What is CMMC Compliance?
CMMC Compliance, or Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification, is a framework established by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) to assess and enhance the cybersecurity posture of contractors. It provides structured guidelines that improve security across the Defense Industrial Base (DIB). Achieving CMMC Compliance ensures proper safeguards for Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
Why CMMC Compliance Matters
Cyber threats targeting the defense supply chain have grown more sophisticated and damaging. Nation-state actors, insider threats, and rogue devices pose an ever-increasing risk. Inconsistent cybersecurity standards across DoD contractors created vulnerabilities that adversaries could exploit.
The CMMC framework addresses these challenges by requiring third-party audits and certifications to verify that cybersecurity practices are being properly implemented and maintained. This ensures a unified, high-security baseline across all contractors, regardless of size or contract scope.
Without CMMC certification, contractors risk being disqualified from bidding on DoD contracts—making compliance a business-critical priority.
CMMC Compliance Levels Overview
The CMMC Compliance framework consists of five certification levels, each demonstrating a company’s cybersecurity maturity and reliability. These levels are cumulative, meaning organizations must meet all lower-level requirements before advancing, ensuring they can effectively safeguard sensitive government information.
To earn certification, contractors must address standards across 17 domains, 43 capabilities, 171 practices, and 5 processes. Contractors falling short in either practices or processes will only be certified at the level where all criteria are fully met.
Not all DoD contractors need to reach Level 5; the required level depends on the nature and sensitivity of the information handled and the associated threat environment.
CMMC Compliance Levels
Level 1 – Basic Cyber Hygiene
- Processes: Performed
- Practices: Basic cyber hygiene
Level 1 focuses on protecting Federal Contract Information (FCI) and includes only the fundamental cybersecurity practices required by 48 CFR 52.204-21 (“Basic Safeguarding of Covered Contractor Information Systems”). At this level, organizations must implement basic security measures to ensure compliance but are not required to have documented processes.
Level 2 – Intermediate Cyber Hygiene
- Processes: Documented
- Practices: Intermediate cyber hygiene
Level 2 requires contractors to document their cybersecurity practices and policies to ensure consistent and repeatable implementation. This level serves as a bridge between Level 1 and Level 3 CMMC Compliance, incorporating a subset of the security requirements from NIST SP 800-171, along with additional practices from other standards and references.
Level 3 – Good Cyber Hygiene
- Processes: Managed
- Practices: Good cyber hygiene
Level 3 requires a documented cybersecurity plan that covers missions, goals, resources, training, and stakeholder responsibilities. This level fully incorporates NIST SP 800-171 and addresses protection of CUI. DFARS clause 252.204-7012 also applies, reinforcing CMMC Compliance standards for DIB contractors.
Level 4 – Proactive
- Processes: Reviewed
- Practices: Proactive
Level 4 involves reviewing and measuring the effectiveness of cybersecurity practices and implementing corrective actions. It includes enhanced controls to counter Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), based on Draft NIST SP 800-171B.
Level 5 – Advanced/Progressive
- Processes: Optimizing
- Practices: Advanced/proactive
Level 5 focuses on the continuous improvement of cybersecurity processes across the organization. It strengthens protections against APTs by incorporating advanced techniques and optimizing security controls, ensuring the highest level of Compliance.
From DFARS to CMMC Compliance
Prior to CMMC Compliance, DFARS clause 252.204-7012 mandated that contractors protect DoD data within their systems. While those requirements still apply, CMMC Compliance introduces third-party certification to verify adherence to essential security practices and controls.
By requiring CMMC Compliance, the DoD ensures a consistent cybersecurity baseline across its supply chain. This certification framework enhances the DIB’s resilience against cyber threats and ensures all contractors can adequately protect FCI and CUI.
Next Steps for CMMC Compliance
To achieve Compliance, contractors should assess their current cybersecurity posture and begin preparing for certification. This involves reviewing existing practices, identifying gaps, and aligning with the technical requirements of the desired Compliance level.
Sepio supports DoD contractors through the CMMC Compliance process. Our platform delivers full-spectrum coverage across all certification levels, especially the rigorous demands of Level 5 Compliance.
How Sepio Supports CMMC Compliance
Sepio is a pioneer in Rogue Device Mitigation (RDM) and delivers unparalleled hardware visibility through its Asset Risk Management (ARM) platform. By identifying hidden threats across USB and network interfaces, Sepio empowers organizations to meet the visibility and control requirements essential for CMMC Compliance.
