Medical Device Cybersecurity: More Critical Than Ever
Connected medical devices are transforming healthcare by enabling real-time monitoring, diagnosis, and treatment. They communicate over networks to collect and share patient data, improving outcomes and care delivery. However, this widespread use raises serious cybersecurity concerns, making strong connected medical device security essential.
With their growing prevalence, the global market for connected medical devices is projected to reach $60 billion by 2027, a significant increase from $38 billion in 2020. This growth amplifies the urgency for robust connected medical device security measures, ensuring the safety and privacy of patients’ data and the seamless functionality of these critical devices.
More people now depend on connected medical devices to manage their health daily. These devices, part of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), face many cyber risks. They can threaten patient privacy and device safety. In the past year, the healthcare sector has seen a rise in such threats, emphasizing why protecting connected medical devices is crucial. Staying alert, understanding the risks, and implementing mitigation strategies helps keep patient data safe and private.

Connected Medical Device Security
The Risks of Stolen Patient Data
The rise of connected medical devices, many of which lack standardized security measures, introduces varying levels of vulnerability. These devices collect and transmit sensitive patient information, which can be exploited if not properly secured.
Unauthorized access to medical databases can harm both patients and healthcare organizations. These databases hold sensitive personal, insurance, and financial data. A data breach violates patient privacy and can result in regulatory penalties, lawsuits, and significant financial losses for healthcare providers. Protecting patient data is critical to avoiding these risks.
Healthcare Organizations also need to comply with General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). To ensure protection of patient’s data and privacy.
Hacker-Controlled Medical Devices
Cyberattacks pose a serious risk to connected medical devices. Hackers can break into personal medical equipment and cause harm beyond stealing patient data. They can control devices by changing settings or turning them on and off. This can be life-threatening for patients who rely on these devices for daily health care. Protecting IoMT security is vital to keep patients safe.
Disruption in Patient Care
Malware attacks are one of the most common threats to connected medical devices. Hackers use malware to take control of important files and systems, often demanding a ransom to restore access. During the pandemic, some hackers blocked hospitals from accessing life-saving files until they were paid. Prioritizing the security of connected medical devices keeps patient safety first, even as cyber threats evolve.
Damage to Reputation and Credibility
Cyberattacks can seriously damage the reputation and credibility of healthcare providers. After a data breach, patients and stakeholders may lose confidence in the organization’s ability to protect sensitive information. Trust is essential in healthcare, and once lost, it is difficult and costly to rebuild. Securing connected medical devices not only protects patient data but also preserves institutional trust and integrity.
How Can Healthcare Organizations Protect Connected Medical Devices?
Connected medical devices offer tremendous benefits in patient care, but they also present multiple cybersecurity challenges. To fully harness their potential while minimizing risks, healthcare organizations must implement effective cybersecurity strategies through the following approaches:
Orchestrated Firmware Updates
A key advantage of connected medical devices is their ability to be regularly updated. During these firmware updates, it is essential to ensure careful orchestration and that only authorized parties can make changes to the devices.
Should an update failure occur, there must be a contingency plan in place. This plan could involve rebooting the device and restarting the update or replacing the device altogether. Additionally, patients need clear instructions on how to configure their devices on their home network. Proper installation allows you to establish an encrypted connection between the medical devices and the IoMT.
Secure Custom Software
Healthcare institutions often rely on proprietary software to manage connected medical devices. Therefore, it is vital to embed security measures throughout the software development lifecycle. Many developers now specialize in secure healthcare software, with targeted training programs boosting the industry’s cybersecurity expertise.
In addition, medical staff and administrators should receive regular cybersecurity training to identify vulnerabilities and proactively mitigate threats before exploitation occurs.
Enhancing Connected Medical Device Security with Physical Layer Visibility Fingerprinting
In networks with many connected medical devices, some vulnerabilities can go unnoticed, especially when relying on manual reports and employee actions. This leaves openings for hackers to enter the system and add unauthorized devices, putting security and patient data at risk.
A proactive solution is to implement physical layer visibility fingerprinting for every device on the network. This technique significantly enhances connected medical device security by providing automated, real-time identification and risk assessment of all devices.
Sepio’s Asset Risk Management
Sepio is the only company in the world offering physical layer visibility through fingerprinting. With Sepio’s Asset Risk Management (ARM), no device goes undetected. Each device gets a unique digital fingerprint, strengthening your cybersecurity posture. Sepio automatically identifies if a medical device becomes vulnerable or if unauthorized devices and connections appear on the network.
