Why is Cybersecurity Critical for Airports and the Aviation Industry?
Airport cybersecurity is a critical part of maintaining the safety and efficiency of air travel within the aviation industry. With increasing digitalization, airports handle sensitive information, from passenger data to flight operation systems, making them attractive targets for cyberattacks. In addition to ensuring safety and privacy, cyber-physical security for airports & airlines also protects the aviation industry’s economic interests by safeguarding operational continuity and public trust.
Airports are part of a nation’s critical infrastructure. As a result, they are constant targets for cyberattacks, terrorists, hacktivists, and rival nations. Moreover, airports provide an access point to the state, facilitating the movement of travelers and goods in and out of the country. Some states do not even have a coastline, making it impossible to engage with the rest of the world without an airport infrastructure.
Airport Cybersecurity Risks
As airports increasingly depend on interconnected information systems, the range of airport cybersecurity threats continues to grow. Consequently, these cyberattacks vary widely in scope and technique, ranging from traditional phishing schemes to sophisticated hardware-based attacks.
What are the Most Common Cyber Threats Faced by Airports?
- Social Engineering and Phishing Attacks: Hackers frequently employ social engineering tactics, such as phishing, to deceive airport employees into disclosing credentials or granting unauthorized access. For example, these schemes often involve impersonating trusted sources and manipulating individuals into revealing sensitive information. As a result, hackers can then use this information to infiltrate airport information systems.
- Malware: Airports are prime targets for malware cyberattacks, where malicious actors take control of key systems or data and demand payment to release them. Malware attacks can disrupt operations, compromise data-security, and cause significant financial loss. In 2020, San Francisco International Airport suffered an cyberattack on two of its websites, while Albany Airport was infected with malware via a contractor.
- Hardware-Based Attacks on Airport Systems: Hardware-based cyberattacks involve the installation of hardware attack tools to create backdoors into the network. These cyberattacks can go undetected for months, enabling hackers to map out and exploit system vulnerabilities. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems are essential components of airport cybersecurity, but on their own, they are not enough to counter today’s changing and sophisticated threats.
- Internal Threats and Human Error: Airports must also consider the threat posed by employees, either through malicious intent or simple human error. A single mistake, such as using weak passwords or connecting unauthorized devices, can result in a security breach. Security awareness training helps mitigate these risks.
Vulnerable Entry Points for Airport Cyberattacks
Hackers exploit various entry points to breach airport networks, often targeting the weakest links in the system. As the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices within the network grows, so does the risk of unauthorized access. The more connected devices in operation, the greater the vulnerability to potential cyberattacks.
- IoT Devices: Airports rely heavily on Internet of Things (IoT) devices, including security cameras and access control systems. However, these devices are often vulnerable to cyberattacks, giving hackers multiple access points into the airport’s network. Therefore, implementing strong application security and data protection protocols is essential to defend against these threats.
- Employee Security Vulnerabilities: Personal technology used by airport employees, such as laptops, smartphones, and connected printers, can unintentionally serve as entry points for cyber attackers when linked to the airport’s network. Without proper security controls, these endpoints may introduce vulnerabilities that compromise sensitive systems and data.
- USB-Based Attacks: USBs can easily be weaponized by hackers, spoofed as legitimate peripherals, and used to gain unauthorized access. These hardware-based cyberattacks allow hackers to infiltrate networks without immediate detection, posing a serious threat to airport cybersecurity. Learn more about USB attacks.
Airport IoT Cybersecurity: Emerging Cybersecurity Challenges
The growing reliance on IoT devices in airport operations simultaneously introduces new cybersecurity risks. The vast number of connected devices creates multiple entry points, each with its own cybersecurity challenges. Common risks associated with airport IoT include unauthorized access, data interception, and system manipulation.
For instance, a compromised baggage handling system could lead to lost luggage or operational delays, negatively impacting customer experience and the airport’s reputation.
The Risks of Internet-Connected Devices in Airports: From security cameras to baggage scanners, airports rely on a wide range of internet-connected technologies. If compromised, these systems can provide hackers with access to sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
Securing Critical Equipment: Even equipment like x-ray machines can be vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers could manipulate these systems to avoid detecting illicit materials. This poses a significant threat to security and safety.
