Understanding Cybersecurity Risks in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is a cornerstone of any nation’s critical infrastructure, delivering everything from routine check-ups to life-saving treatments. Yet cybersecurity risks in healthcare are on the rise, as hackers increasingly see the sector as a high-value target. Healthcare delivery organizations (HDOs) store vast amounts of sensitive data, rely on continuous operations, and have little tolerance for disruption, factors that make them especially vulnerable to cyberattacks and emerging threats.
Cybersecurity risks in healthcare aren’t just about stolen data. With limited budgets, stretched resources, and competing priorities, hospitals and providers are often unprepared for modern cyber threats. The real challenge is finding ways to protect systems without getting in the way of patient care. Yet, with the industry’s deep reliance on technology, these risks have a direct impact on both safety and quality of care.
While many healthcare organizations focus on software-based protections, they often overlook a critical blind spot: the network’s physical layer. At this level, rogue or compromised hardware can bypass even the strongest defenses, creating hidden threats and vulnerabilities. Without clear visibility into these hardware risks, hospitals put patients, staff, and essential services at serious risk of cascading consequences.
This article explores the main cybersecurity risks in healthcare, looking at the actors, attack methods, outcomes, and vulnerabilities that continue to threaten the industry, and why having clear visibility into hardware assets is essential for safeguarding both patient safety and national security.
Threat Actors and Their Motives
Understanding who targets healthcare and why is key to managing cybersecurity risks. Threat actors range from state-sponsored groups seeking strategic advantage to cybercriminals after financial gain. Each introduces unique risks that can affect patient safety, disrupt operations, and put sensitive healthcare data at risk.
- State-sponsored actors target healthcare organizations to steal intellectual property, gather insights into national healthcare policies, or disrupt operations. Such attacks can put patient safety at risk, compromise critical infrastructure, and even threaten national security.
- Terrorists seek to inflict both psychological and physical harm by targeting healthcare services. Attacks on hospitals and clinics can have far-reaching effects, potentially causing fatalities and spreading fear throughout communities.
- Cybercriminals focus on financial gain, exploiting healthcare’s limited tolerance for downtime. Ransomware attacks and data theft, including sensitive patient information and intellectual property, highlight the very real cybersecurity risks in healthcare, threatening both trust and the continuity of operations.
- Hacktivists carry out attacks to make political or social statements. Healthcare organizations can become unintended targets in these campaigns, increasing cybersecurity risks and disrupting operations.
Healthcare Cyberattacks and Their Consequences
Cyberattacks on healthcare tend to be more costly than the global average. Remediation and downtime are especially expensive because healthcare organizations operate in time-sensitive environments. These factors highlight the serious cybersecurity risks providers must manage.
Cyberattacks also bring significant indirect costs. Healthcare institutions face some of the world’s highest regulatory fines, often reaching seven figures, if their systems are not properly secured. On top of that, reputational damage can drive patients and partners away after an attack.
According to research by Morphisec, 27% of patients would switch healthcare providers if their current provider experienced a cyberattack. Repairing reputational damage, if it can be repaired at all, adds another financial burden. In healthcare, however, the impact goes beyond money, undermining patient trust, safety, and even national stability, underscoring the sector’s critical cybersecurity risks.
Major Cyberattacks to Healthcare Organizations
- Ransomware remains a prevalent threat to healthcare organizations. The HHS 405(d) Post, Volume XV, notes that: “Damage from ransomware is growing fast as more and more attacks successfully target medical infrastructure.” Such attacks don’t just disrupt operations, they can disable life-saving equipment, compromise patient care, and even increase mortality. This shows that cybersecurity risks in healthcare go beyond digital loss and can result in real physical harm.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks disrupt operations and may cover up other attacks. While less frequent, they can significantly impact patient services, especially when carried by hacktivists.
- Data breaches target sensitive patient data and intellectual property. With large stores of personal and medical information, healthcare organizations are especially attractive to hackers. On average, breaches in this sector cost $10 million, well above the global average, highlighting the serious financial and operational risks healthcare providers face.
