Cyber Security Threats in Healthcare
Cybersecurity threats in healthcare are escalating as hospitals and healthcare systems increasingly rely on digital technologies. Patient records, medical devices, and operational infrastructure are often connected to the internet, exposing them to cyber threats that can jeopardize both privacy and patient safety. A single cyber attack can disrupt care and endanger lives.
In what scenario would you be willing to answer invasive and personal questions without thinking twice? That’s right, at a doctor’s appointment. Patients trust healthcare professionals to protect their personal information. However, despite this trust, cybersecurity threats in the healthcare industry remain rampant. The healthcare sector experiences some of the highest numbers of data breaches, making it notoriously vulnerable to cyber healthcare attacks. Hackers often target healthcare systems for valuable data.
The Healthcare Cybersecurity Investment Gap
Unfortunately, cybersecurity risks in healthcare often persist due to insufficient investment. Healthcare organizations allocate only 4-7% of their revenue to healthcare IT security, while other industries, such as finance, spend up to 15%. This lack of investment leaves critical systems open to exploitation by a potential attacker. Healthcare and cybersecurity must become a higher priority to avoid devastating attacks that impact patient safety and organizational integrity.
The High Value of PHI and PII
The healthcare industry is a prime target for cybercriminals. Personal information and Personal Health Information (PHI) is especially valuable on the black market, fetching about $363, compared to $2 for Personally Identifiable Information (PII). Cybercriminals can exploit PHI to steal identities, file fraudulent insurance claims, and even obtain medications under false pretenses. This grim reality underscores the urgent need for improved computer-security measures in healthcare.
Types of Cybersecurity Threats in Healthcare
Malware and Operational Disruptions
Malware is a major cyber security threat in healthcare, often causing both data breaches and operational breakdowns. Attacks like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) can bring down servers, disrupting access to patient records, lab results, elevators, and even life-saving equipment. In healthcare, these disruptions aren’t just inconvenient, they can be fatal.DDoS attack can implicate them, too.
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware is one of the most damaging cybersecurity threats in healthcare. Attackers encrypt systems and demand high ransoms, averaging nearly $30,000 in 2018, to restore access. Paying doesn’t guarantee data recovery and only encourages more attacks. Many hospitals remain unprepared, especially when it comes to IoT device security.
Many healthcare organizations remain unprepared for cybersecurity threats in healthcare. While doctors and medical staff prioritize patient care, cybersecurity awareness is often lacking. Healthcare employees may inadvertently contribute to cyber security threats in healthcare through negligent online behavior, making the industry more vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Insider Threats and Lack of Cybersecurity Awareness
The healthcare sector struggles with insider threats, where employees inadvertently increase vulnerability to cyberattacks. Many healthcare workers lack adequate cybersecurity training, making them susceptible to social engineering tactics used by attackers. Phishing emails, often containing malicious links, can lead to malware installation and significant data breaches.
BYOD and IoT Security Risks
The increasing adoption of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policies increase the number of access points to the organization’s network. This of course increases the number of ways a perpetrator can carry out an attack. Additionally, the healthcare industry is becoming more accepting to Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Hospitals are now connecting many of the apparatus used within them to the internet. Many of them are vitally important to a patient’s well-being, such as heart monitors and infusion pumps. These connected healthcare devices provide more points of entry to the organization’s network and, if hacked, can be lethal. The increase in the amount of internet-connected devices also means possible exposure to IoT security vulnerabilities.
Consequences of Cybersecurity Threats in Healthcare
The rise of BYOD and IoT devices has expanded the attack surface, making cyber security threats in healthcare more difficult to contain. Weak security protocols and limited employee awareness allow malicious actors to exploit systems, leading to ransomware, data breaches, or DDoS attacks.
These cybersecurity threats in healthcare put patient safety at risk, disrupting critical care, delaying treatments, and potentially endangering lives. The financial impact is equally severe, with fines, lawsuits, and recovery costs often reaching millions.
Protecting against cyber security threats in healthcare is no longer optional, it’s essential to safeguard patient data and preserve institutional trust.
Strengthening Healthcare Against Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats in healthcare continue to evolve, with attackers targeting vulnerable medical devices, patient data, and critical hospital infrastructure. Traditional security solutions often fall short in detecting rogue hardware and unmanaged assets, leaving healthcare organizations exposed. Sepio’s Cyber Physical Systems (CPS) Protection Platform delivers a hardware-centric security approach, ensuring complete asset visibility and Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) enforcement, in the following areas:
Comprehensive Asset Visibility: Sepio’s AssetDNA technology detects spoofed hardware and unauthorized devices at the Physical Layer, uncovering shadow IT risks that could threaten patient safety.
