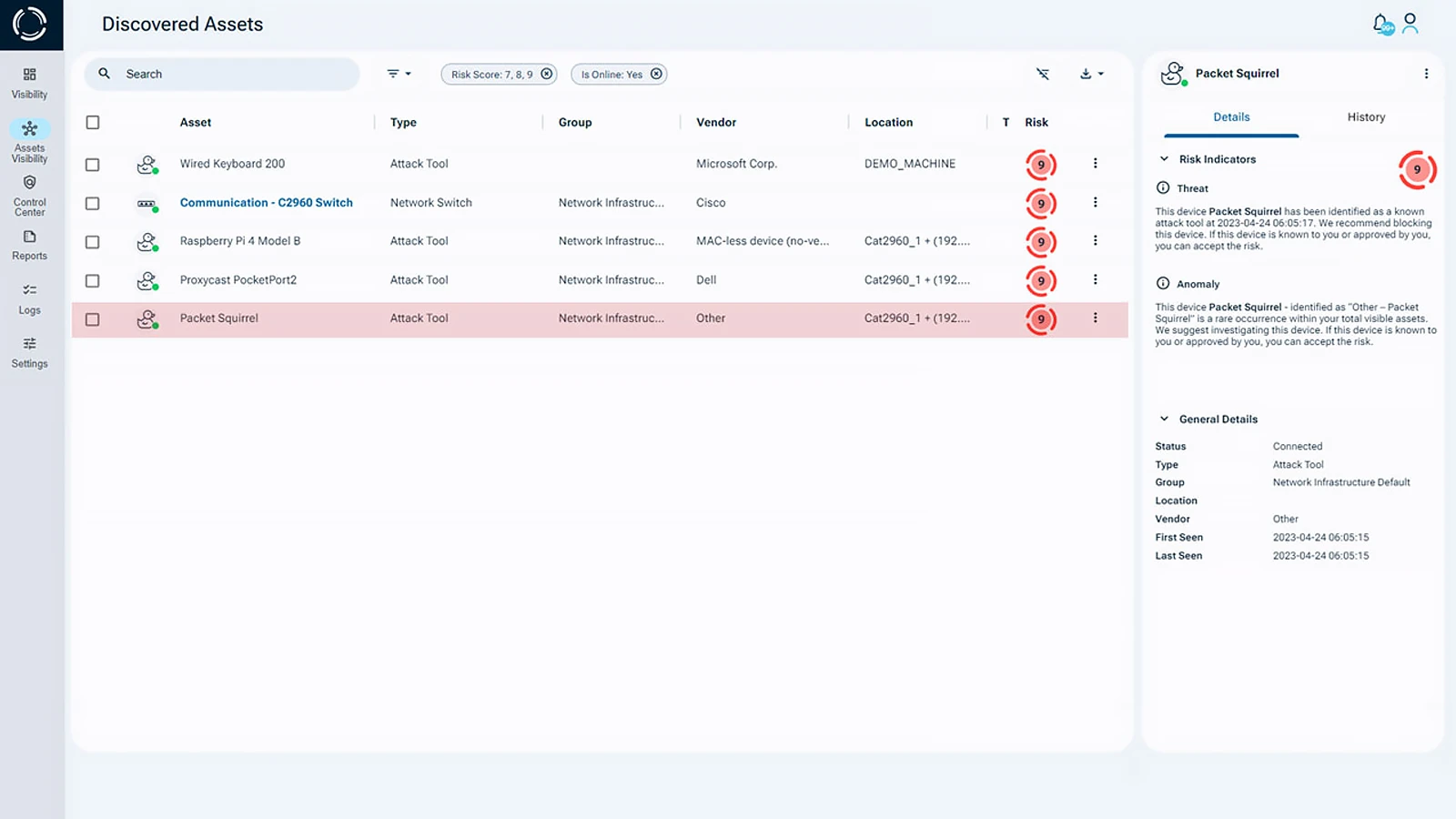
Sepio’s platform also prioritizes assets based on their risk levels and enforces granular hardware access controls, automatically blocking devices that violate predefined rules or are identified as known attack tools.
Seeing all network assets is a critical prerequisite for hardware defense. But what you see is only as useful as what you can do with this knowledge.
Sepio’s policy enforcement mechanism enables hardware access control, by enforcing a strict set of policies based on the device’s identity. It instantly detects any devices which breach the pre-set policy. It automatically instigates a rogue device mitigation process to block the device. Thus, preventing malicious actors from successfully carrying out hardware-based attacks.
Mitigate Rogue Device Risks
Talk to an expert to learn how Sepio’s patented rogue device detection technology can help you gain control over your asset risks and protect your network from unauthorized devices.
Download the Rogue Devices Threat Report (pdf)



