What are Network Security Threats?
Network security threats are malicious activities designed to compromise the integrity, confidentiality, or availability of an organization’s data and systems. These threats continue to evolve as cybercriminals develop increasingly sophisticated attack methods, putting organizations of all sizes at risk. A successful breach can lead to data loss, operational disruption, regulatory penalties, and long-term reputational damage.
Protecting against network threats requires a proactive approach, one that includes advanced threat detection, real-time monitoring, strong authentication, and granular access controls. A comprehensive network security strategy is essential for maintaining compliance and safeguarding critical assets from today’s dynamic threat landscape.
In this blog, we will explore some network security threats examples, highlighting common attack methods and their potential impact on organizations. To maintain a strong defense, organizations must identify security threats to a network before they can be exploited. Cyber attackers leverage vulnerabilities such as misconfigured systems, weak authentication methods, and unpatched software to infiltrate networks. Recognizing these risks early allows businesses to implement robust security measures, such as encryption, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection. By staying ahead of potential threats, organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity posture and reduce the likelihood of costly breaches.
Network Device Dormancy Risks
Network security threats emerge when devices like PCs and network printers go dormant due to inactivity or power-saving settings, making them invisible to network security management tools (turning into ‘MACless’ assets).
Impact: Dormant devices miss critical security patches and updates, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation. This oversight can lead to significant threats in network security and non-compliance with financial regulations. Unmonitored dormant devices may expose financial institutions to unauthorized access, leading to potential data breaches.
Moreover, the failure to monitor these dormant assets means financial institutions may not detect unauthorized access attempts. This could result in potential financial losses and damage to their reputation. Hence, addressing device dormancy is vital for maintaining a secure network.

Mitigation Strategies for Device Dormancy Risks
Deploy Sepio’s Zero Trust Hardware Access solution: Sepio’s advanced hardware security management to see all network hardware devices. Including those that have become dormant. Sepio’s technology can detect and manage ‘MACless’ assets, ensuring they remain visible and monitored, reducing network security threats.
Integrate continuous monitoring with Sepio’s solution: Implementing continuous monitoring with Sepio’s hardware management solution allows financial institutions to track both active and dormant devices within the network. This ensures that all devices are accounted for and receive essential updates, minimizing potential vulnerabilities. Continuous monitoring enhances network security by providing real-time visibility into the state of each device. It also ensures that devices meet the necessary security standards.
Enforce rigorous update policies using Sepio’s automated compliance checks: To enforce rigorous update policies across all devices, financial institutions can leverage Sepio’s automated compliance checks. These checks mandate regular updates and patches for all hardware, regardless of their operational state. This ensures that even dormant devices maintain their security posture. This proactive approach prevents vulnerabilities and ensures compliance with financial regulations.
Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) Attacks on Network Printers
Threats in network security such as Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attacks pose significant risks by intercepting and altering communications between devices, such as modifying data sent to network printers. Such attacks undermine application security and can lead to unauthorized document changes, resulting in financial discrepancies, misinformation, and legal complications.
Impact: These attacks can lead to the unauthorized alteration of printed documents. Potentially causing misinformation (i.e., altered IBAN codes), financial discrepancies, and legal issues, further escalating network security threats.

Mitigation Strategies for Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Implement Network Protection with Sepio’s Zero Trust Hardware Access: By utilizing Sepio’s Zero Trust Hardware Access (ZTHA) solution, financial institutions can ensure that all network devices, including printers, are authenticated and verified. This process occurs before the devices are allowed to communicate within the security network. This rigorous verification process significantly reduces the risk of MiTM attacks, ensuring robust network security.
Regular Device Integrity Checks with Sepio’s Security Suite: Conducting regular integrity checks with Sepio’s security network suite allows financial institutions to ensure that their devices, including network printers, are not compromised. By maintaining the integrity of communications, institutions can mitigate the risks associated with MiTM attacks, preserving data security and trustworthiness in their operations.
Enhanced Visibility and Monitoring of Hardware Assets: Sepio’s monitoring solutions provide enhanced visibility into all connected hardware within the network. By tracking device activity in real time, financial institutions can quickly identify any anomalous or unauthorized actions. This enables prompt responses to potential threats. This heightened visibility is crucial for strengthening both data security and network security.
Mitigating Network Security Threats: Best Practices
The most effective way to defend against network security threats and attacks is by building a security-first culture and ecosystem. Here’s how financial institutions can get ahead:
- Sepio’s Hardware Vulnerability Assessments: Conducting thorough hardware vulnerability assessments is essential for financial institutions to identify and rectify vulnerabilities within their security network. Sepio’s solutions are designed to perform comprehensive assessments of all hardware devices, helping institutions to bolster their network security and protect against cyber threats. Regular assessments ensure that devices comply with industry standards and remain resistant to attacks.
- Education and Awareness on Network Security Threats: Equipping employees with knowledge about the latest threats in network security and application security is crucial. Utilizing Sepio’s insights allows financial institutions to create ongoing educational programs that inform staff about potential risks, especially those targeting hardware components. When employees are aware of these threats, they can better recognize and mitigate risks, enhancing the overall security posture of the network.
