What Does BYOD Stand For?
BYOD stands for Bring Your Own Device. In cybersecurity, it refers to employees using personal devices to access company systems, requiring security controls to prevent data breaches, malware, and unauthorized access. BYOD is popular because it saves costs, increases productivity, and lets people use the devices they already know. As more people work remotely, it is important to manage security and control access to company networks.
BYOD gives employees more freedom and helps them balance work and personal life. But it also comes with risks. Personal devices can be harder to protect, which makes companies hesitate about using BYOD.
Benefits of BYOD
BYOD helps companies save costs since they do not have to buy hardware. Employees already know how to use their own personal electronics, so they need less training.
A study by Samsung and Frost & Sullivan, employees who use their own smart phones gain nearly an extra hour of work each day, boosting productivity by 34%.

BYOD also gives workers more flexibility, for example, to work from home (WFH). They can manage both work and personal tasks on the same device, which improves work-life balance and job satisfaction.
Security Risks of BYOD
Even though BYOD saves money and boosts productivity, it can create cybersecurity risks. For example, personal laptops do not always have strong protection. That makes them easier targets for malware, data leaks, and unauthorized access.
About half of all companies that allow BYOD have faced cybersecurity problems from employee personal electronics.
Why are BYODs Risky?
Many personal devices lack encryption, security software, or device management. These gaps make it easier for hackers to break in, especially if they are connected to public Wi-Fi or unsafe networks.
Even well-meaning employees can make mistakes, like installing unsafe apps. That’s why it’s so important to manage BYOD use carefully.
BYOD in Workplaces
A big challenge with BYOD is controlling personal electronics across the organization. While IT teams often set security policies, personal devices are usually outside their direct control. Without proper oversight, keeping every connected asset secure becomes a tough task. That’s why companies need clear BYOD policies. These policies should protect company data while also respecting employee privacy.
Companies should use asset management tools to:
- Monitor personal devices.
- Apply security updates.
- Encrypt data.
- Control network access.
Dangers from Peripherals
Peripheral devices like USB drives and chargers can be dangerous. Some are designed to carry out hardware attacks. Even a cheap or BadUSB can install malware.
Offering free USB drives or chargers, are common methods used to trick employees and spread malware that bypass traditional security tools. That’s why a strong asset management system is key to blocking threats.
Spoofed Devices
Spoofed devices are another major threat in a Bring Your Own Device environment. These peripherals look like normal equipment but are actually fake. By taking advantage of blind spots at Layer 1, they can avoid detection by common security tools like NAC and IDS. This allows them to carry out harmful actions without triggering any alerts.
Lost/Stolen Devices
Lost or stolen laptops are a constant risk in BYOD environments. Without strong asset management, companies face serious security threats. If a device isn’t properly protected, attackers can quickly access sensitive data. With over 70 million devices lost or stolen each year, companies need a way to remotely wipe data and block access to their network.
How to Improve BYOD Security
To reduce risks, companies should offer SETA programs, Security Education, Training, and Awareness. These programs teach employees how to avoid tricks like social engineering and how to stay safe online. Additionally, creating robust BYOD policies is crucial. This ensures the separation of personal and business data on employee devices, helping protect sensitive information.
While SETA significantly reduces mistakes caused by human factors, it is not a failsafe solution. Hardware attack tools can evade traditional security, highlighting the need for physical layer data to detect and manage all connected assets.
A strong asset management system is essential for BYOD security. It allows organizations to remotely wipe stolen devices and block unauthorized access to sensitive data. To address these threats effectively, organizations need to focus on seeing what’s happening at the physical layer. By finding and accounting for all assets, they can establish a solid foundation for Bring Your Own Device network security. This approach protects digital systems, reduces risks, and ensures better control over network access.
Sepio’s Endpoint and Network Security
Sepio’s platform shows exactly which assets are connected to your network. With deep network visibility, it checks every asset, whether it is IT, OT, IoT, or BYOD. Moreover, Sepio’s policy enforcement mechanism and Rogue Device Mitigation capabilities instantly stop any not allowed or rogue hardware. This supports a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) by stopping threats at the first line of defense.
