Energy Sector Security: Why It Matters?
Cybersecurity in the energy sector is of paramount importance as the sector increasingly embraces digital transformation. With increasing digitization and interconnectivity, the sector faces new vulnerabilities, making it more susceptible to cyber attacks. These threats can have devastating consequences, disrupting critical services that nearly every other industry relies on. A successful cyberattack on energy infrastructure could result in widespread damage, both economically and to national security.
Cybersecurity in energy sector is vital due to the industry’s role as part of a nation’s critical infrastructure. As energy providers adopt new technologies to enhance efficiency, they simultaneously expose themselves to more sophisticated cyber threats—including malware, phishing, data breaches, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. To mitigate these evolving risks, cybersecurity must remain a top priority.
Cyber Security Threats in Energy Sector: Key Threat Actors
Cyber security threats in energy sector stem from a wide range of malicious actors, each with distinct motives:
- State Actors: Cybersecurity in energy sector is increasingly challenged by nation-state attackers who target energy systems for espionage and sabotage. Advanced hacking techniques allow these actors to infiltrate systems and even cause physical damage to the equipment used by energy providers. With vulnerabilities in cybersecurity in energy sector, state-sponsored groups are increasingly capable of conducting such attacks, heightening the risk to the industry.
- Terrorists: Like state actors, terrorists see the energy sector as an ideal target due to a country’s dependence on its services. Although terrorists may lack the technical skills to carry out sophisticated cyberattacks, their intent is often to cause physical damage, which could disrupt energy systems and lead to broader national crises.
- Cybercriminals: Many times, perpetrators of cyberattacks are merely criminals seeking financial gains. The energy sector can provide monetary rewards in several ways. An immediate financial payout can come from a successful ransomware attack. Alternatively, cybercriminals may deploy attacks that result in data theft, whereby the information obtained can be sold on the dark web.
- Hacktivists: Activist groups, such as Anonymous, are turning to cyber tactics to make a statement. Many activist groups oppose activities carried out by the energy sector and wish to protest against them. Cybersecurity in Energy Sector is essential to prevent these attacks, which can be deployed as a statement of opposition against energy sector projects or general agendas.
The Visibility Challenge in Energy Sector Security
A robust strategy for cybersecurity in energy sector must include comprehensive visibility into all hardware assets connected. However, energy organizations often struggle to fully protect their hardware assets, especially in today’s complex IT/OT/IoT environment. The lack of device visibility makes it difficult to enforce strong hardware access policies, leaving systems vulnerable to attacks such as ransomware, data leakage, and data breaches.
Malicious actors often exploit these gaps, taking advantage of blind spots in security systems. Rogue devices, such as USB HID-emulating devices or physical layer network implants, can bypass traditional security measures, evading detection by existing security software solutions. These covert devices give attackers a way to infiltrate critical systems undetected, increasing the risk of compromised data and system failure. Cybersecurity in Energy Sector must address these blind spots with advanced device visibility solutions.
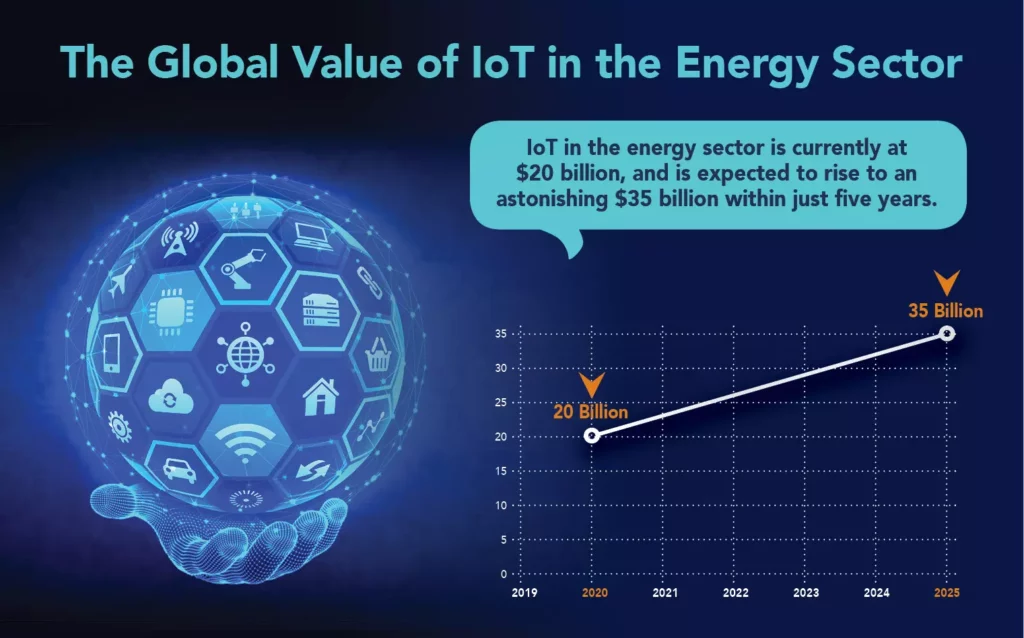
Cyber Security Prevention Strategies
To effectively mitigate the growing cyber threat landscape, energy organizations must focus on securing their infrastructure with advanced cybersecurity solutions. This includes implementing encryption protocols, strengthening authentication mechanisms, and ensuring that cloud security measures are in place to protect sensitive data. Security experts also recommend security awareness training to help employees recognize the signs of social engineering attacks like phishing.
As the energy sector continues to digitize, maintaining visibility over all connected devices and applying robust firewall protections are essential to safeguarding against malware, hacking, and other cybersecurity threats in the energy sector. A proactive approach to security risks is crucial in ensuring the protection of sensitive information and preventing security breaches that could disrupt operations and cause lasting damage.
Physical Layer Cybersecurity
Sepio’s platform focuses on mitigating hardware-based attacks, that explore vulnerabilities in physical devices. These attacks often go undetected by traditional security solutions as they operate on the physical layer. Sepio’s Asset DNA technology is physical layer-based, detecting rogue devices based on their existence rather than behavior. This allows it to discover all managed, unmanaged, and hidden devices on a network.
Sepio employs machine learning algorithms to accurately identify the true source of asset risk. Avoiding misleading profile perceptions and behavioral assumptions. The platform prioritizes assets based on their risk levels and enforces granular hardware access controls. Automatically blocking devices that breach preset rules or are identified as known attack tools.
- Comprehensive Asset Visibility: Sepio enables the complete physical layer visibility of all connected assets on your network. This includes devices connected via USB or network interfaces.
- Hardware-Based Risk Assessment: The platform assesses the risk associated with each hardware asset. Identifying potential vulnerabilities and threats from malicious devices (Hardware Cyber Security).
- Real-Time Risk Management: Sepio provides robust risk management capabilities for all hardware assets. It detects and mitigates risks in real-time, ensuring your infrastructure remains secure (Asset Risk Management).
- Detection and Mitigation of Malicious Assets: The solution detect and mitigate risks from malicious assets in enterprise environments. It covers a wide array of devices, ensuring comprehensive protection.
- Blocking and Control Options: Sepio can block each USB port, disabling risky assets immediately upon connection. This real-time blocking capability plays a crucial role in preventing potential security breaches (Preventing USB Attacks).
- Policy Configuration: Users can easily configure granular policies tailored to their specific needs or opt for Sepio’s default settings. These policies help manage and control the usage of USB and network interfaces effectively.
See Every Known and Shadow Asset
Talk to an expert. It will help you understand how to use Sepio’s patented technology to gain control of your asset risks.
Read the paper Cybersecurity in Energy Sector (pdf)





