Connected Devices
Connected devices, also known as the Internet of Things (IoT), are physical items with sensors, software, and communication tools. These features let them connect and share data with other devices over the internet. Examples include smartphones, smartwatches, home appliances, and even coffee makers. You’ll also find IoT in self-driving cars, smart TVs, and industrial machines. These devices make life easier and work more efficient. However, they also bring new security risks.
Connected Devices Security Issues
Recently, a security researcher proved that a smart coffee maker can be hacked. The device acted as a Wi-Fi access point and created an unencrypted, unsecured connection to its app. This flaw made it easy for hackers to use the coffee maker as a way into the network. Imagine what could happen if a harmless-looking kitchen appliance launched an attack on your router or other connected devices.
In more risky incidents, hackers have managed to take control of modern car systems. As cars become increasingly connected and software driven, they offer many benefits, but also introduce significant weak spots. In 2015, two security researchers performed a controlled test where they took control of a car remotely over the internet. The results were scary. While the experiment took place in a controlled setting, it revealed the serious security risks associated with connected systems in modern vehicles. If hackers took advantage of similar weak spots in connected devices, the results could be serious.
This cases highlights the growing need for robust security measures to address the growing attack surface created by connected devices.
Connected Devices Security Risks
The rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has led to the growth of smart homes, cities, and industries. In these spaces, connected devices talk to each other to automate tasks and boost efficiency. As these devices become cheaper, more people are using them. If this trend continues, experts expect that by 2030, each person will own about 15 IoT devices.
However, this widespread adoption introduces significant security challenges, including:
- More Access Points: Every connected device creates an additional potential entry point for attackers to exploit.
- Data Breaches: Compromised devices can leak sensitive data, resulting in severe privacy and security incidents.
- Unauthorized Access: Weak or default authentication mechanisms can allow threat actors to take control of devices remotely.
- Lack of Monitoring: As the number of connected devices grows, maintaining visibility and control over them becomes increasingly difficult.
- Hardware-Based Attacks: Traditional cyber security solutions often overlook threats originating from rogue devices or malicious hardware implants.
As more connected devices appear, they create more ways for attackers to get in. This is a big concern for IoT security. At the same time, the need to watch and manage these devices keeps growing. But the more devices there are, the easier it is to miss weak spots.
This is particularly dangerous in an era where hardware attacks are becoming more common. Traditional security software is not designed to detect or defend against threats coming from rogue hardware. Because of this, attackers can break in without being noticed. Organizations may be fully exposed and not even know an attack happened.
Network Attack Tools
Hardware tools can carry out many types of attacks. These include data theft, malware, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), and Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attacks. They often stay hidden while doing so. These tools have been around since at least 2008. Back then, they cost about $20,000. But as these attacks became more common, the tools got cheaper and easier to use. Today, a device like the USB Rubber Ducky, based on the concept known as BadUSB, can be bought for as little as $50.
As more devices connect to the internet, and hardware attacks become easier to launch, the future of connected environments raises serious concerns. While technology has clearly improved our lives, we must also recognize the growing security risks. Therefore, it’s essential for individuals and organizations to take strong protective measures. By doing so, they can enjoy the benefits of connected devices, safely and fully.
