According to Gary Lineker, former England player, soccer is “a simple game. Twenty-two men chase a ball for 90 minutes.” While that is the general concept, soccer is a far more complicated sport that relies on well-thought-out strategies and tactics. And just like all other industries, soccer – and sport in general – has found a valuable friend in technology to advance those strategies and tactics. Technology also plays a crucial role in cybersecurity scoring – helping organizations assess and strengthen their defenses. Just as soccer teams analyze data to improve performance, businesses must evaluate and strengthen their cybersecurity posture to defend against growing risks. In fact, technology has brought more benefits to soccer than just match performance. However, no matter what you’re using technology for, as long as you’re using it, you become a target for cyberattacks. And soccer is no exception. There are cybersecurity risks even related to soccer.
Cybersecurity Scoring: Protecting Valuable Data in Sports
The value of data in sport is nothing new, yet technological advancements have made dramatic improvements in the collection and analysis process. In soccer, data helps increase the chances of winning, whether improving player performance or refining team tactics and strategies. Therefore, vast amounts of data from matches and training are collected and analyzed. Soccer players are equipped with numerous sensors that track their location, distance covered, fitness levels, muscle activity, and many other metrics. This data is analyzed to improve weaknesses, prevent injuries, and assess tactics. Furthermore, real-time data collection enables more effective tactical and strategic decisions during matches. Cybersecurity in sport is critical here, as the protection of this data ensures that it isn’t exploited by malicious actors.
Why Data Makes Them a Target
Matches themselves provide an abundance of data about the team’s performance and their opponent’s, which is extremely beneficial to match analysis. Actionable conclusions are drawn from this data, enabling teams to perform more effectively in future games. Soccer, with an estimated 3.5 billion fans, has the largest fan following of any sport. The popularity of soccer has made it one of the most expensive sports globally. Naturally, soccer teams want to maintain this success by providing fans with the best possible experience – both on and off the pitch. Data plays a crucial role in this. Soccer teams collect as much data as possible about their fans to enhance engagement and maintain their loyalty, which often translates into financial support. In fact, many methods used to keep fans engaged also generate more data, ranging from games and competitions to exclusive content and subscriptions. Without the right cybersecurity scoring strategy, this data could easily fall into the wrong hands. Cybersecurity in sport ensures that these data collection processes are secure and resistant to attack.
How Malicious Actors Exploit Valuable Soccer Data
It’s simple – data is valuable. But not just to the team collecting it. This means different malicious actors will see soccer teams as worthy targets for a data breach. Rival teams might carry out a reconnaissance attack, snooping around to see what data the victim team possesses and how they use it to their advantage. The attacking team can then adjust their strategies and tactics accordingly to outperform their opponent. For financially motivated cybercriminals, team, player and fan information can sell for high amounts. However, the more obvious reason soccer attracts financially motivated cybercriminals is that there is a LOT of money in soccer. Cybersecurity scoring can help prevent these kinds of breaches by assessing the level of protection provided by each defense layer.

Cybersecurity Scoring Impact: Real-World Attacks in Soccer
In 2017, the transfer fee of Neymar from Barcelona to Paris Saint-Germain was just more than $250 million. And the total amount of transfer fees in 2019 amounted to $7.35 billion. With such high transfer fees, it is no surprise that, in 2020, a bad actor hacked into a Premier League club’s managing director’s email to try and pocket a $1.3 million transfer fee through a man in the middle attack (MiTM). While this attack got intercepted at the last minute, it doesn’t mean attackers can’t score a goal (and they have, but more on that later), so soccer teams need to view the cybersecurity match just as important as the match on the field.
Securing IoT Devices in Soccer
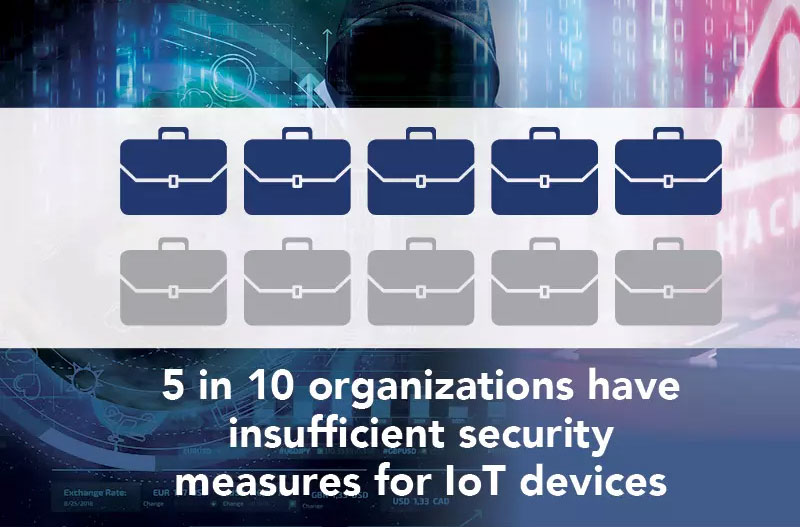
Soccer teams rely on IoT devices for data collection – and for less important tasks. But no matter what the device is used for, it requires the highest levels of security since all IoT devices act as a point of entry to an organization’s network. Worryingly, however, half of organizations do not implement sufficient security measures on their IoT devices. Thus leaving them extremely vulnerable to attack. Remember when I mentioned that attackers have successfully attacked soccer teams?
Protecting Against Hardware-Based Attacks
One such attack exploited an English Soccer League club’s CCTV IoT Cameras to gain deeper access to the network through lateral movement. Thought a CCTV camera’s only use was to provide security? Well, in this case it did the exact opposite. It was a simple lack of physical security that allowed the attacker to initiate the attack and a further lack of network segmentation that enabled lateral movement. And, with soccer stadiums full of people (well, hopefully, they will be again in the near future), it is easy for a hardware-based attacker to slip in and out of the crowd and quickly implant a Rogue Device. So, whatever information the attacker is after, any of the IoT devices in use can act as an access point to that information.
Cybersecurity Scoring with Sepio’s Hardware Access Control
Hardware-based attacks are extremely threatening due to their covert nature. Rogue Devices operate on the Physical Layer which goes uncovered by existing security solutions. A lack of Physical Layer visibility means that a victim will only know it is a victim when it’s too late. But with Sepio’s Asset Risk Management (ARM) solution, this need not be the case. Sepio’s solution provides entities with the Physical Layer coverage they need to obtain complete device visibility. And, in doing so, also protects against hardware-based attacks. As the leader in Rogue Device Mitigation (RDM), Sepio’s solution identifies, detects and handles all peripherals; no device goes unmanaged.
In addition to the deep visibility layer, a comprehensive policy enforcement mechanism recommends on best practice policy and allows the administrator to define a strict, or more granular, set of rules for the system to enforce. Such capabilities enable a Zero Trust Hardware Access (ZTHA) approach. When a device breaches the pre-set policy, Sepio automatically instigates a mitigation process that instantly blocks unapproved or Rogue hardware. Give us just 24 hours to show you that we’re the player your team is missing for a clean sheet.
Gain Complete Visibility of Your Assets
Unlock the power of Sepio’s patented technology. Schedule a demo today, and our experts will show you how to take control of your asset risks, identify every known and shadow asset, and enhance your security posture.