- Intellectual property theft is another major threat. Research, drug formulas, and proprietary technologies are highly valuable to both state-sponsored groups and financially driven actors, making healthcare’s innovations a prime target.
- Insider threats come from employees or contractors, whether intentional or accidental. Because they have access to sensitive data and systems, strong monitoring and access controls are essential to reduce cybersecurity risks in healthcare.
Layer 1 Vulnerabilities and Hardware-Based Cybersecurity Risks in Healthcare
Layer 1 vulnerabilities play a key role in healthcare cybersecurity risks, as hackers increasingly exploit hardware weaknesses. Hardware cybersecurity is a specialized area, and existing solutions, like Network Access Control (NAC), Endpoint Protection Systems (EPS), Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), or Internet of Things (IoT) network security, do not provide Layer 1 visibility.
As a result, healthcare providers often lack full asset visibility, making it difficult to detect vulnerable or rogue devices. This blind spot lets hardware attacks bypass cybersecurity measures, even strict Zero Trust protocols. Without clear insight into what is operating within the infrastructure, organizations have limited control over their assets, leaving them highly vulnerable to hardware-based attacks. Ultimately, hidden hardware threats increase cybersecurity risks and can put patient safety at stake.

Hardware-based attacks need physical access to the organization. Specifically, rogue devices must be inside the infrastructure to carry out an attack. Moreover, several weaknesses in healthcare environments make this access easier, increasing the risk of such attacks.
Key Vulnerabilities in Healthcare Cybersecurity
Interconnected Environment
Healthcare delivery systems are highly interconnected, letting attackers move from one compromised device to others across the network. The increasing number of devices, along with IT and OT integration through IoMT, creates more entry points and potential threats.
Limited network segmentation and a lack of Layer 1 visibility leave vulnerable IoMT devices vulnerable. This puts other medical equipment at risk and highlights critical cybersecurity risks in healthcare from hardware threats.
Remote and Accessible Devices
Remote work and connected devices create additional entry points. IoMT devices and traditional endpoints, such as laptops, often store or provide access to sensitive data, making them prime targets. The spread of remote access points continues to heighten cybersecurity risks in healthcare and expand the threat landscape.
Supply Chain Exposure
Suppliers can introduce vulnerabilities, acting as gateways for rogue or compromised devices. Even highly secured healthcare entities are at risk if third-party hardware is exploited. Data sharing and integration with suppliers expand the attack surface, as seen in COVID vaccine distribution breaches. These weaknesses highlight critical cybersecurity risks in healthcare stemming from the supply chain.
How Sepio Mitigates Hardware Cybersecurity Risks in Healthcare
Sepio’s Asset Risk Management platform identifies, assesses, and mitigates all known and shadow assets at any scale, in real time. By leveraging physical layer data, it provides complete asset visibility and uncovers hardware-level risks that traditional cybersecurity tools cannot detect.
Using physical layer data, Sepio generates a DNA profile for every asset, ensuring accurate risk assessment free from misleading assumptions. This centralized, reliable visibility enables organizations to manage all assets with confidence.
