What is Shadow IT in the Context of Networking?
Shadow IT assets are any hardware, software, or cloud-based services used within an organization without the knowledge or approval of the IT department. These unauthorized tools often emerge when employees use personal devices, third-party applications, or unapproved platforms to perform work tasks. Shadow IT creates security gaps, increases organizational risk, and makes it harder for IT to maintain control and visibility over the network.
While often adopted for efficiency, these unauthorized assets pose serious security risks. When connected to the corporate network, they can create hidden vulnerabilities that cybercriminals may exploit, resulting in data breaches, compliance failures, and other damaging cyberattacks.
Effectively identifying, managing, and mitigating shadow IT assets is key to securing a network and meeting regulatory standards.
Shadow IT Assets Risks
Each shadow IT asset that connects to the corporate network increases the organization’s attack surface, creating new vulnerabilities for cybercriminals to exploit. Without centralized management, IT teams struggle to detect unusual behavior or respond swiftly to threats. This lack of visibility enables prolonged attacker dwell time, raising the risk of data exfiltration, malware infections, and compliance violations.
To learn more about the different levels of shadow IT and their impact, refer to the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) guidance on Shadow IT.
Unauthorized Network Connections
Unauthorized network connections are a common way shadow IT assets introduce security risks. Here are some examples:
- Personal Devices: When an employee connects a personal router, external drive, or application to the network, it becomes unmanaged. These connections enable file sharing, unapproved software installation, or bypassing security controls. As a result, the risk of data leaks and cyber threats increases.
- Rogue Access Points: Setting up an unauthorized wireless access point, whether for convenience or malicious intent, creates a shadow network connection. This weakens network security, making it easier for attackers to intercept traffic or gain unauthorized access to sensitive systems.
- Compromised Devices: If a network-connected device (such as a printer, IoT device, or server) is infected with malware, it can establish unauthorized connections to external servers. These compromised devices operate outside IT’s visibility, allowing cybercriminals to steal data or launch attacks from within the network.
What are the Security Risks of Shadow IT Assets?
Unauthorized network connections are risky because they lack proper supervision and security controls. IT security teams implement strict network configurations and protocols to protect the organization. However, when shadow IT assets bypass these protections, they introduce serious cybersecurity threats, including:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Unauthorized connections often lack firewalls, encryption, or endpoint protection, creating weaknesses that attackers can target.
- Spreading Malware: Shadow IT devices may already be compromised, allowing malware to spread across the network and infect critical systems.
- Data Breaches: Without the right access controls and monitoring, sensitive data can be exposed or stolen, causing compliance violations and financial losses.
These risks grow in regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and government. Shadow IT can cause serious privacy and data handling violations.
Mitigating Shadow IT Assets Risks
To reduce shadow IT risks, organizations must improve network visibility and educate employees about the dangers of unauthorized devices. They should also enforce strict security policies.
This includes conducting regular audits, implementing device control solutions, and fostering a culture of transparency and communication between employees and IT.
Sepio’s Asset Risk Management (ARM) platform helps organizations gain full network visibility and detect unauthorized connections, reducing the risks posed by shadow IT assets. By securing all network-connected devices, IT teams can minimize the attack surface and protect against potential cyber threats.
Common Shadow IT Scenarios Handled by Sepio
Sepio helps IT teams detect and mitigate Shadow IT through hardware-based visibility, continuous monitoring, and automated reporting. Key scenarios include:
- Rogue Wireless Access Points: Detection of unsupervised or unauthorized access points not managed by the corporate Wireless LAN Controller, preventing unapproved network extensions.
- Unauthorized Wireless Configurations: Identification of random MAC addresses, operational devices on guest Wi-Fi, and BYOD devices on production networks, ensuring proper segmentation and policy compliance.
- Non-Compliant or Risky Devices: Flagging devices with poor reputations, dual-use assets, or personal devices in unauthorized locations, helping enforce corporate device policies.
- Wired Network Misconfigurations: Discovery of unmanaged or unsupervised switches, multiple devices on the same port, or assets operating in incorrect VLANs, reducing exposure of sensitive network segments.
- Rogue Virtual Machines (VMs): Detection of VMs running on unauthorized hypervisors or connected to wrong VLANs, maintaining secure and compliant virtual environments.
Through query filters, tagging, and scheduled reports, Sepio enables proactive monitoring, early detection, and rapid remediation of Shadow IT incidents—helping organizations maintain control, visibility, and compliance across all network assets.
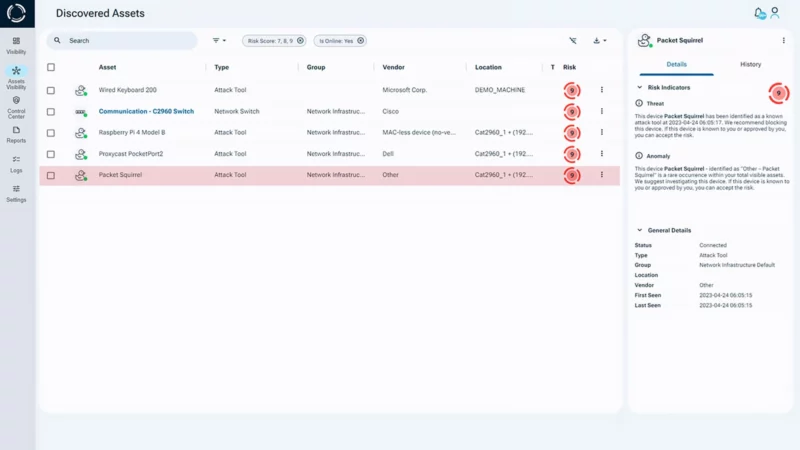
Endpoint Device Security
The Sepio Agent provides lightweight, hardware-based protection for endpoints. It allows precise control over USB devices, letting only approved peripherals while blocking rogue ones. This ensures the secure use of removable media without disrupting productivity. Operating with minimal system impact, the agent delivers strong protection without consuming significant resources.
