What are Hardware Attacks?
Hardware attacks in cyber security are among the most overlooked threats. Hackers use weaknesses in hardware to get past traditional security tools like Network Access Control (NAC), Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS). In many cases, these attacks involve rogue hardware that look like everyday items, such as USB drives, chargers, or keyboards. Because of this disguise, attackers can sneak into networks without being noticed.
Most security policies focus on software and network traffic. However, they often overlook hardware threats from physical devices. This creates a blind spot where hardware attacks can go unnoticed. As a result, organizations face serious risks from emerging threats. To stay safe, companies must recognize the danger of hardware-based attacks. They also need cybersecurity tools that can spot rogue hardware. This is essential for keeping strong protection across the entire organizations.
Hardware Attacks in Cybersecurity
Humans are still the weakest link in cybersecurity. In fact, a study by Proofpoint found that careless insiders cause 62% of all incidents. This is a big risk, especially when people lack training and awareness. For example, employees often plug in devices without thinking about security. As a result, they become easy targets for phishing, hacking, and other cybercrimes.
Rogue hardware take advantage of this weakness by looking harmless or hiding inside other devices. Because of this, it’s very hard to spot them without special detection tools. They often seem normal to the naked eye, making identification difficult.

Hardware Attacks Through Everyday Devices
Attackers can embed malicious hardware attack tools within a seemingly harmless mouse or keyboard, exploiting network vulnerabilities. A Raspberry Pi is a small single-board computer. It’s small enough to hide inside one of these HIDs, making it almost impossible for users to detect. Though not made for hacking, a Raspberry Pi can be a powerful hardware attack tool. It can steal data, sniff network traffic, and carry out attacks like man-in-the-middle (MiTM) schemes.
A BadUSB hardware attack tool can look like a Microsoft mouse. But it can type commands, run code, and break into systems. These kinds of hardware threats are becoming more common. That’s why strong hardware cybersecurity is essential. We must find and stop hardware attacks before they do damage.

Using an iPhone Charger as an Attack Tool
The “NinjaCable” is a USB hardware attack tool that looks just like a regular iPhone charger, but it can cause serious harm. The idea isn’t new. Its design is based on an NSA tool called COTTONMOUTH.
Hackers use the NinjaCable to take advantage of human trust. It works like a normal charger, while secretly launching attacks like malware or stealing data in the background.
First, no one questions an iPhone charger. If your phone dies at work, you’ll likely grab the nearest charger without thinking. You rarely stop to ask if it could be a harmful device.
Second, smartphones are always linked to both work and personal accounts. This gives attackers more ways to strike from almost anywhere. Instead of sneaking a NinjaCable into a secure office, they can now use public charging stations to launch their hardware attacks.
At charging stations, people often plug in their phones quickly, just thinking about getting power. But this can be risky. A tactic called “juice jacking” lets hackers steal personal or work data from the device. As phones connect more to both personal and work systems, hidden hardware threats become even more dangerous.
The Threat of Malicious USB Thumb Drives
One common type of hardware attack uses fake USB drives. But how can you tell a normal USB from a dangerous one? The truth is, you can’t.
For example, a USB drive that looked like a Best Buy gift was sent to a hospitality company. It seemed harmless but was actually loaded with malware. Other tools, like the Rubber Ducky, also look like normal USB drives. But once plugged in, they can type commands, install malware, or run harmful scripts automatically.
Hardware Attack Tools are Invisible
Rogue devices are especially dangerous because they look harmless. They stay hidden from firewalls and intrusion detection systems. They also bypass any human-based authentication checks. Once connected, they can give attackers full access to an organization’s systems.
Even the most advanced cybersecurity models, like Zero Trust Architectures, often fail to stop hardware threats. These attacks take advantage of a core weakness: Zero Trust relies on verifying identity and behavior. But rogue hardware can fake identities and operate without raising any alarms.
Hardware attack tools are discreet, allowing them to move freely within an organization. As a result, they break key Zero Trust principles like microsegmentation and least privilege access. Moreover, they do not raise red flags to the human eye, avoid detection by traditional cybersecurity tools, and can carry out many harmful actions.
But if you think all hope is lost, think again. Specialized solutions do exist to defend against these hardware threats. While no system is entirely invulnerable, proactive, cybersecurity measures can significantly strengthen your organization’s defensive posture and close the gap traditional tools leave behind.