Securing Network Connected Devices
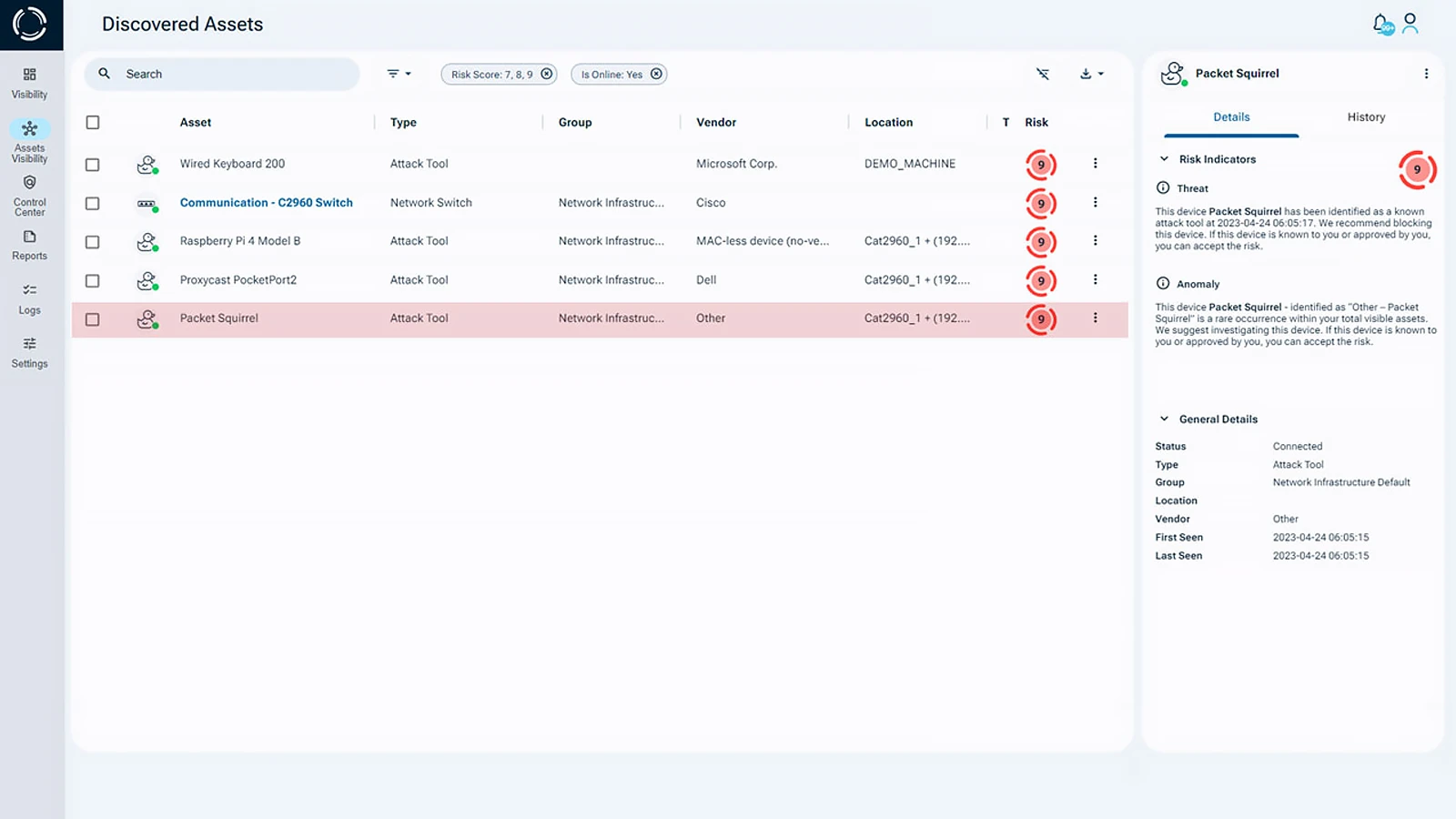
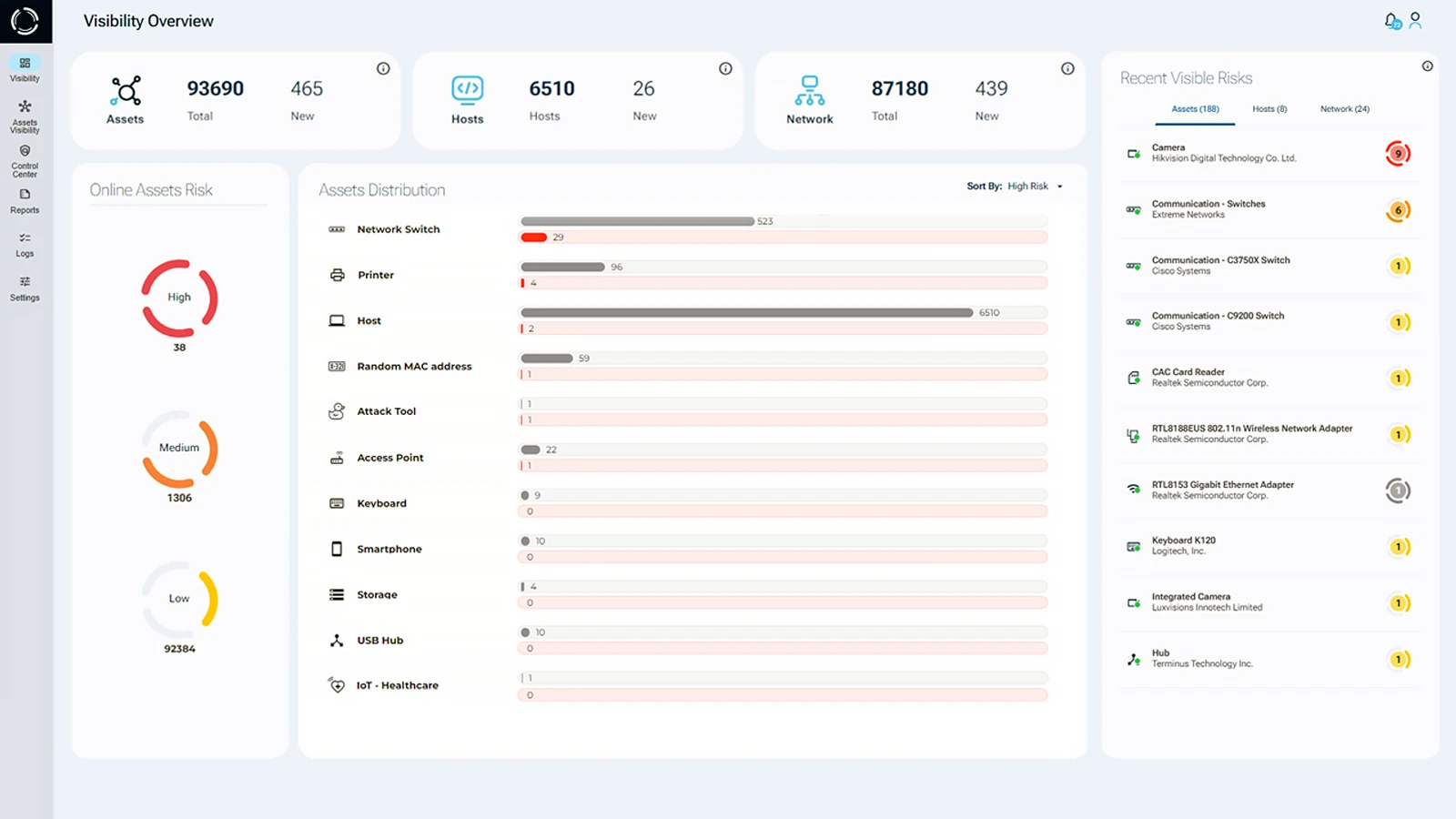
Sepio’s Cyber Physical System Protection Platform, offers the best view over all IT, OT, IoT, connected devices. By analyzing physical layer data, Sepio detects risks in real time, without depending on network traffic. As a result, you gain faster, more reliable threat detection across your entire environment.
Using Asset DNA, the platform gives precise information about every asset. This level of detail eliminates false positives and provides a trusted view into Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS). Additionally, Sepio assigns dynamic risk scores to each device, helping organizations prioritize security threats and improve compliance.
With Sepio, organizations gain policy control to automatically reduce threats. Furthermore, the platform integrates smoothly with NAC, SOAR, and other tools. Thanks to its scalable and lightweight architecture, Sepio ensures rapid installation, transforming asset risk management with both speed and efficiency.
Take Action to Secure your Network
Protect your business from the growing risks of connected devices. In addition, enhance your IoT security and protect your critical infrastructure. With Sepio’s patented technology, you can manage risks more easily and with greater confidence.
See every known and shadow asset. Prioritize risks.
Talk to an expert. It will help you understand how to use Sepio’s patented technology to gain control of your asset risks.