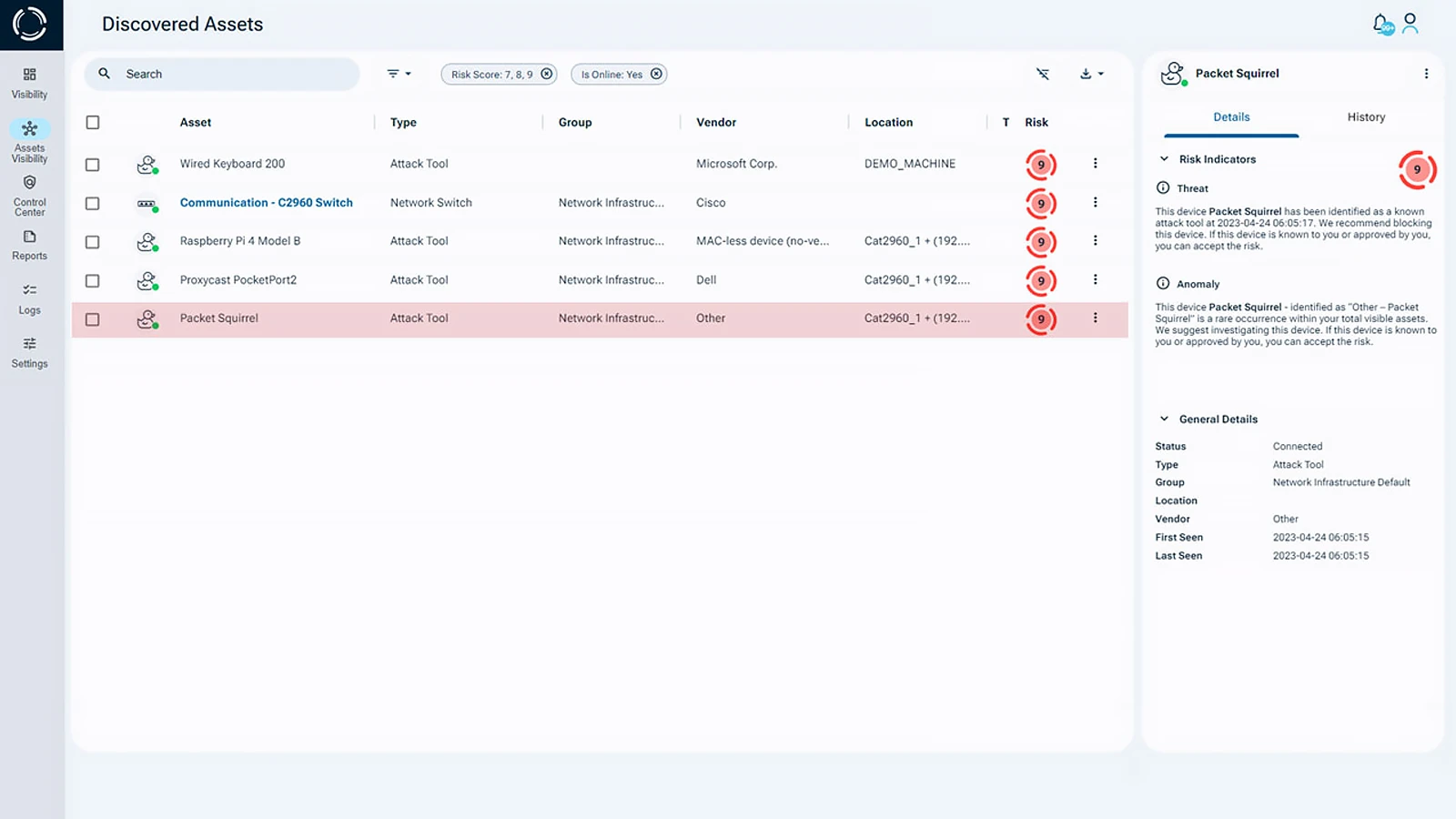
Sepio’s Discovered Assets
Sepio is the only solution in the world that provides true physical-layer visibility through hardware-based fingerprinting. This enables the detection and prevention of malicious hardware-based threats, which are often invisible to traditional cybersecurity tools.
