What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a cybersecurity framework based on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models, Zero Trust assumes that threats can originate both inside and outside the organization. Every user, device, and workload must be continuously authenticated, authorized, and validated before accessing enterprise resources.
A key component of Zero Trust is microsegmentation, which restricts lateral movement within the network by enforcing granular access controls. Combined with identity-based authentication, this approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber attacks. By implementing Zero Trust and microsegmentation, organizations can strengthen their security posture and protect sensitive data from evolving threats.
Zero Trust Case
In this Zero Trust case, a corporate bank discovered a compromised palm-vein scanner, posing a significant security risk. The breach threatened the bank’s Zero Trust framework, which relies on identity-based access control to verify users and devices. To mitigate the risk, the bank implemented microsegmentation, isolating critical systems to prevent unauthorized access and contain potential threats. By reinforcing its Zero Trust strategy, the bank enhanced its cybersecurity posture, ensuring continuous verification and protection against evolving threats.
Micro-Segmentation and Identity-Based Access Control
Microsegmentation is a critical component of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), enhancing security by dividing networks into smaller, isolated segments. Each segment requires separate access authorization, limiting east-west traffic (lateral movement) and significantly reducing the attack surface. This approach strengthens data security and minimizes the risk of data breaches.
A core principle of Zero Trust is the principle of least privilege (PoLP), ensuring users can only access the resources necessary for their roles. Identity-based access control enforces this, using authentication methods like multi-factor authentication (MFA), which can be done in three ways:

One of the most secure authentication methods is biometric security, as it is difficult to bypass. However, in this case, an attacker executed a Man-in-the-Middle (MiTM) attack to manipulate the palm-vein authentication system, compromising the Identity and Access Management (IAM) system that supports Zero Trust. This breach undermined the effectiveness of microsegmentation, allowing the attacker to escalate privileges and move laterally through the network, bypassing security controls.
Strengthening Network Security with Sepio’s Platform
This case study underscores the importance of device visibility and stronger security in preventing unauthorized access. Sepio’s platform provides comprehensive Rogue Device Mitigation, identifying, detecting, and managing all devices within an enterprise to enhance endpoint security with physical layer visibility and threat intelligence.
By leveraging advanced fingerprinting technology and Machine Learning, Sepio creates a unique digital fingerprint for each device based on its electrical characteristics. This fingerprint is then cross-referenced against an extensive threat intelligence database to identify potential risks, ensuring precise device detection and security enforcement.
With complete network-wide device visibility, Sepio enables organizations to enforce granular security policies, swiftly responding to rogue hardware and unauthorized devices. This approach strengthens Zero Trust microsegmentation, preventing attackers from bypassing identity-based access control and other security measures.
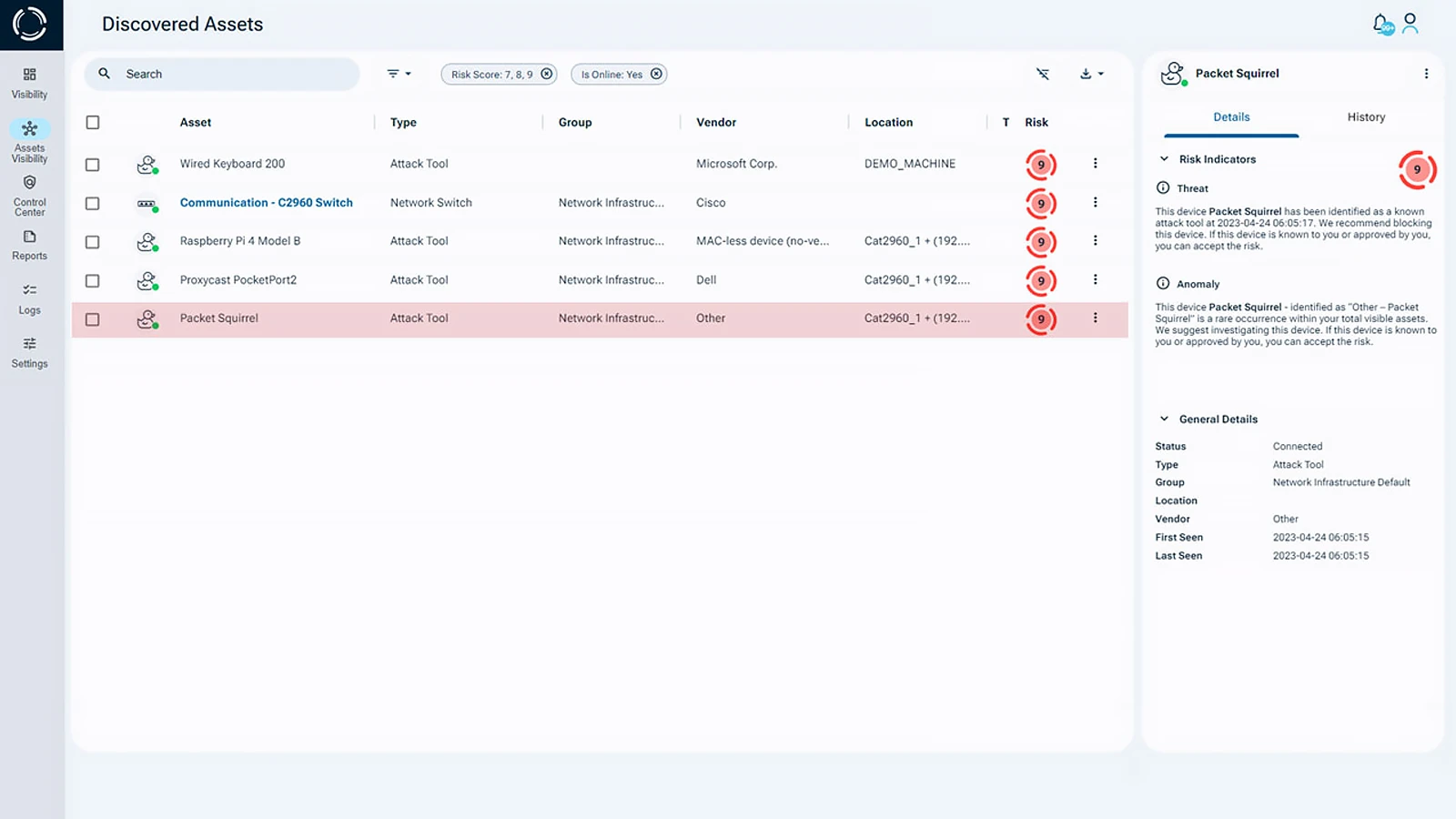
By implementing Zero Trust Hardware Access (ZTHA), organizations reinforce the “never trust, always verify” principle at the physical layer, ensuring that all known and shadow assets are visible, prioritized, and protected. Sepio’s platform delivers proactive defense, closing security gaps and safeguarding critical infrastructure against emerging threats.
Enhancing Zero Trust Hardware Security with Sepio
This case study demonstrates how Sepio’s platform strengthens enterprise security by addressing device visibility gaps and defending against sophisticated hardware cyber threats. By integrating microsegmentation, identity-based access control, and Rogue Device Mitigation, organizations can effectively implement a Zero Trust Architecture and achieve comprehensive protection against evolving attacks.
To learn how to enhance your network security management and leverage Zero Trust microsegmentation, connect with our experts. Discover how Sepio’s patented technology can help you mitigate cybersecurity risks, prevent malware, and safeguard your organization’s data integrity.
Download the Zero Trust Case Study





