Raspberry Pi Security
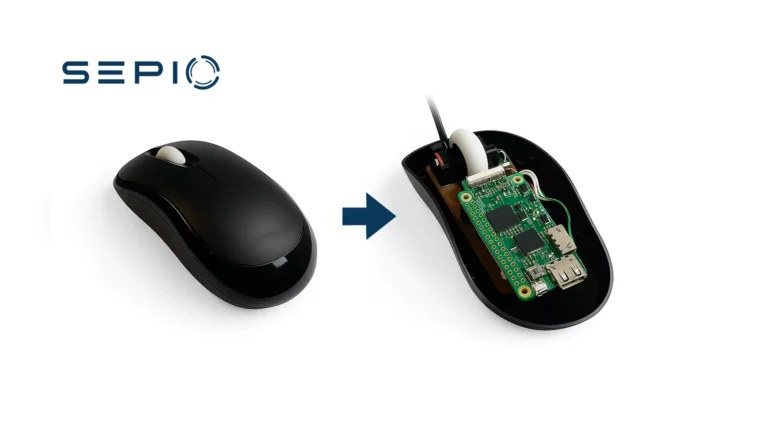
The Raspberry Pi is a small (credit card-like size), inexpensive, portable computer that connects to real-world objects. It contains all the basics of any computer including a processor, memory and graphics processor. As such, it is capable of doing everything one would expect a regular computer to do, such as browsing the internet, playing high-definition videos, creating spreadsheets, accessing word processing, and more. While originally designed for ethical purposes, its versatile capabilities can also be exploited for malicious activity. As a result, Raspberry Pi security has become a critical concern, as the device can be repurposed through a payload to execute rogue actions.
In this article, we explore the Raspberry Pi security vulnerabilities. Regardless of its intended use, the device’s ability to execute dangerous cyberattacks makes it a potential threat to networks and systems.
Raspberry Pi Security Vulnerabilities
Raspberry Pi devices, while innovative and practical, reveal significant security vulnerabilities that expose networks and critical systems to advanced cyber threats. Strengthening Raspberry Pi Security requires awareness of tools that exploit these vulnerabilities.
PoisonTap
PoisonTap is designed for Raspberry Pi and exploits the existing trust in various mechanisms of a machine and network. It creates a cascading effect of information exfiltration, network access, and installation of semi-permanent backdoors, often bypassing firewalls and other security measures.
P4wnP1
P4wnP1 is a highly customizable USB attack platform for the Raspberry Pi Zero or Raspberry Pi Zero W that allows one to connect the hardware attack tool into a host computer. As a HID or network interface. This tool can exploit vulnerabilities in authentication mechanisms and bypass endpoint protections.
Bypassing Network Access Control (NAC)
Network Access Control (NAC) software supports network visibility and access management through policy enforcement on devices and users of corporate networks. To bypass, an attacker must access a device that has already been authenticated. In this case, a Raspberry Pi can be used to spoof the identity of a legitimate, authenticated device. Once the genuine device logs into the network, the attacker can smuggle network packets from the Raspberry Pi by overwriting the MAC address, making it appear as if the packets are originating from the authenticated device.
This breach of Raspberry Pi Security gives the attacker full access to the organization’s network, enabling lateral movement. From there, the attacker can carry out a variety of attacks, including data breaches, malware installation, or even more sophisticated threats like Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs). This highlights the critical need for strong Raspberry Pi Network Security measures to mitigate such risks.
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attack
An Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attack, carried out with a Raspberry Pi, is a major threat to organizations. Due to its sophisticated and targeted nature, APTs often target government agencies or critical infrastructure providers, posing risks to national security. Nation-state or state-sponsored hackers typically conduct these attacks. APTs can access sensitive data and remain unnoticed for extended periods, employing advanced intrusion detection evasion techniques.
These risks demonstrate the urgent need for effective Raspberry Pi Security strategies across both physical and digital environments.
Raspberry Pi in Healthcare: Ventilator Vulnerabilities
The Raspberry Pi, with its computer-like capabilities, can control a medical ventilator. It sets air pressure, opens and closes valves, and regulates the level of breathing assistance needed. Since a ventilator has relatively low demands, the Raspberry Pi Zero is ideal for this purpose. However, computer-controlled ventilators increase entry points for hackers targeting the healthcare industry. Healthcare data breaches expose sensitive information like Personal Health Information (PHI), which sells for 100 times more than Personally Identifiable Information (PII) on the black market.
Physical Layer Security Risks
The Raspberry Pi pose significant security risks due to their covert nature. Their small size allows them to be discreetly embedded within peripherals or networks, evading detection by security professionals. When used as USB attack tools, security software identifies them as legitimate HID devices, bypassing intrusion detection systems. When acting as network implants, they operate on the Physical Layer, outside the coverage of security software, making them vulnerable to unauthorized access and exploitation.
Many enterprises struggle with securing their hardware assets due to a lack of visibility. This can lead to security breaches, such as ransomware attacks, data leakage, or cybercrime. To address these challenges, complete visibility into hardware assets is essential for enforcing strong security policies. Attackers often exploit network vulnerabilities through USB Human Interface Device (HID) emulation or network implants.
In addition to deep visibility, a comprehensive policy enforcement mechanism recommends best practices. It allows administrators to define strict or more granular rules for the system to enforce.
Raspberry Pi Network Security and Rogue Device Mitigation
Sepio is the leader in the Rogue Device Mitigation (RDM) market and is disrupting the cybersecurity industry by uncovering hidden hardware attacks operating over network and USB interfaces. With a focus on Raspberry Pi Security and other hardware attack tools, Sepio’s solution, identifies, detects and handles all peripherals. Ensuring no hardware asset goes unmanaged.