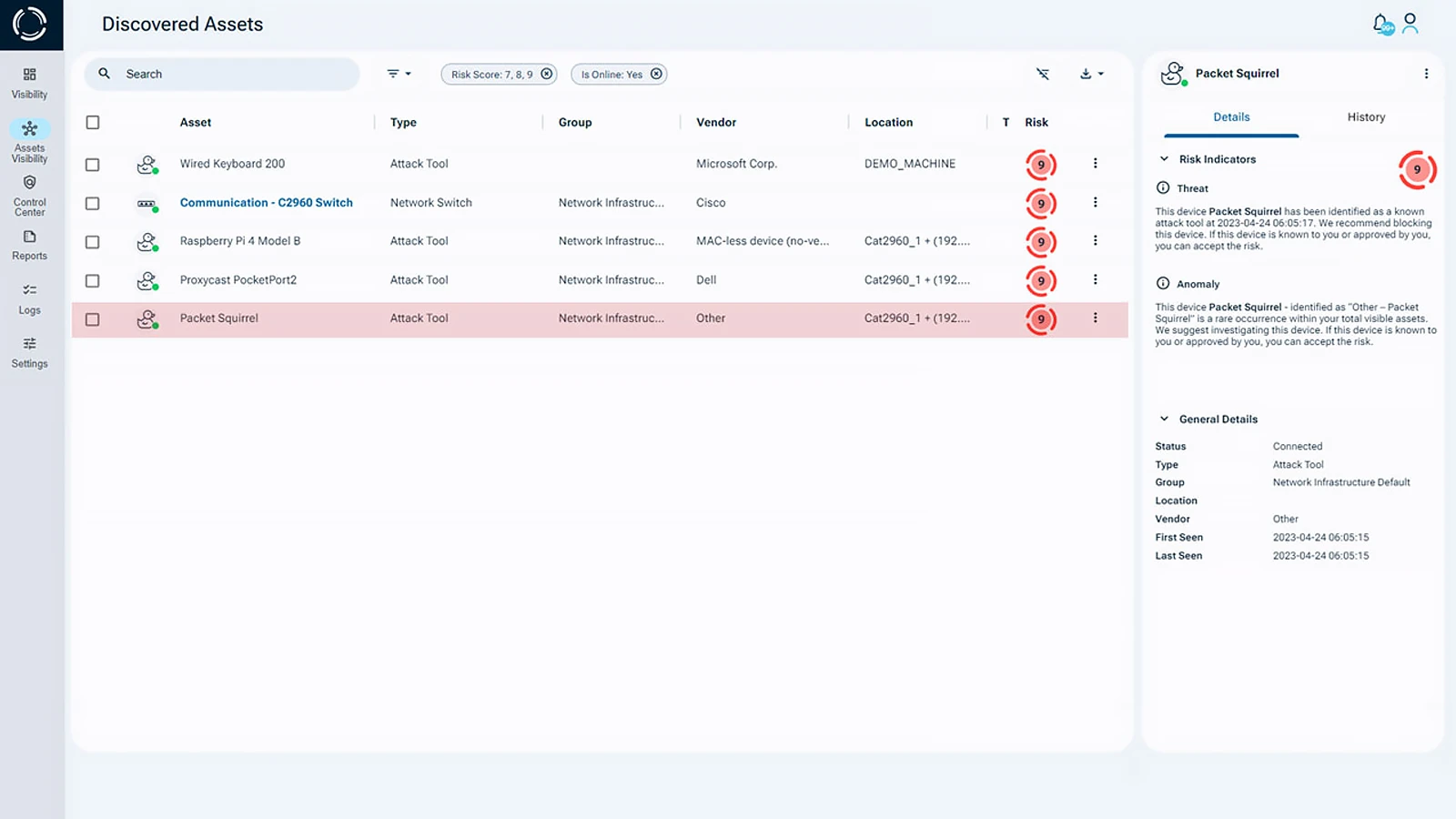
Protecting all connected assets, whether personal or company-owned, takes more than basic security tools. It requires a full strategy that includes asset management, encrypted connections, and constant monitoring. These steps help make sure every BYOD used for work is secure.
Secure your BYOD Environment
BYOD allows employees to use personal electronics for work. While this offers many benefits, it also causes security risks that need to be managed. With Sepio’s platform, you can ensure robust computer security. This protects all assets, whether remote or in office as soon as they connect to your network.
Talk to an expert to learn how to protect your BYOD environment and gain control over every connected asset.