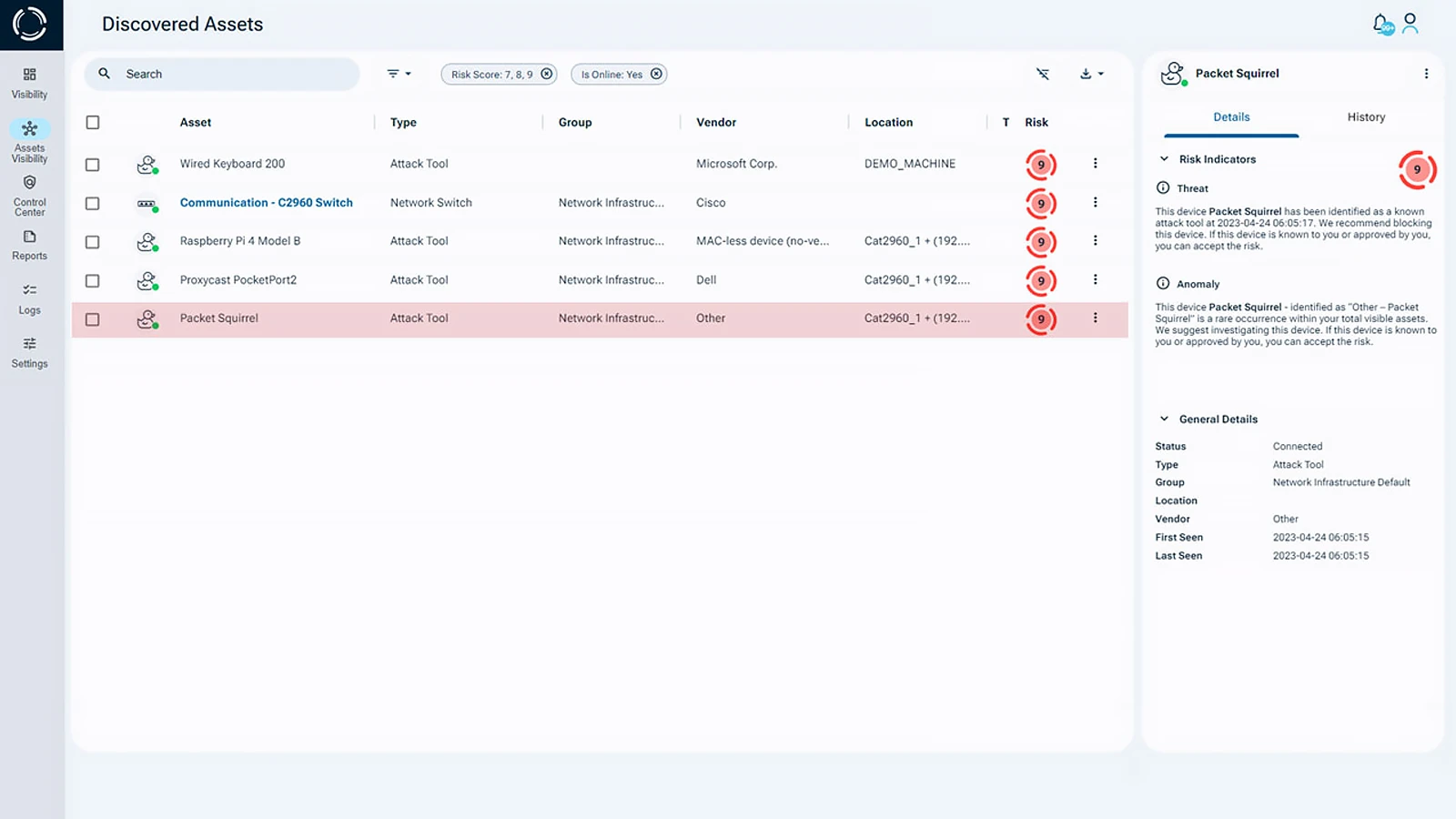
Granular Policy Enforcement: AI-driven policy automation ensures only trusted devices access critical systems. Policies adapt in real-time, minimizing attack surfaces and preventing unauthorized access.
Continuous Monitoring & Risk Assessment: Sepio provides precise device tracking across hospital networks and IoT environments, enabling swift response to cybersecurity threats in healthcare while ensuring compliance.
Trafficless Approach for Unmatched Visibility: Unlike traditional security tools, Sepio’s trafficless model delivers full visibility across encrypted and unencrypted environments without disrupting medical operations.
Protect Your Healthcare Organization with Sepio
With cybersecurity threats in healthcare on the rise, it is critical for hospitals, clinics, and medical research institutions to adopt advanced security measures. Sepio’s hardware-centric Zero Trust approach ensures that every device is accurately identified and continuously monitored, helping safeguard patient data and operational integrity.
Strengthen your healthcare security today. Schedule a demo with Sepio to see how AssetDNA technology can help you prevent and mitigate cybersecurity threats in the healthcare industry.