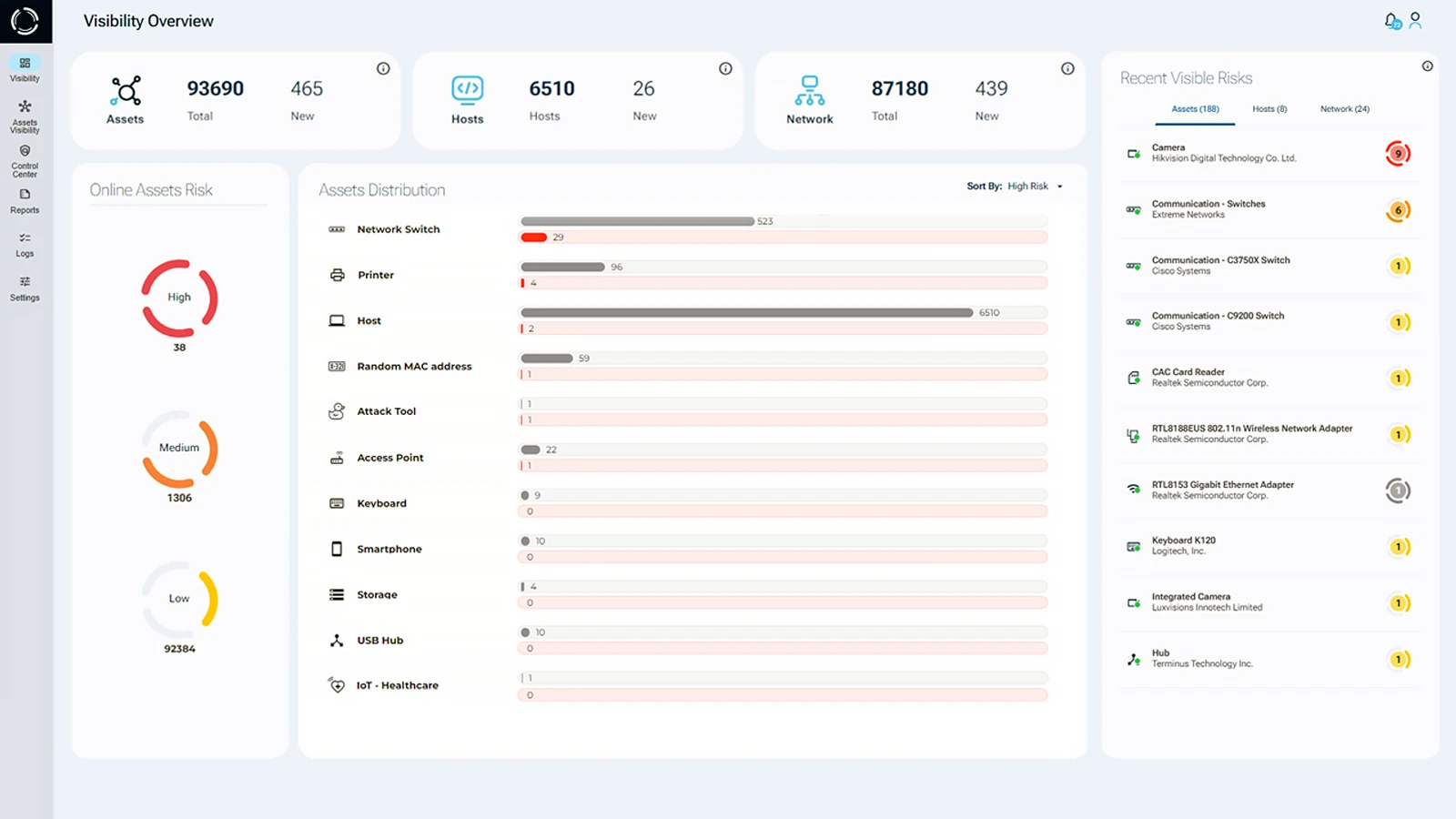
Achieve CMMC Compliance with Sepio
Getting CMMC certified is not just about checking boxes, it’s about protecting national security interests. With Sepio, you’re equipped with the tools needed to meet stringent DoD requirements while improving your overall cybersecurity resilience.
Schedule a demo today and see how Sepio can help your organization reach, and maintain, CMMC Compliance across all levels.




