What is Peripheral Hardware?
Peripheral hardware refers to external devices that connect to a computer or system to enhance functionality or add features. These devices operate outside the central processing unit (CPU) and typically connect via USB, Ethernet, wireless, or other interfaces. Common examples include keyboards, mice, printers, external hard drives, USB flash drives, scanners, webcams, and monitors.
In today’s rapidly changing technological landscape, peripheral hardware is an essential component of computer environments. These devices not only increase productivity and efficiency but can also become critical targets or vectors for cyber threats. Hackers often exploit vulnerabilities in peripheral hardware to initiate cyberattacks, bypassing traditional security measures. Understanding how peripheral hardware works and ensuring its security are key to preventing breaches and protecting both personal and business networks.
The Importance of Peripheral Hardware in Modern Computing
Peripheral hardware devices play a significant role in expanding the functionality of computers and other electronic devices. For instance, an external hard drive allows users to store large volumes of data without overburdening the computer’s internal storage. Similarly, printers and scanners enable businesses to handle documentation and communication seamlessly. These devices form a crucial bridge between the user and the system, enhancing the overall experience and making complex tasks more manageable.
However, with the rise of bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies, peripheral hardware has become even more prevalent in both home and corporate environments. This increased usage, unfortunately, creates new security risks. Without proper monitoring, compromised peripheral devices can serve as gateways for data breaches and intrusions, putting sensitive data at risk.
Common Peripheral Hardware Devices
Some common examples of peripheral hardware devices include:
- Keyboards and Mice: Essential input devices for computers, they translate user actions into digital signals for processing.
- Printers and Scanners: Output devices that enable the physical reproduction of digital documents and the digitization of physical documents.
- External Hard Drives and USB Flash Drives: Portable storage solutions that allow users to transfer and back up data easily.
- Monitors and Projectors: Display devices that provide visual output from computers, useful in both personal and professional settings.
Each of these devices, while invaluable, can also become potential entry points for malicious activity if not properly managed and secured.
Manipulated Hardware Devices
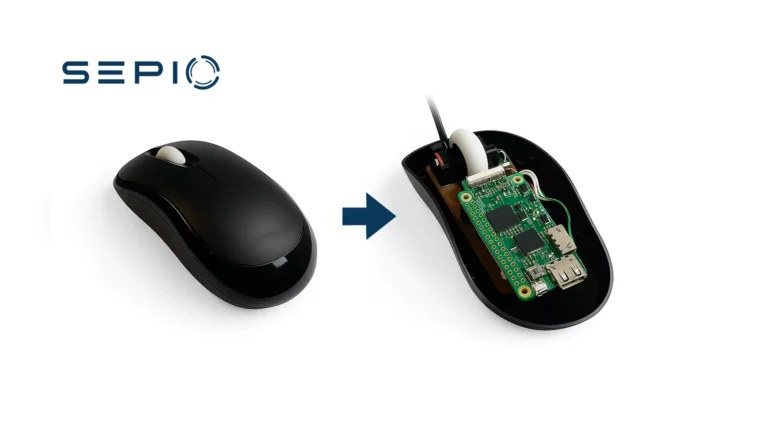
The Raspberry Pi is a flexible platform that supports a wide range of peripheral hardware devices. Designed as a small, low-cost computer, it handles tasks such as internet browsing, HD video playback, and basic productivity. However, when manipulated, a Raspberry Pi can turn into a rogue device, potentially running covert activities with harmful intent.
Manipulated Raspberry Pi Device
In the natural gas industry, a altered Raspberry Pi was discovered inside a peripheral hardware device. A Microsoft mouse had been hiding the Raspberry Pi module, remaining hidden within the environment for months.
The module programmed the Raspberry Pi to execute a PowerShell script, constructing and activating a concealed communication channel through the wireless interface. This allowed it to bypass the air-gapped environment and exfiltrate highly sensitive data, facilitating a security breach.

Peripheral Hardware Security & Asset Risk Management
Sepio provides deep visibility into the Physical Layer (L1), finding changed hardware like rogue Raspberry Pi devices and identifying exactly which endpoint they’re connected to. This enables faster investigation and mitigation of hardware-based attacks.
