USB Attacks are among the most covert and neglected cybersecurity threats facing organizations today. In an age dominated by digital transformation, attackers exploit vulnerabilities in USB devices or the USB protocol to compromise information security and gain unauthorized access. These sophisticated USB attack tools have evolved significantly, presenting serious risks to data integrity and operational continuity. As a result, the need for comprehensive USB cyber security solutions has never been more essential.
USB Attacks have also surfaced during penetration testing (PT) exercises conducted for some of our customers. These simulated breaches often highlight gaps in incident response procedures and security policies. Spoofed USB devices used in PTs reveal how easily attackers can bypass traditional defenses, reinforcing the critical importance of robust security awareness programs and effective cybersecurity training.
What are USB Attacks?
These bad devices, often referred to as Bad USB devices, appear in different forms. From seemingly benign USB dongles to connectors embedded within a computer’s USB-C power supply. Or even stealthily integrated into docking stations, providing remote keylogging, harvesting a user’s login credentials. Their hostile capabilities are diverse and far-reaching. Beyond merely presenting malware, without user privilege elevation, they can siphon off sensitive data. Execute secret extractions, manipulate files and setups.
A notorious exemplar of this threat is the USB Rubber Ducky. This human interface device scripting attack tool, impersonating as a legitimate keyboard, by spoofing its VID (Vendor ID), PID (Product ID) and ClassIDs. Despite its safe name, it can be programmed to execute cyber attacks. Its ability to mimic a keyboard allows it to bypass many security measures that would normally prevent unauthorized access. By exploiting this capability, an attacker could execute a wide range of malicious activities. From installing malware to stealing sensitive data or even taking control of the entire system. This underscores the importance of practicing good cybersecurity hygiene and being cautious when plugging in unknown or untrusted USB devices. If you find a USB device lying around or someone offers you one, think twice before plugging it in.


The Shortcomings of Contemporary Cybersecurity
Bad USB attacks manipulate device firmware to perform malicious activities such as data theft, malware injection, and system compromise. Detecting these attacks is difficult because their actions often mimic legitimate device behavior. This leaves organizations vulnerable to compromised systems and breaches that can go unnoticed.
Regrettably, most existing cybersecurity mechanisms lack sufficient capabilities to effectively counter these subversive hardware attacks. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions, while advanced, primarily focus on discovering and responding to payload attacks started by bad USBs. While successfully handling, legitimate USB devices – thumb drives, USB cameras and mobile phones, they consistently fail to monitor the subtle events of these spoofing USB tools (Bad USB) being connected or disconnected from host systems. This is a cybersecurity risk than leaves organizations vulnerable to USB attacks.
A automatic security measure, adopted by many organizations, is the blanket disabling of all USB ports. Yet, this strategy is fraught with weaknesses:
Ubiquity of USB-C
With the adoption of USB-C power supplies in modern computer devices, merely sealing off USB ports doesn’t protect systems from cybersecurity threats.
The widespread adoption of USB-C connectors for various functions, including power supplies, makes it impractical to completely seal off USB ports. Many modern devices use USB-C ports not just for data transfer but also for charging and various peripherals. Disabling USB ports entirely would disrupt the normal operation of these devices.
Operational Disruption
The act of blocking USB functions can accidentally disrupt organizational processes by rendering genuine peripherals like keyboards or mice nonfunctional. This is especially true in hybrid environments. Where employees are working from home, using their own, available, USB peripherals (Work From Home Cyber Security).
Overall, these flaws highlight the need for more comprehensive and nuanced approaches to cybersecurity. Organizations should consider a combination of strategies that protect against USB-based security threats while still authorizing legitimate and essential USB functionality to avoid functional interruption.
USB Cybersecurity Solution
To counter these threats, advanced solutions like Sepio’s platform offer a comprehensive approach to remediation and mitigation. Sepio performs a detailed analysis of an organization’s hardware ecosystem, identifying potential risks and ensuring robust protection against DDoS attacks, malware injections, and ransomware campaigns.
Sepio delves deeper, inspecting the intrinsic Hardware Bill of Material (HBOM) components. This involves identifying the physical profile of every hardware device during its connection event at the physical layer. This capability enables to discover and profile every peripheral device. Including identifying and discovering the USB devices that are attack tools or embedded within legit USB devices.
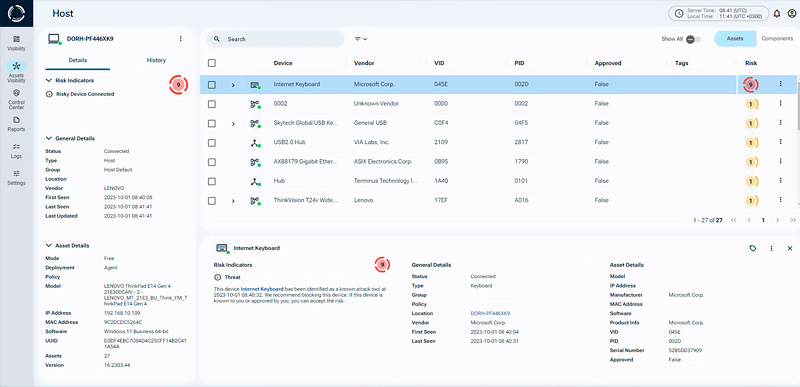
How to Protect your Organization from USB Attacks
USB-based cyber attacks are becoming increasingly complex and sneaky, emphasizing the need for proactive measures:
- Implement security training programs to raise security awareness about USB threats and social-engineering tactics.
- Enforce stringent security policies that include device encryption and application security protocols.
- Leverage advanced tools like Sepio’s platform for real-time incident response and threat detection.
By addressing USB-based threats with innovative solutions, organizations can build resilience against a wide range of cybersecurity risks and ensure their systems remain protected in an era of ever-evolving cyber threats.
Protect Your Organization from USB Attacks Today
USB attacks, including drop attacks and other USB threats, pose a significant risk to organizations. From malicious Bad USB devices to sophisticated tools masquerading as legitimate peripherals, these attacks can compromise your IT infrastructure.
Don’t leave your organization vulnerable to USB attacks. See every known and shadow asset in your ecosystem and protect against potential USB threats. Request a demo to learn more about preventing USB attacks on your network.