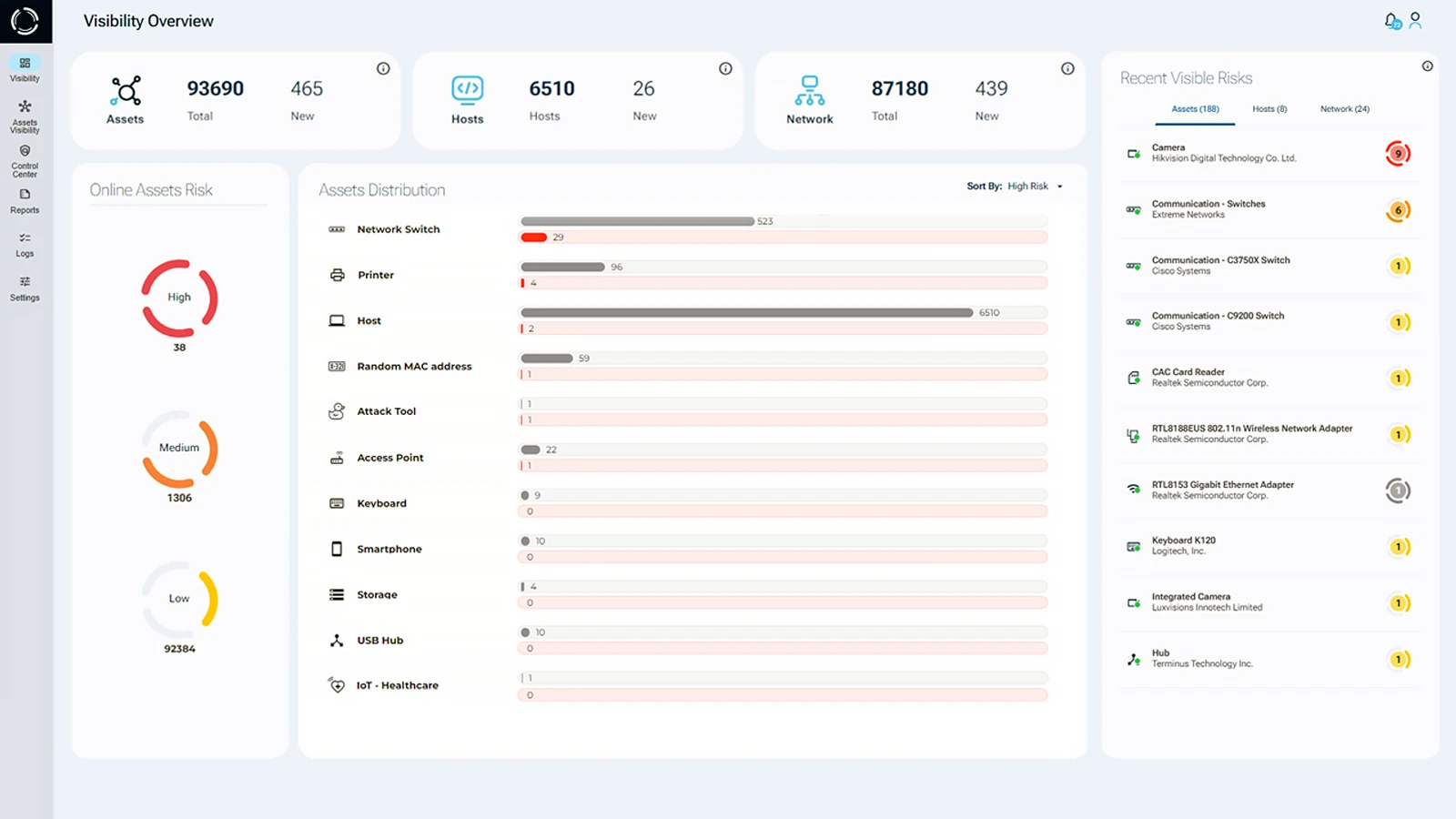
With Sepio’s technology, you can automatically detect and assess the security of connected medical devices. It helps you spot vulnerabilities in real time and ensures that only trusted devices access the network.
See Every Asset, Prioritize Risks, and Strengthen Security
Sepio’s solution provides full visibility into every known and shadow asset across your network. By prioritizing and mitigating risks effectively, Sepio empowers healthcare organizations to adopt a proactive approach to connected medical device cybersecurity.
Talk to an expert to learn how our patented technology can help you gain full control over your asset risks. This ensures a more secure and reliable network for connected medical devices.