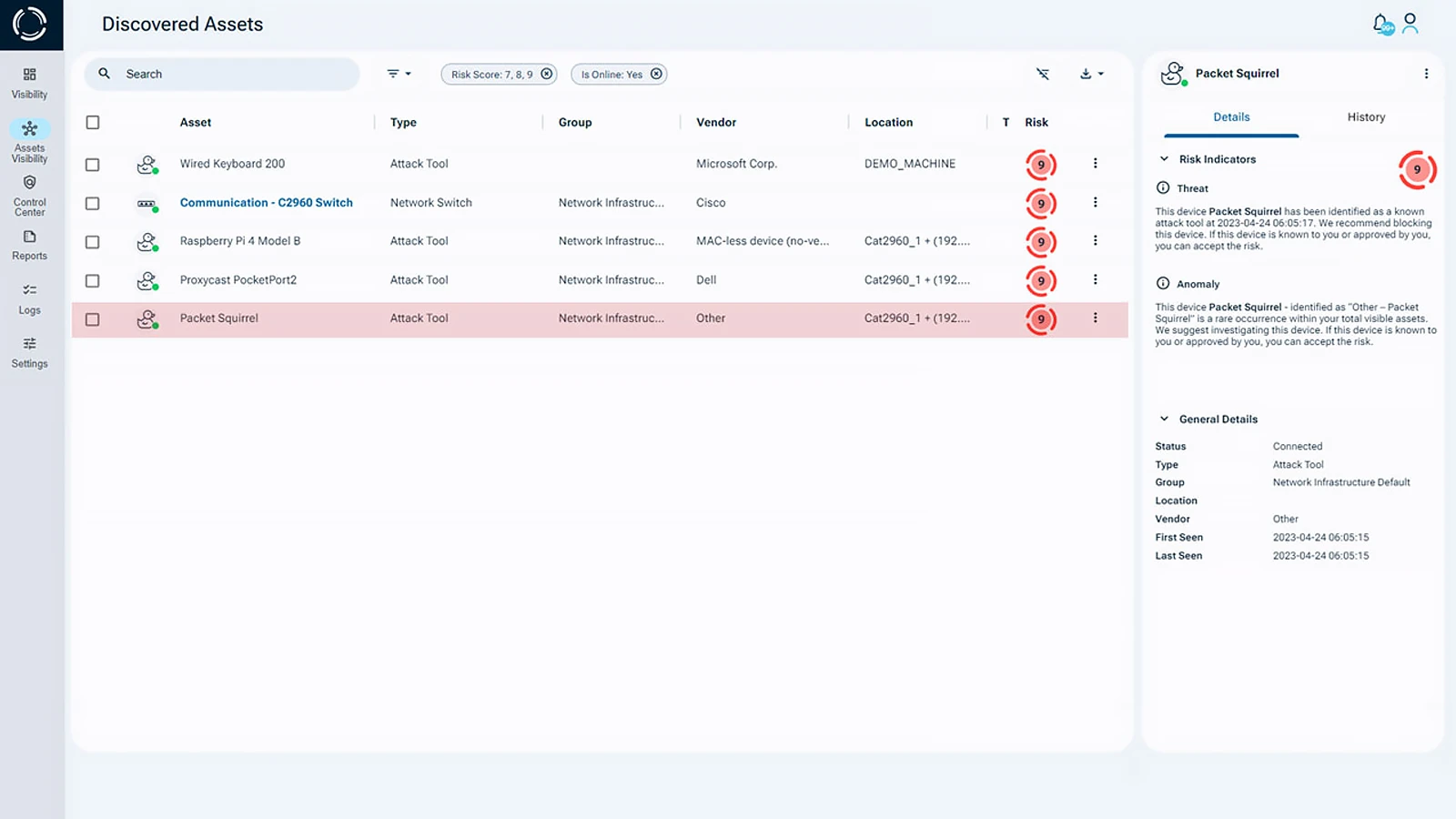
Cybersecurity at Airports and the Aviation Industry
Airports must adopt strong cybersecurity solutions to fight the growing range of cyber threats in aviation. Sepio’s platform helps reduce these risks by offering broad protection against hardware-based attacks. These attacks are among the most stealthy and damaging threats airports face today.
- Zero Trust Hardware Access (ZTHA): Helps airports ensure that only authorized endpoints connect to critical systems. This reduces the risk of data leaks and unauthorized access. The strategy requires continuous monitoring and verification of all devices trying to connect. This helps create a secure environment for airport operations.
- Comprehensive Device Visibility: Complete visibility into all devices operating within airport networks is a key component of robust cybersecurity. Solutions like Sepio’s platform offer real-time monitoring and identification, allowing security teams to detect and block potential hardware-level cyberattacks.
- IoT Security Protocols: Since IoT devices are essential yet vulnerable components of airport infrastructure, implementing strong IoT security solutions is essential. This involves regular device authentication, secure firmware updates, and continuous monitoring to detect any anomalies that could indicate cyber threats.