Detecting Hardware Attack Tools
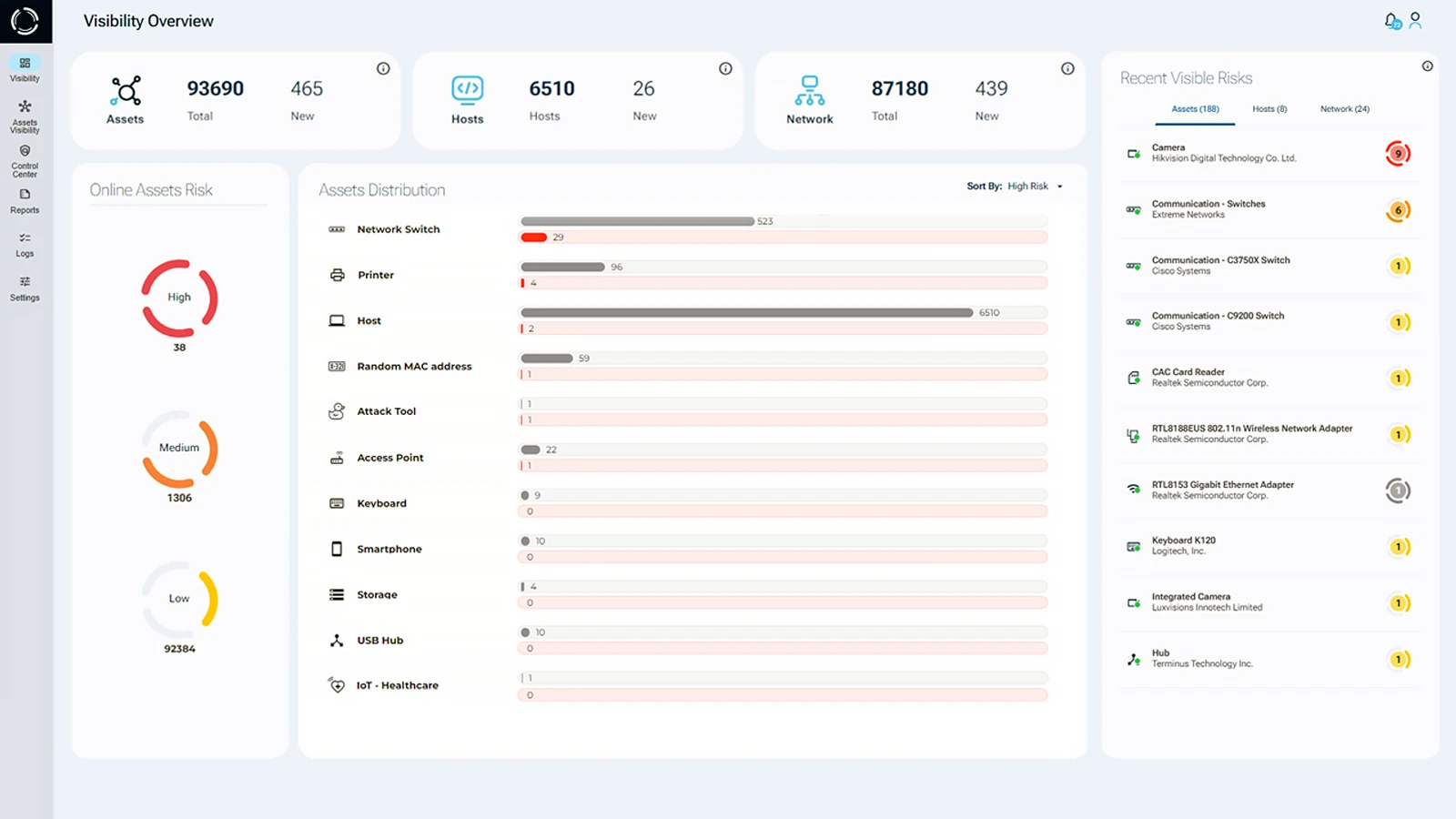
Sepio has developed a solution to provide a panacea to the gap in device visibility through physical layer fingerprinting. As the leader in Rogue Device Mitigation (RDM), Sepio finds, detects, and manages all peripherals. No asset is left unmanaged.