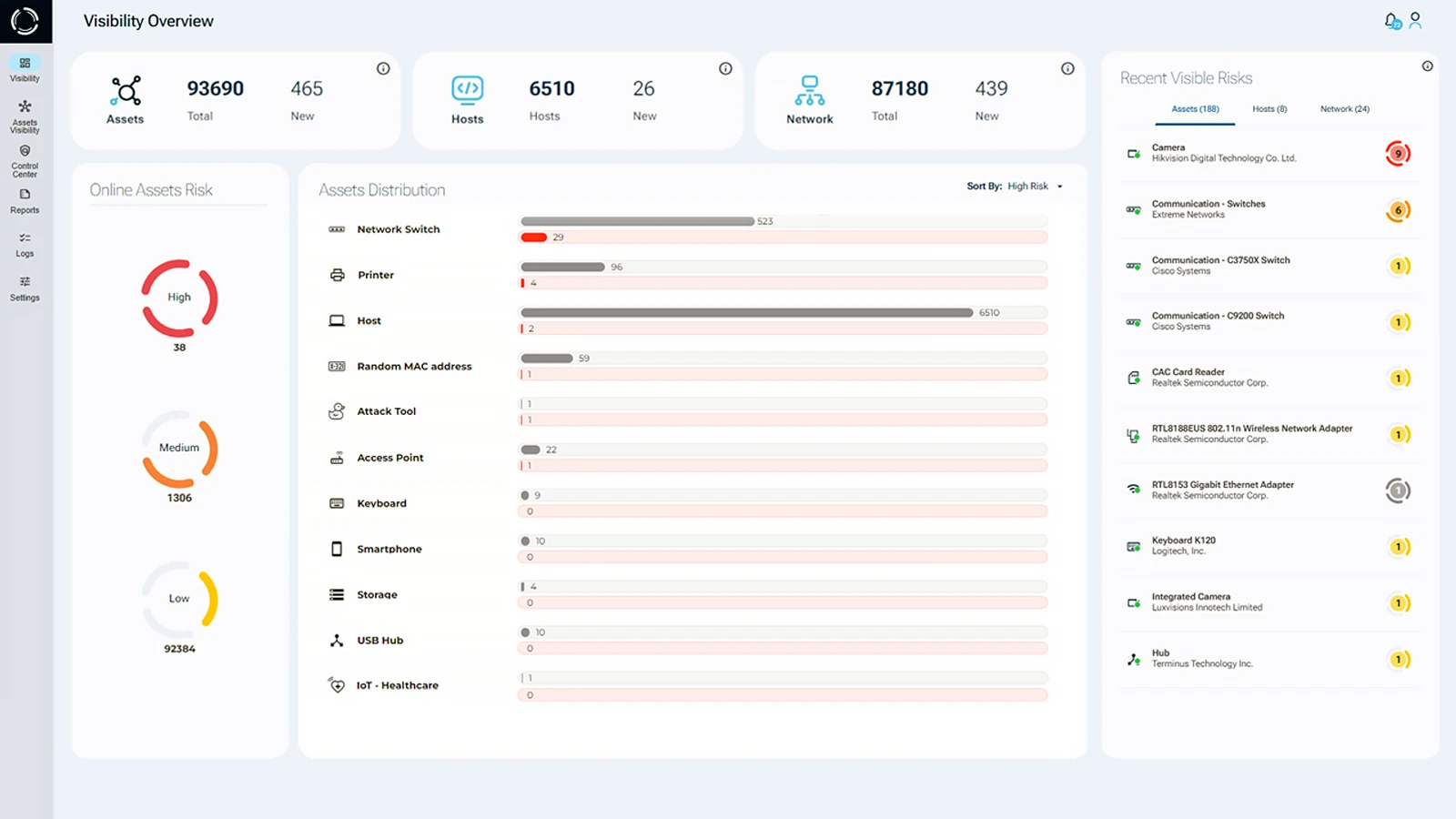
Sepio is the only company in the world to undertake Physical Layer fingerprinting of all connected peripherals. By comparing each fingerprint against a known database of malicious hardware, Sepio automatically detects and blocks attacks before they can cause harm.
With Machine Learning, the software analyses device behavior to identify abnormalities, such as a Raspberry Pi acting as a keyboard.
Complete Visibility of All Hardware Assets: Achieve unparalleled visibility into all hardware assets, including endpoint peripherals and IT/OT/IoT assets. Sepio’s unique Physical Layer hardware fingerprinting technology neutralizes Raspberry Pi security threats and other rogue hardware risks. With data augmentation from endpoints and networks, Sepio helps enterprises to detect all connected assets. This ensures a strong cybersecurity posture that addresses Raspberry Pi Security risks.
Full Control Through Predefined Policies: Sepio empowers organizations to simplify compliance and enhance security through enterprise-wide predefined policies. Unlike traditional methods that depend on baselining or allowlisting, Sepio delivers comprehensive protection at the hardware level, effectively mitigating threats such as rogue Raspberry Pi activity on the network.
Rogue Hardware Mitigation (RDM): Swiftly mitigate hardware-based attack tools with Sepio. By delivering complete visibility and control at the hardware level, Sepio effectively addresses Raspberry Pi network security risks, ensuring no hidden or unauthorized assets evade detection.
Discover Every Raspberry Pi Network Threats
Talk to an expert. Discover how Sepio’s patented technology can help your organization detect and neutralize Raspberry Pi vulnerabilities, strengthening your network security posture and eliminating rogue hardware threats at the source.
Read the Raspberry Pi Security e-Book (pdf)