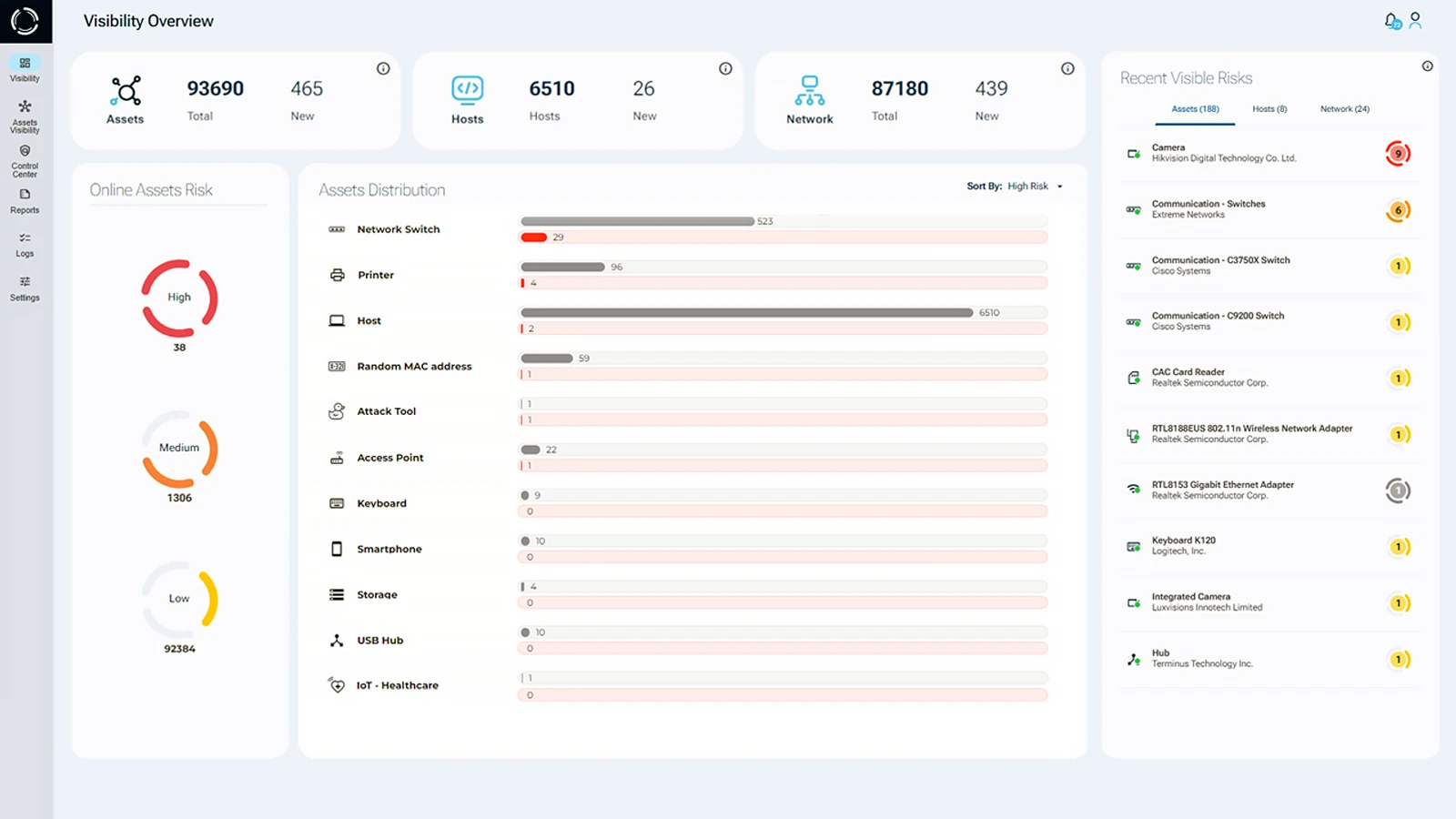
Each asset is assigned an Asset Risk Factor (ARF) score, derived from its DNA profile, business context, and predefined policies. This score prioritizes risks from high to low, enabling teams to respond rapidly, identify regulatory gaps, and prevent potential crises. Additionally, continuous monitoring, AI-driven analytics, and OSINT-based threat intelligence enhance IT efficiency while strengthening overall asset cybersecurity.
Protect Your Organization Against Cybersecurity Risks in Healthcare
Sepio enforces hardware usage policies automatically. Assets violating rules or identified as threats are immediately blocked, enabling instant and automated risk mitigation.
With a trafficless approach, Sepio scales across entire ecosystems without resource-heavy analysis, IT disruption, or compliance concerns. Implementation takes less than 24 hours.
Sepio integrates seamlessly with existing cybersecurity tools such as NACs, EDRs, XDRs, and Zero Trust solutions, enhancing their effectiveness and providing greater value from IT and security investments.
Ready to enhance your cybersecurity? Schedule a demo to see how we can protect your healthcare organization!
Managing Hardware Related Risks in Healthcare (pdf)