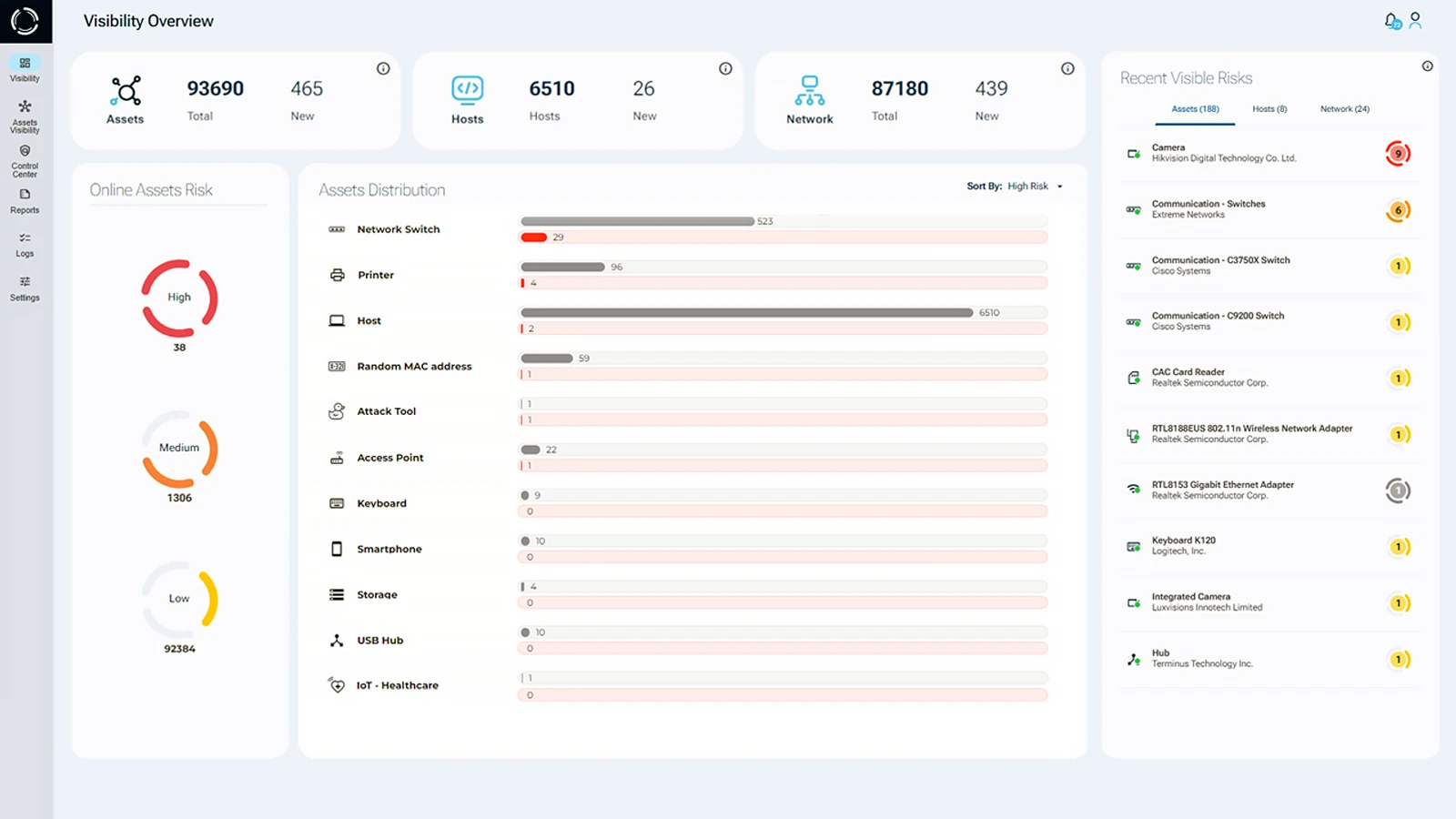
Partnering with Cybersecurity Experts
As cyber threats continue to evolve, airport cybersecurity remains a critical priority for both national security and the aviation industry. Implementing robust cybersecurity strategies protects the digital infrastructure of airports. It also protects travelers, employees, and assets from growing cyber risks.
By partnering with advanced cybersecurity vendors like Sepio, airports can stay one step ahead of emerging threats. Moreover, such collaborations strengthen defenses, secure the future of air travel, and help build public trust in an increasingly digital and connected world.
Additionally, federal resources such as the TSA Surface Transportation Cybersecurity Toolkit provide valuable best practices and frameworks for protecting transportation infrastructure.
Stay Ahead of Airport Cyberattacks
Take a step toward securing the future of your airport operations, schedule a demo. With Sepio’s advanced technology, you can protect passengers, sensitive data, and ensure continuous airport services.
Let Sepio be your trusted partner in the fight against changing cyber threats, enabling you to stay one step ahead.