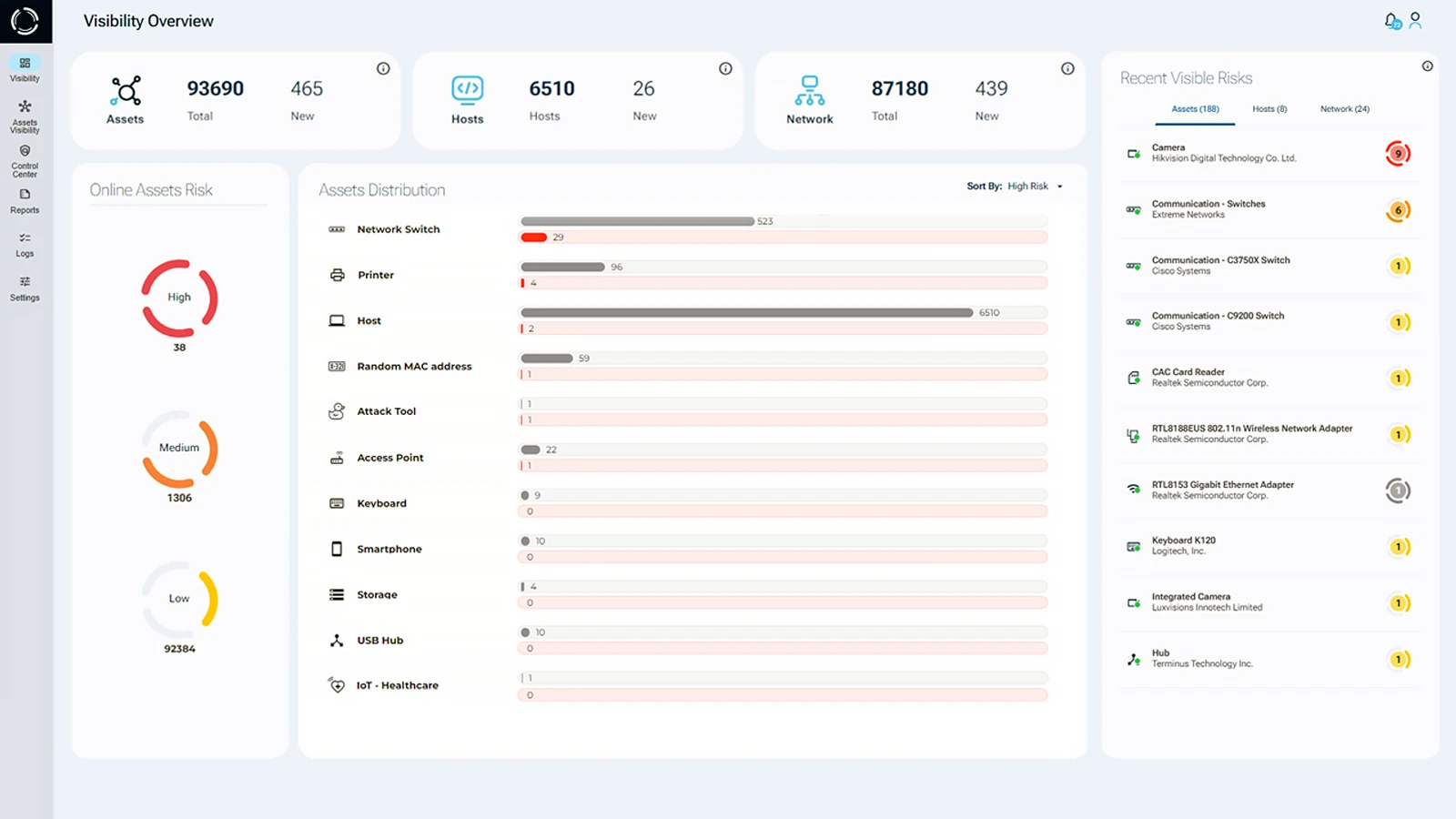
Harnessing Physical Layer insights, Sepio reveals the true source of asset risk, far beyond the capabilities of conventional monitoring tools. Seamlessly integrating with your existing security stack, Sepio increases effectiveness by providing independent, scalable, and useful asset intelligence across IT, OT, IoT, and peripheral devices.