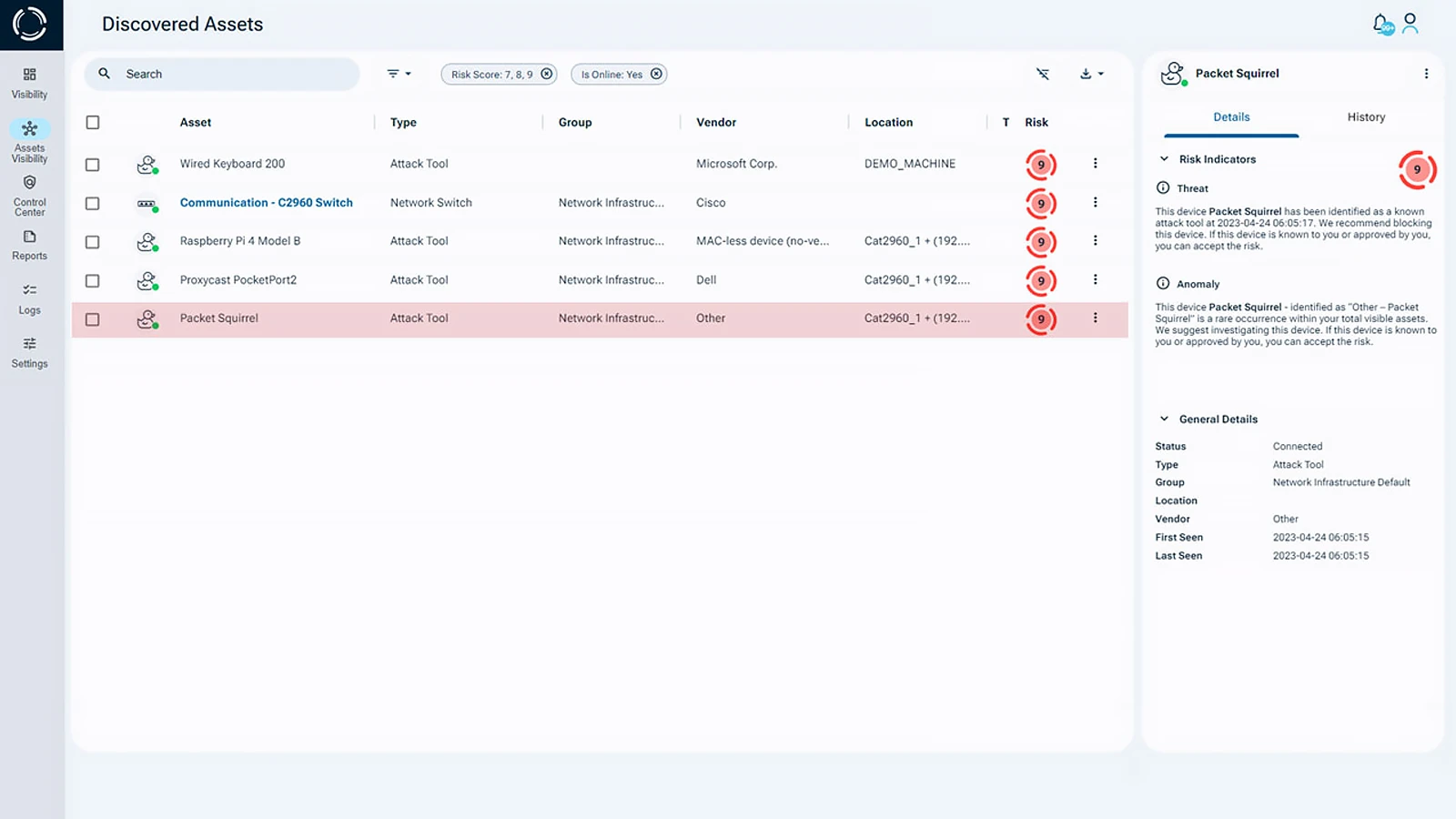
Sepio’s policy enforcement and mitigation features block unauthorized devices instantly. This helps prevent human error and removes the need to constantly watch over network devices. Even careful employees can miss these hardware threats. That’s why automated hardware protection is essential.
Additionally, Sepio’s deep visibility capabilities and integration with existing tools, such as NAC, EPS, and SIEM, ensure that organizations maximize their cybersecurity investments. As a result, with Sepio, clients benefit from a Zero Trust Hardware Architecture (ZTA) approach.
Network and Endpoint Hardware Security
Sepio doesn’t scan network traffic or use discovery tools. That means it won’t touch any private or sensitive data. Setup is quick and easy. In just 24 hours, we help reduce employee mistakes and strengthen your company’s cybersecurity. Your employees are your biggest strength, but also a big risk. Sepio helps you lower that risk with a powerful hardware cybersecurity solution.
Secure your organization against hardware attacks with Sepio’s patented technology. Schedule a demo to see how we enhance your cybersecurity hardware protections.