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance with Sepio: With Sepio’s hardware security management, ensure that your network adheres to the latest financial regulations. Sepio’s solution helps maintain cybersecurity compliance by providing detailed visibility and control over all hardware devices. Ensuring that they meet legal and security standards.
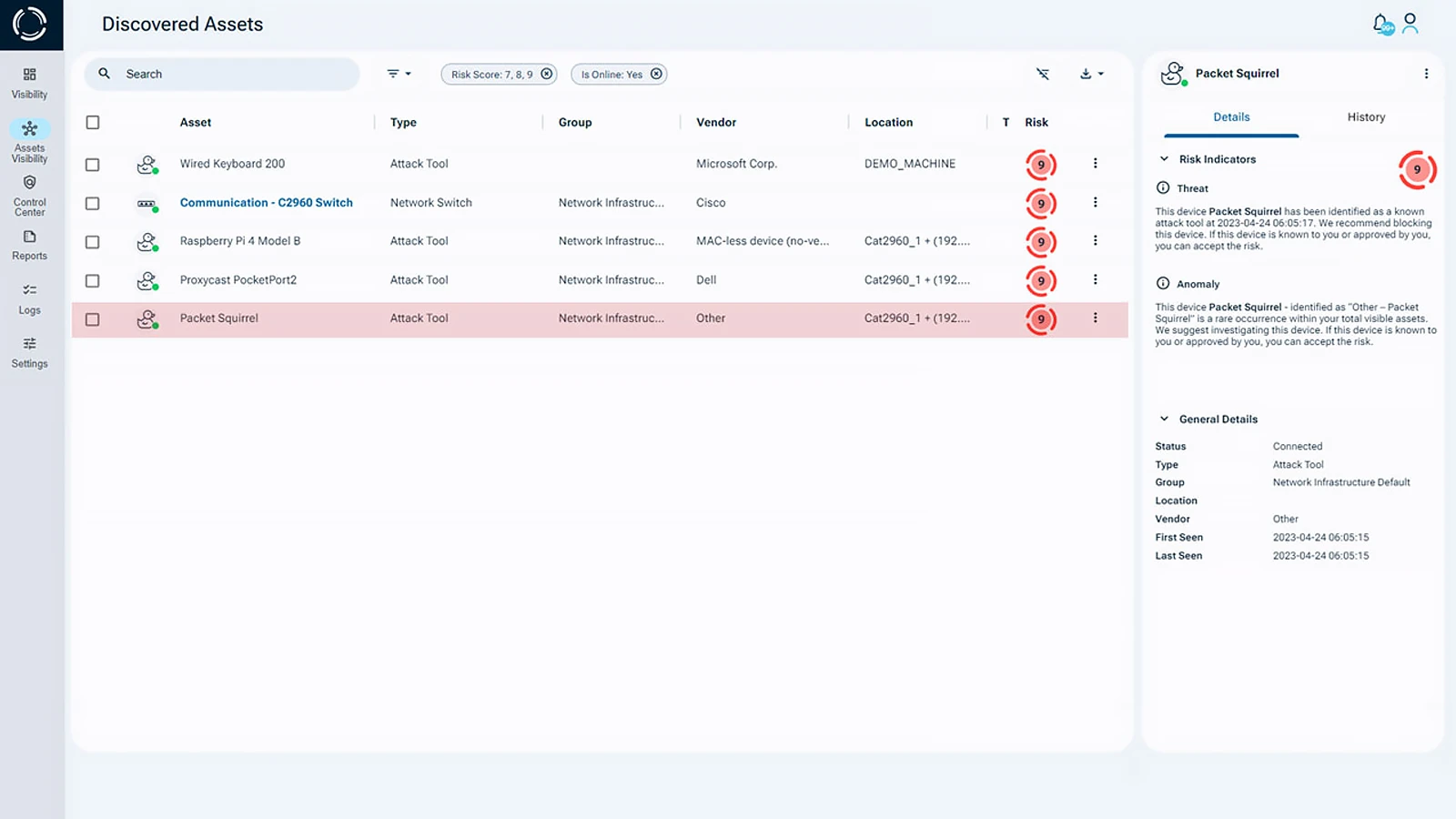
Prioritizing Network Security Threats
When it comes to securing networks, financial institutions must focus on visibility, validation, and control. Sepio’s patented solutions detect hidden risks, expose dormant assets, and thwart network security threats and attacks based on physical layer behavior.
Sepio’s unique capabilities reveal hidden threats and provide robust protection, ensuring that financial operations are compliant with strict regulations. Additionally, they are secured against the most elusive threats, thereby maintaining and strengthening the trust of their clients.
Enhance Your Network Security
Partner with Sepio to strengthen your defenses against network security threats. Discover how our solutions protect assets, ensure compliance, and safeguard client trust. Let’s build a secure network together!
Schedule a demo and discover how our advanced hardware security management solutions can protect your assets, ensure compliance, and maintain the trust of your clients. Let’s build a robust security network together!
Read the Network Security Threats Brief. (pdf)