By setting USB policies and real-time alerts, Sepio enables organizations to prevent the use of unauthorized removable storage, a common vector for malware and data exfiltration.
Network Device Security
The Sepio Scan Engine identifies and profiles network-connected hardware by interacting directly with network infrastructure using secure protocols. It supports scalable deployment across complex environments and gathers detailed asset intelligence for real-time risk assessment. Frequent scans ensure updated inventories and accurate detection of policy violations.
Unlike traditional asset discovery tools that rely solely on software-level data, Sepio’s hardware fingerprinting ensures that even spoofed or hidden devices are accurately detected.
Identifying and mitigating these threats requires continuous monitoring and full asset visibility. Solutions like Sepio’s Asset Risk Management platform help organizations detect, control, and eliminate shadow IT assets before they lead to data breaches or cyberattacks.
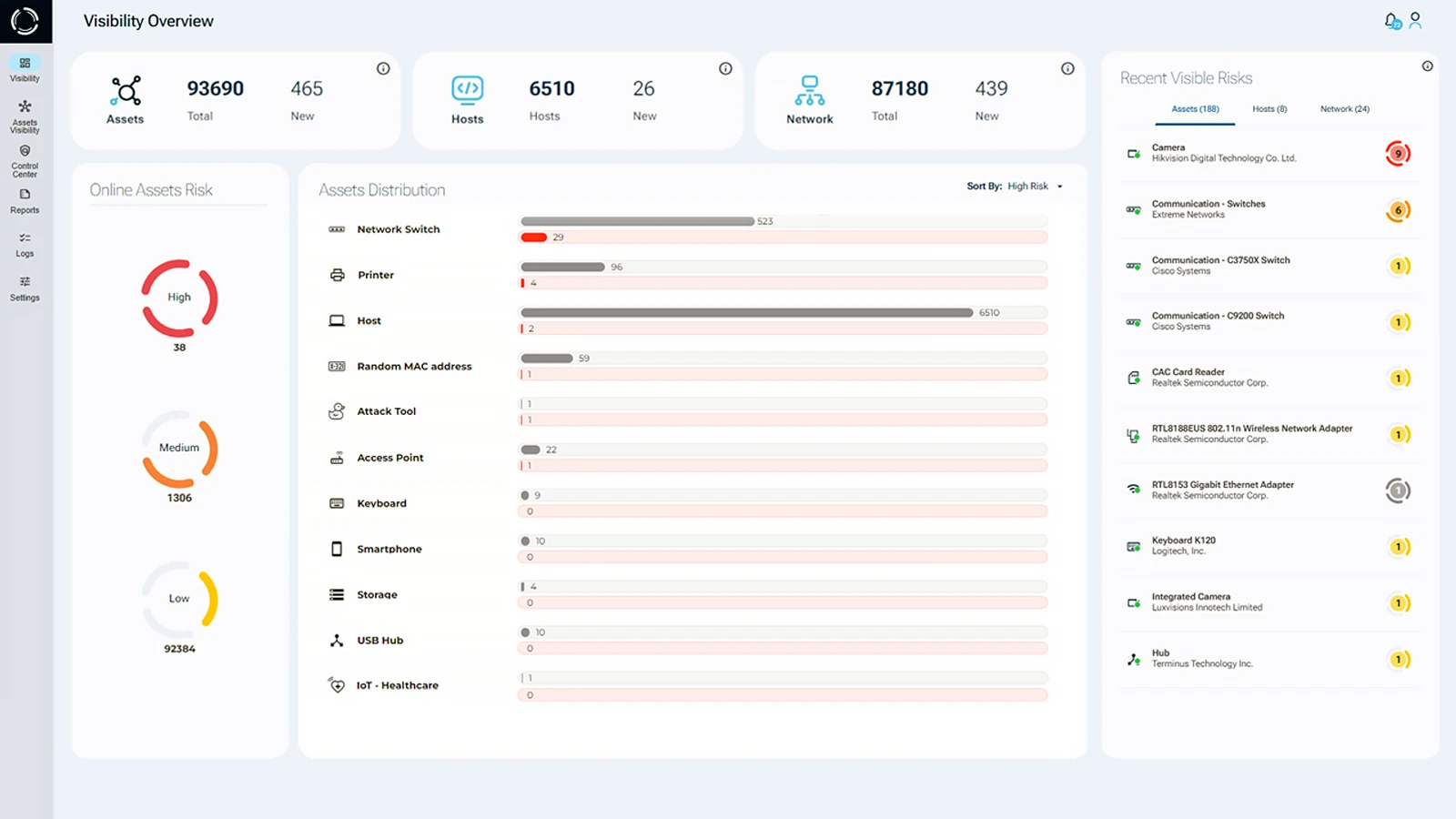
Manage Your Network Devices Effectively
Gaining full visibility into network devices is crucial for eliminating blind spots caused by shadow IT assets. By using physical layer data, organizations can detect and mitigate unauthorized devices that traditional security solutions overlook.
With Sepio, IT teams are empowered to make informed decisions, reduce risk exposure, and strengthen their overall cybersecurity posture.
Shadow IT is not just a security problem; it is also a business challenge. Understanding and addressing shadow IT enables organizations to maintain trust, meet compliance standards, and ensure smooth operations.
Schedule a demo today to see how Sepio helps secure your network against shadow IT risks.