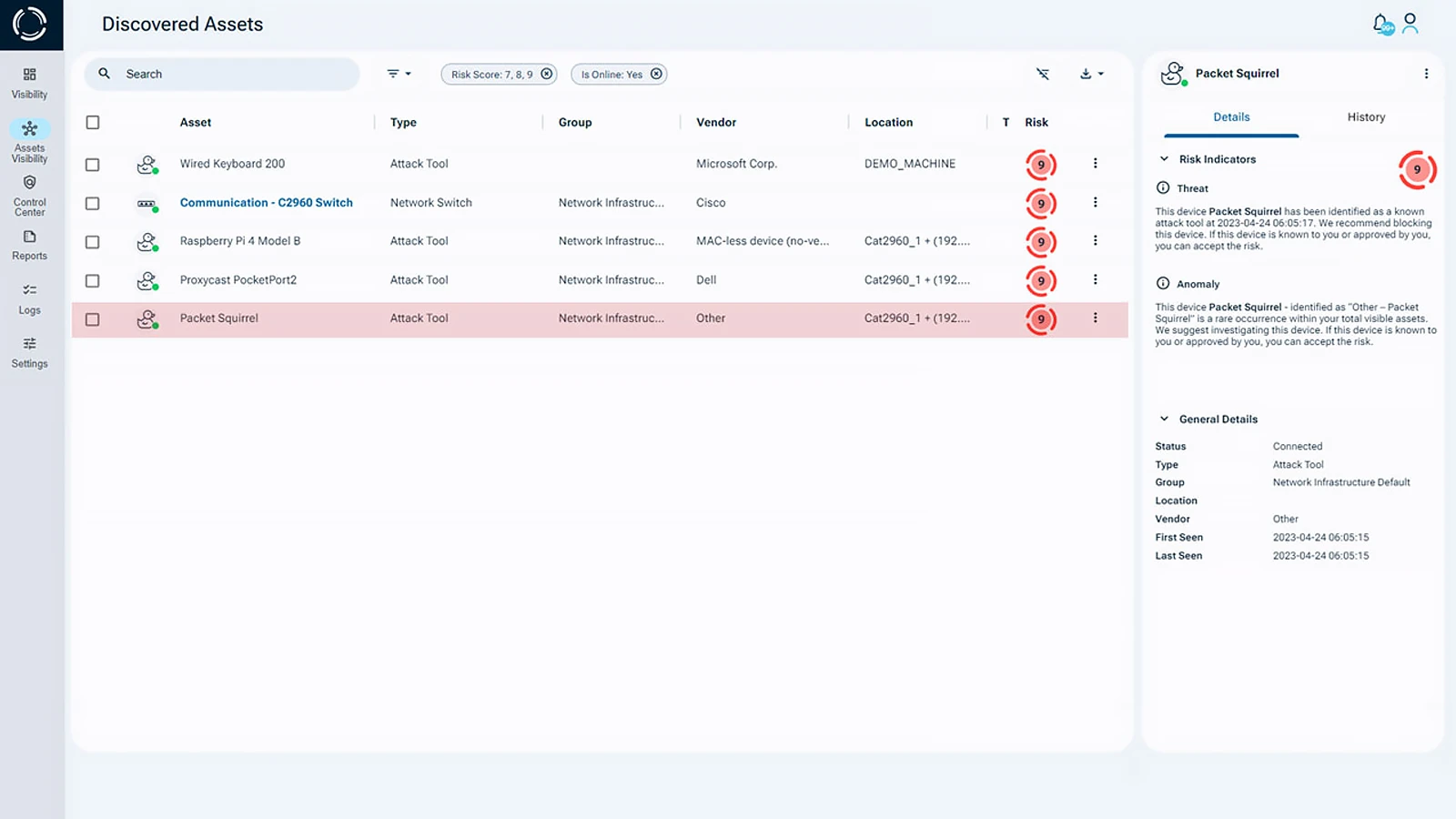
Sepio’s patented Asset DNA technology builds a unique profile for every connected asset, even those lacking standard identifiers. Unlike behavioral analysis tools prone to deception and false positives, Sepio delivers precise, data driven visibility into Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS), immune to spoofing and tampering.
With automated risk scoring based on Asset DNA, business context, location, and predefined rules, Sepio categorizes threats as high, medium, or low risk, enabling security teams to prioritize remediation, address compliance gaps, and prevent threats from escalating. Continuous monitoring, enhanced by machine learning, big data, and OSINT, ensures real-time updates and faster response times.
Sepio’s Asset Risk Management (ARM) platform leads the industry in hardware asset visibility, control, and mitigation. It uncovers hidden threats operating across USB and network interfaces, including unmanaged and rogue peripherals. No device goes unnoticed, making sure every asset in your environment is identified, detected, and secured.
Sepio’s Endpoint and Network Security
- Complete Visibility of All Hardware Assets: With all connected devices detected, enterprises benefit from a greater overall cybersecurity posture. Gaining full visibility of all hardware devices, from Raspberry Pi on peripheral hardware devices to endpoint peripherals and connected devices (IT/OT/IoT), Sepio uses unique physical layer hardware fingerprinting technology and data augmentation from endpoints and networks.
- Full Control Through Predefined Policies: Sepio delivers rapid setup with predefined policies, no baselining or whitelisting needed. Granular rules based on device traits trigger automatic blocking of rogue hardware via integrated platforms, ensuring instant, hands-free risk mitigation and compliance.
- Rogue Device Mitigation (RDM): Sepio offers threat mitigation upon discovery of rogue or threatening devices, including the identification of Raspberry Pi on peripheral hardware devices. Integrations with existing security platforms such as NACs and SOARs enhance remediation and risk mitigation efforts.
Protect your Network from Manipulated Peripheral Devices
See every known and shadow asset. Prioritize and mitigate risks before they grow into cyber attacks. Talk to an expert to learn how Sepio’s patented technology helps control asset risks. Enhance network security and prevent costly data breaches and intrusions.
Read the Manipulated Peripheral Device (pdf)





